Now Reading: Advancing Spatial Transcriptomics with Computational Array Techniques
-
01
Advancing Spatial Transcriptomics with Computational Array Techniques
Advancing Spatial Transcriptomics with Computational Array Techniques
Speedy Summary:
- The article discusses various advancements in spatial transcriptomics and high-resolution molecular imaging techniques.
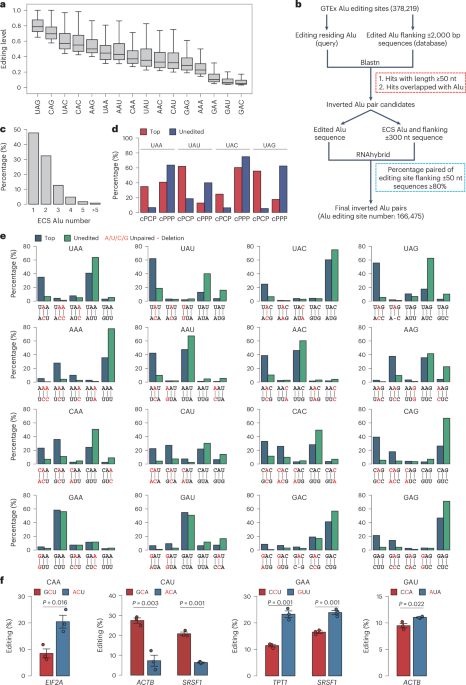
- These technologies enable a detailed analysis of RNA profiles, gene expression, and spatial organization within tissues at single-cell levels.
- Key methodologies mentioned include Slide-seq, DNA microscopy, volumetric imaging using molecular networks, and multi-omic sequencing with deterministic barcoding.
- Applications have spanned neuroscience (e.g., mouse hippocampus studies), tissue section analyses, and genome-wide projections revealing human genomic folding principles.
- References highlighted are from major scientific journals like Science, Nature Methods, and Cell.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The discussed advancements in spatial transcriptomics hold significant potential for India’s biomedical research sector. With robust scientific talent pools across the country, integrating these technologies can propel India’s genomics research to new heights. These techniques could help address pressing healthcare challenges by exploring disease mechanisms at unprecedented resolution or tailoring precision medicine approaches for genetic disorders prevalent in india. Leveraging this knowledge would require investments in bioinformatics infrastructure and fostering interdisciplinary collaborations-a promising yet resource-intensive pathway.
Read moreQuick Summary:
- This raw text primarily consists of references to scientific articles, tools, and methodologies associated with advancements in genomics and computational biology.
- Topics mentioned include DNA sequencing frameworks, spatial transcriptomics technology, dimensionality reduction techniques (UMAP), single-cell experimentation methods (CellBender), time-lapse developmental analysis of cells in mice, and advanced algorithmic solutions for scientific computing.
indian Opinion Analysis:
the advancements outlined in the referenced research have potential implications for India’s biotechnology sector. As global efforts in genomics accelerate using computational techniques like UMAP and spatial transcriptomics, Indian scientists and institutions would benefit from integrating such cutting-edge tools into ongoing projects-ranging from healthcare innovation to biodiversity studies. Investments into training, infrastructure growth for high-throughput biology labs could position India as a significant player globally in precision medicine and genetic research. Neutral consideration suggests that progress on such fronts should align with ethical guidelines while keeping accessibility to these technologies affordable across different demographics within the country.
