Now Reading: 6 Easy-to-Grow Edible Plants for Small Spaces
-
01
6 Easy-to-Grow Edible Plants for Small Spaces
6 Easy-to-Grow Edible Plants for Small Spaces

Swift Summary
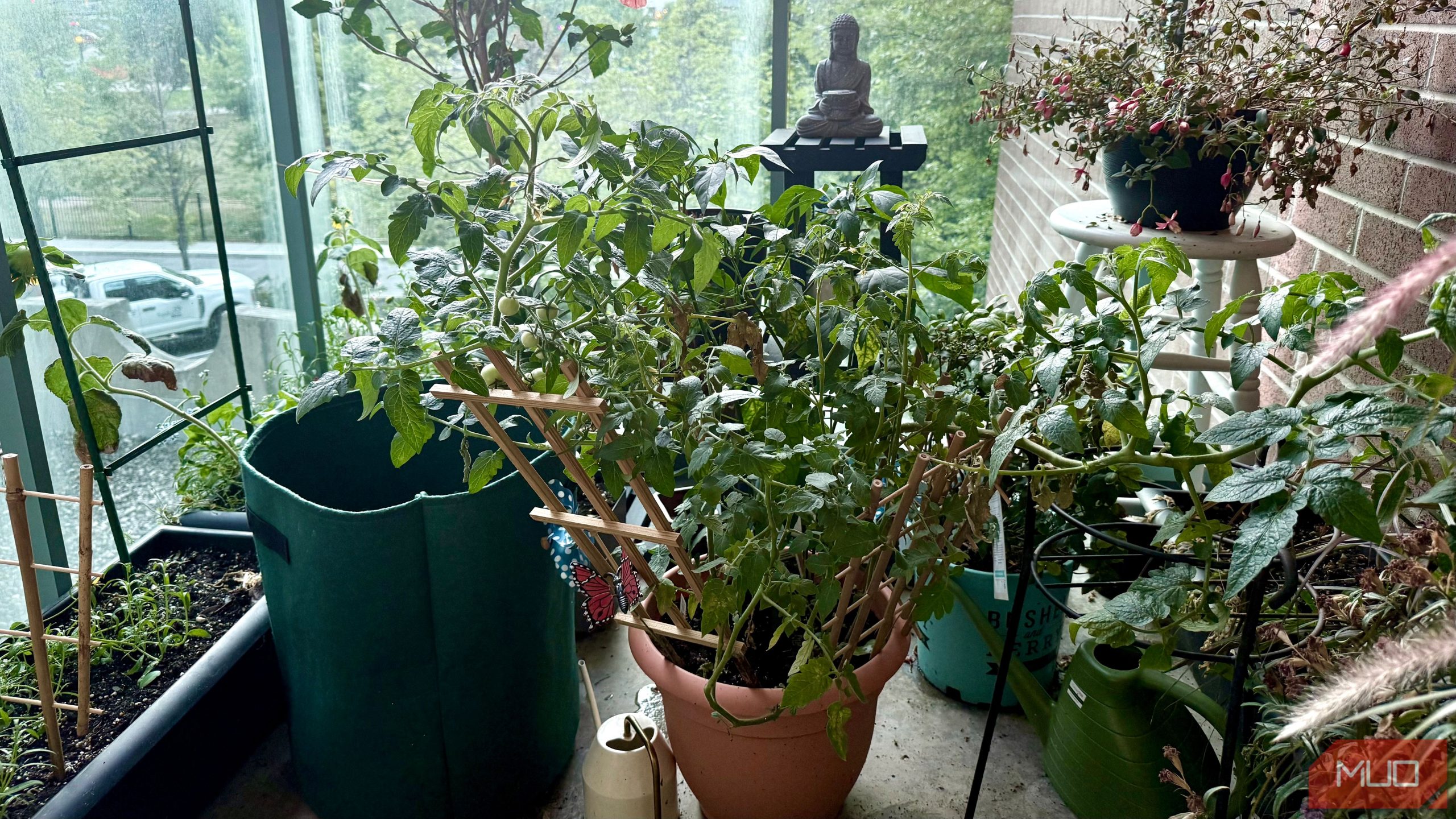
- Tomatoes:
– Easy to grow for a continuous summer harvest. Non-hybrid varieties can be grown using the slice-and-plant method or store-bought seeds/seedlings can be used.
