Now Reading: वक्फ बचाने की लड़ाई को स्वतंत्रता संग्राम का दूसरा अध्याय- मोहम्मद सुलेमान
-
01
वक्फ बचाने की लड़ाई को स्वतंत्रता संग्राम का दूसरा अध्याय- मोहम्मद सुलेमान
वक्फ बचाने की लड़ाई को स्वतंत्रता संग्राम का दूसरा अध्याय- मोहम्मद सुलेमान

Quick Summary
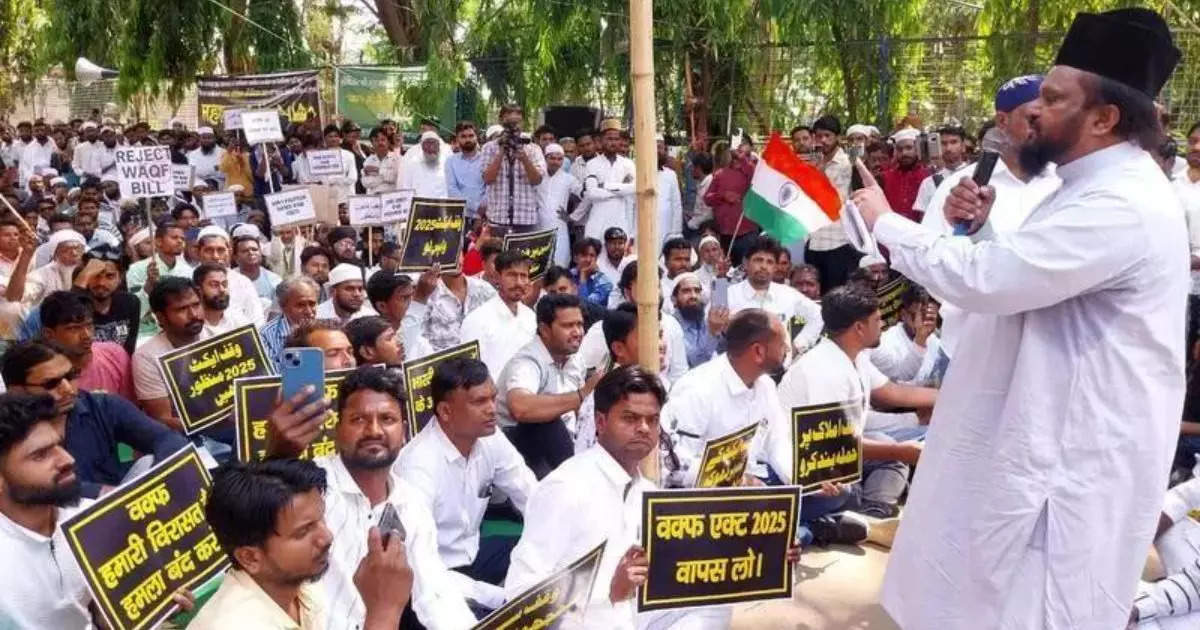
- protests against new Waqf law: Various Muslim organizations, led by the All India Muslim Personal Law board (AIMPLB), are strongly opposing the recently amended Waqf law across India, organizing a ‘Waqf Bachao Abhiyan.’
- Major event in Delhi: AIMPLB held a large conference named ‘Tahaffuz-e-Auqaf Karwaan’ at TalKatora Stadium in Delhi. Prominent leaders including AIMIM chief Asaduddin Owaisi were present.
- Core concerns raised: Critics argue that the amended law undermines Waqf properties’ nature and autonomy, violating Islamic principles and constitutional religious freedoms.
– Specific points of contention include allowing non-Muslim members on waqf boards and granting district officials authority to evaluate property values.
- Strong statements made:
– Mohammed Suleman from Indian National League compared the movement to a “second freedom struggle.”
– AIMPLB President Khalid Saifullah Rahmani emphasized adherence to the Constitution over political party agendas.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The widespread protests against amendments to India’s Waqf laws indicate significant concerns among parts of the Muslim community regarding perceived threats to religious autonomy and constitutional rights. Voices like those of AIMPLB and prominent Muslim leaders suggest fears that these changes could reduce community control over traditionally governed assets. The inclusion of non-Muslims on Waqf boards and expanded powers granted to district officials are seen as key breaches affecting trust in governance.
This issue highlights potential challenges for societal harmony if sections of civil society feel their cultural or legal safeguards are diminished, calling for careful government dialog with stakeholders. Striking an effective balance between modernization efforts in laws governing public properties like Waqfs while respecting diverse faith groups’ traditions is critical for effectively managing this matter within India’s secular framework.
Such developments demand inclusive deliberation ensuring all concerns-legal or spiritual-are addressed within India’s democratic values.