Link for further reading is embedded through source-provided citations.Quick Summary:
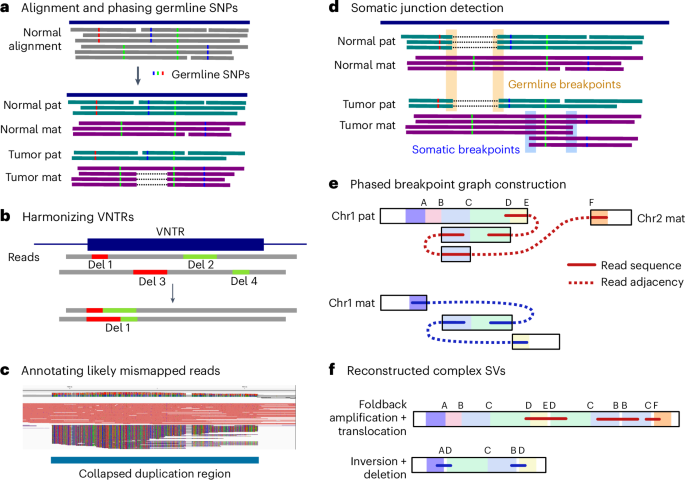
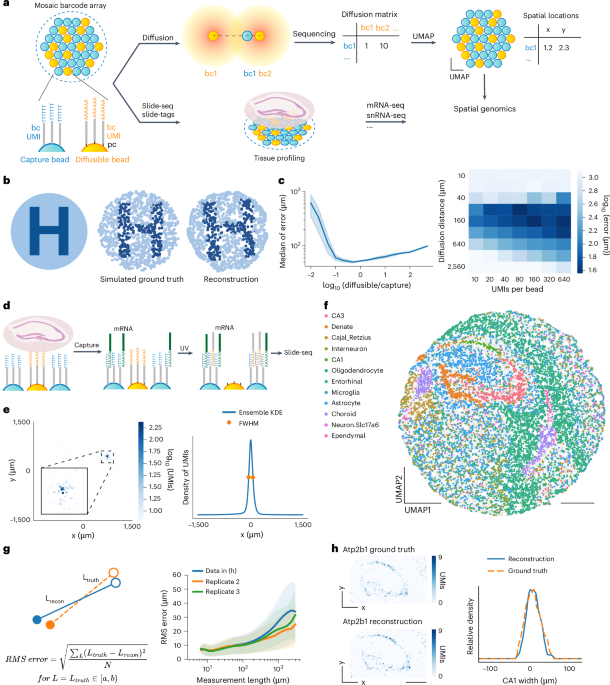
- A groundbreaking study,led by researchers at Harvard University and the Broad Institute,features scalable spatial transcriptomics through computational array reconstruction.
- The method uses innovative techniques for analyzing spatial gene expression patterns in tissues.
- It focuses on improving precision in reconstructing bead-based arrays critical to genomic analysis.
- The research received support from entities like NIH and New York Stem Cell Foundation.
- Authors have affiliations with institutions including Harvard University,Massachusetts General Hospital,and Broad Institute.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This technological advance in spatial transcriptomics has significant implications for India’s scientific community. With advancements like this potentially revolutionizing biomedical research globally, India could explore collaborations to integrate such methods into its genomic studies.Steps towards adopting scalable systems can aid in areas like drug discovery or personalized medicine. Neutral evaluation of how Indian institutions might leverage these tools could set the stage for crucial progress while fostering partnerships with international experts.
Read more: PubMed Reference
Quick Summary
- A research article titled “Scalable spatial transcriptomics through computational array reconstruction” has been published in Nature Biotechnology.
- The study presents advancements in spatial transcriptomics, enabling scalable analysis using computational methods.
- Authors of the study include C. Hu, M. Borji,G.J. Marrero, among others.
- The article was received on April 20, 2024, accepted on February 21, 2025, and published on April 3, 2025.
- The DOI for the paper is https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02612-0, and additional details can be accessed via the official publication link.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Advances in spatial transcriptomics have significant scientific potential for India’s rapidly growing biotechnology and genomic sectors. Computational reconstruction methods could offer cost-effective scalability suited to resource-constrained environments often seen in developing nations such as India. By adopting similar innovations or collaborating internationally with research efforts like this one out of necessity or prospect-india may accelerate impacts within agriculture (crop genomics), precision medicine tailored across its vast diverse population groups which serving aligning SDGs societal pressing goals transforming healthcare/public ecosystems evolving better equitable solutions contributing further national progress .