Now Reading: 6-Million-Year-Old Apex Predator Fossils Unearthed in Dominican Republic
-
01
6-Million-Year-Old Apex Predator Fossils Unearthed in Dominican Republic
6-Million-Year-Old Apex Predator Fossils Unearthed in Dominican Republic

Quick Summary
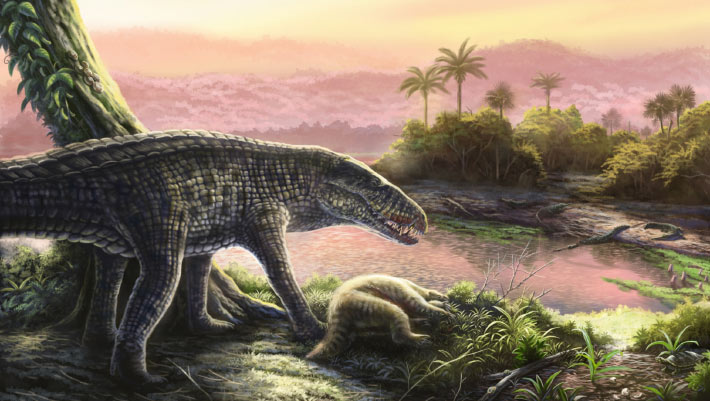
- Research Findings: A study led by the Florida Museum of Natural History examined fossils of sebecid crocodyliforms, apex predators with south American origins, which dominated after the dinosaurs’ extinction.
- Fossils Studied: Investigated fossils included 6-million-year-old remains from the Dominican Republic, 18-million-year-old teeth from Cuba, and a 29-million-year-old tooth from Puerto rico.
- Characteristics of Sebecids:
– Terrestrial predators resembling carnivorous dinosaurs; agile runners with serrated teeth for tearing flesh.
– Some species reached lengths up to 20 feet and had bony armor plates.
- GAARlandia Hypothesis: Researchers suggest temporary land bridges or chains of islands enabled terrestrial animals to migrate between South America and the caribbean in ancient times.
- Ecological Impact: Sebecids were critical apex predators shaping ecosystems for millions of years.Their absence has allowed smaller predators like snakes, birds, and crocodiles to evolve into dominant roles in modern food chains.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery highlights how ancient apex predators like sebecids contributed significantly to regional ecosystems over millennia. The gaarlandia hypothesis offers an intriguing glimpse into prehistoric animal migrations that could refine our understanding of global biodiversity patterns during ancient epochs. while these findings pertain specifically to Caribbean fossil records, similar studies in India could unlock deeper knowledge about migration routes and extinct species unique to the subcontinent. this research reminds us that modern ecosystems are often shaped by vanished predecessors whose extinction paved the way for adaptive niches-offering valuable lessons on sustainability amid current environmental challenges.