Now Reading: 2-Million-Year-Old Teeth Pits Shed Light on Ancient Human Relatives
-
01
2-Million-Year-Old Teeth Pits Shed Light on Ancient Human Relatives
2-Million-Year-Old Teeth Pits Shed Light on Ancient Human Relatives
fast Summary
- Researchers analyzed dental enamel of paranthropus, an extinct human relative, and discovered unique clusters of pits referred to as UCS (uniform, circular, and shallow) pitting.
- UCS pits appear genetic and may serve as evolutionary markers to better trace the human family tree.
- study findings were published in the July issue of the Journal of Human Evolution.
- Researchers studied teeth samples across eastern and southern Africa spanning 3.4 million to 1.1 million years ago; roughly half of south African Paranthropus individuals had UCS-type pitting.
- Comparison with other hominins shows minimal evidence of UCS pitting outside Paranthropus, including rare occurrences in certain members of the Homo genus such as H. juluensis and “hobbits” (H. floresiensis).
- Evidence suggests South African Paranthropus did not evolve directly from local australopithecines like A. africanus. Instead,East African australopithecines might be ancestors.
- The researchers call for more studies, especially using paleoproteomics, to understand gender-associated prevalence or taxonomic importance.
Image:
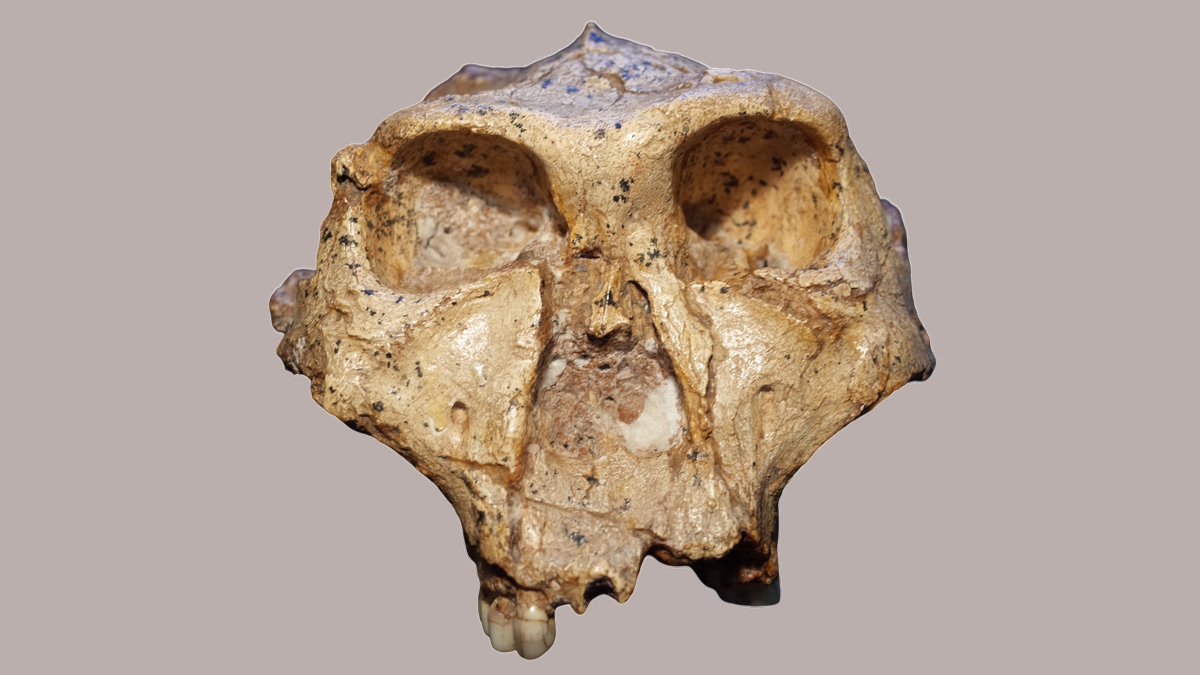
!Skull
A skull studied for dental traits. Image credit: Ian Towle
!tooth Close-up
Clustered pits on tooth enamel suggest genetic traits. Image credit: Ian Towle
Indian Opinion Analysis
This discovery highlights that even seemingly minor features-such as dental enamel patterns-can unlock meaningful insights into evolutionary biology. Although primarily global in its implications for understanding human ancestry, India’s academic interest in paleoanthropology could find relevance here given its focus on ancient populations across South Asia.
For India-which hosts diverse ancient sites like Bhimbetka rock shelters-these studies emphasize how small anatomical details can reframe knowledge about species evolution globally, underscoring the interconnectedness between regions despite geographical divides.
Moreover, interdisciplinary research methods such as paleoproteomics mentioned by researchers echo what Indian archaeological science increasingly applies in its study frameworks today (e.g., genome studies). While further inquiry remains essential before firm conclusions can be drawn about lineage relationships or taxonomic markers based solely on UCS pitting patterns-as conducted robustly elsewhere-it presents a methodological roadmap ripe for adaptation within India’s research ecosystem toward understanding our shared prehistoric ties deeply rooted among evolving hominins worldwide!