– Require full sunlight (6-8 hours/day), well-drained soil, regular watering, and a support stake due to their height (up to 5 feet).
– Low maintainance but require occasional pest control.
- Green Onions:
– Can be regrown from grocery-bought samples by soaking the roots in water before transferring to pots (at least six inches deep).
– Thrive with regular watering, proper drainage, and sunlight. Allow for multiple harvests as they regrow after cutting.
- Chili peppers:
– Prefer hot climates and need sunlight along with good soil for ideal growth.Pot sizes vary based on chili variety (~6-8 inches in diameter).
– Plants may require stakes; yield ample fruit throughout the growing period.
Images included: Photos of unripe tomatoes on plants, green onions potted indoors/outdoors, and flourishing chili plants highlight practical examples of urban gardening.
Indian Opinion Analysis
india’s increasing urbanization has amplified interest in compact gardening solutions like balcony farming. With limited land availability in many major cities, tips on cultivating edible plants such as tomatoes, green onions, and chilies resonate strongly with urban dwellers looking for sustainable food sources.These practices not only encourage self-reliance but also promote recycling principles-like reusing scraps of green onions-and lower reliance on packaged produce.
As India grapples with environmental concerns like rising landfill waste and pesticide overuse in agriculture, such solutions could contribute towards household-level eco-conscious practices while saving costs for families struggling amid high inflation rates. Encouraging this gardening trend through awareness campaigns could have widespread environmental benefits if scaled across metro cities nationwide.
Read more at [Source Link].Quick Summary
- Tomatoes and chilies can be grown in the same pot due to similar growing needs as part of the nightshade family.
- Rosemary is a drought-resistant, versatile herb that needs ample sunlight and proper drainage. Overwatering can cause root rot.It is indeed best suited for outdoor growth but can be brought indoors during winter in colder regions.
- Strawberries thrive well in shallow, wide pots with adequate sunlight and watering. Mulching helps keep berries clean, while garden nets protect them from birds.
- Cilantro can be easily grown from culinary coriander seeds purchased at grocery stores.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discourse on home gardening highlights its potential relevance for India’s urban population dealing with limited space and rising food costs. Herbs like rosemary and cilantro represent cost-effective alternatives to store-bought spices, while strawberries offer a path toward fresh produce even with minimal resources such as balconies or terraces.
From an environmental outlook, small-scale urban gardening practices may nurture sustainable habits such as composting or rainwater harvesting among city dwellers. Policymakers could explore supporting community gardens or initiatives promoting low-maintenance edible plants tailored to diverse climates across India.
Read More HereQuick summary
- Cilantro is an edible plant that thrives in cooler temperatures (18-21 degrees Celsius or 64-70 Fahrenheit) and prefers indirect sunlight paired with consistent watering to prevent soil from drying.
- An issue with cilantro cultivation is bolting-where the plant prioritizes seed production over leaf growth-as a result of hot weather. Indoor cultivation can bypass this problem, while spring and fall are ideal for outdoor gardening.
- When harvesting cilantro, only leaves should be clipped, leaving roots intact for continued growth.
- Suggested companion plants include tomatoes and chilies, which can be combined into fresh salsa recipes using harvested cilantro.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Cilantro’s adaptability to indoor growing conditions makes it a practical choice for Indian households seeking fresh produce in small living spaces or urban areas where traditional gardens might not be feasible. Its preference for cooler climates aligns well with regions experiencing moderate temperatures year-round but may require climate control during hotter periods in tropical zones such as India’s summers.Bolting presents challenges but can be mitigated by careful timing of planting seasons-favoring spring and fall-or leveraging indoor environments under maintained conditions. This low-maintenance solution continues India’s widespread tradition of growing herbs at home while offering culinary enhancements like homemade salsa.
For aspiring gardeners, adhering to precise care basics (lighting requirements, proper watering techniques) assures success in cultivating cilantro without unneeded hurdles.
Read More