Now Reading: 850,000-Year-Old Neck Bone with Cut Marks Raises Cannibalism Mystery
-
01
850,000-Year-Old Neck Bone with Cut Marks Raises Cannibalism Mystery
850,000-Year-Old Neck Bone with Cut Marks Raises Cannibalism Mystery

Quick summary
- Archaeologists in Spain discovered the neck vertebra of a child (aged 2-4) from the hominin species Homo antecessor, dating back 850,000 years, with clear cut marks believed to be evidence of cannibalism.
- The vertebra was unearthed at gran Dolina cave (Sierra de Atapuerca), a site known for longstanding archaeological findings of Paleolithic human remains.
- Researchers, including Palmira Saladié from IPHES-CERCA, suggest that this specific child may have been processed as prey and consumed.
- The cave layer containing the bone also held remains of nine other individuals exhibiting cut marks and fractures indicative of marrow extraction.
- Experts disagree on whether these findings confirm cannibalism-option theories include funeral rituals or other practices unrelated to consumption.
- Homo antecessor, which lived roughly 900,000-800,000 years ago before extinction, is debated among scientists regarding its evolutionary connection to Homo sapiens. Evidence suggests cannibalism may have occurred in multiple early human species globally.
Images:
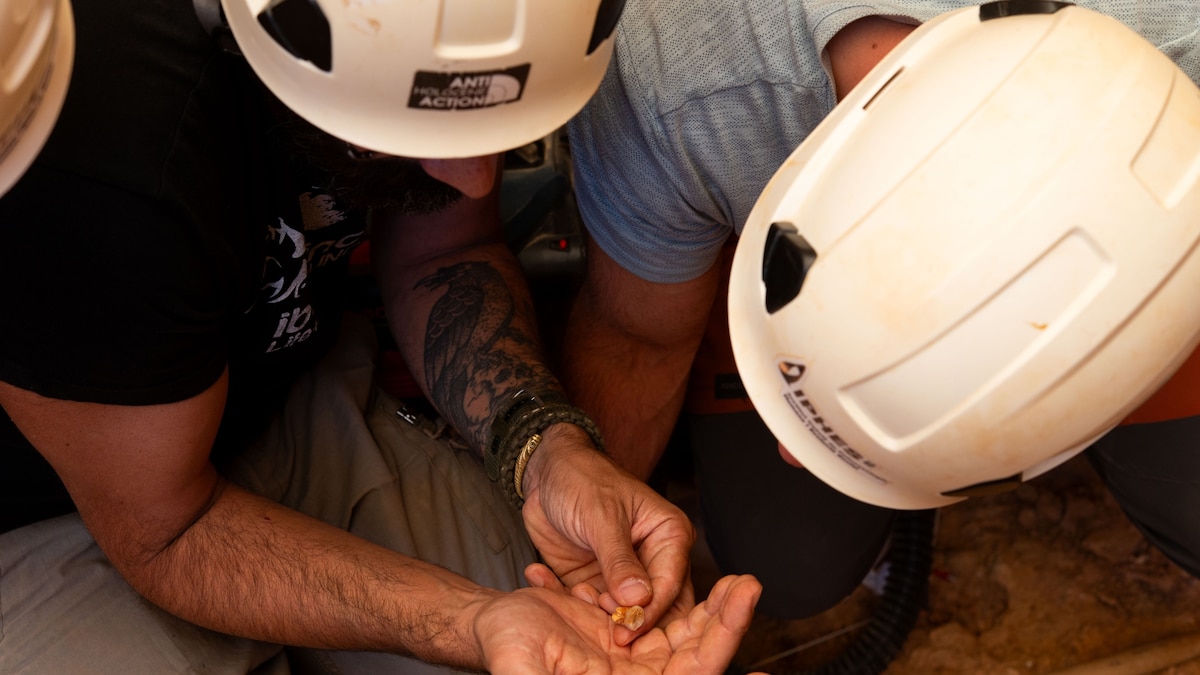
- !MG04.jpg”>child Vertebra: Vertebra showing signs indicative of cannibalism.
- !Tooth Discovery .
Read More: National Geographic Article
Indian Opinion analysis
The discovery highlights notable advancements in understanding prehistoric behaviors among early humans (Homo antecessor). While it reinforces prior evidence of Paleolithic-era cannibalism at sites like Gran Dolina, it also underscores scientific controversies surrounding ritualistic versus survival-driven acts among ancient populations.For India’s academic circles focused on anthropology and archeology studies-especially regarding prehistoric behaviors-the findings invite comparative research with similar discoveries made worldwide (such as Neanderthal remains or Kenyan fossils). It also holds educational value in exploring how evolutionary traits shaped societal norms across human history.
given the ongoing debates about direct ancestry links between species like Homo antecessor and modern humans (Homo sapiens), such discoveries offer critical insights into identifying gaps within our evolutionary timeline-a key subject for global paleoanthropological collaboration where Indian researchers could actively contribute expertise.
While discussions about “why” the acts occurred remain inconclusive due to limited evidence from this era’s fossil records globally, these revelations deepen our recognition for humanity’s complex survival strategies amid harsh environments during prehistory.