Now Reading: Alzheimer’s Risk Linked to Brain’s Outer Regions, Study Finds
-
01
Alzheimer’s Risk Linked to Brain’s Outer Regions, Study Finds
Alzheimer’s Risk Linked to Brain’s Outer Regions, Study Finds
Quick Summary
- A study by Gladstone Institutes and UCSF, published in Neuron, explores the role of vascular and immune cells in neurological diseases.
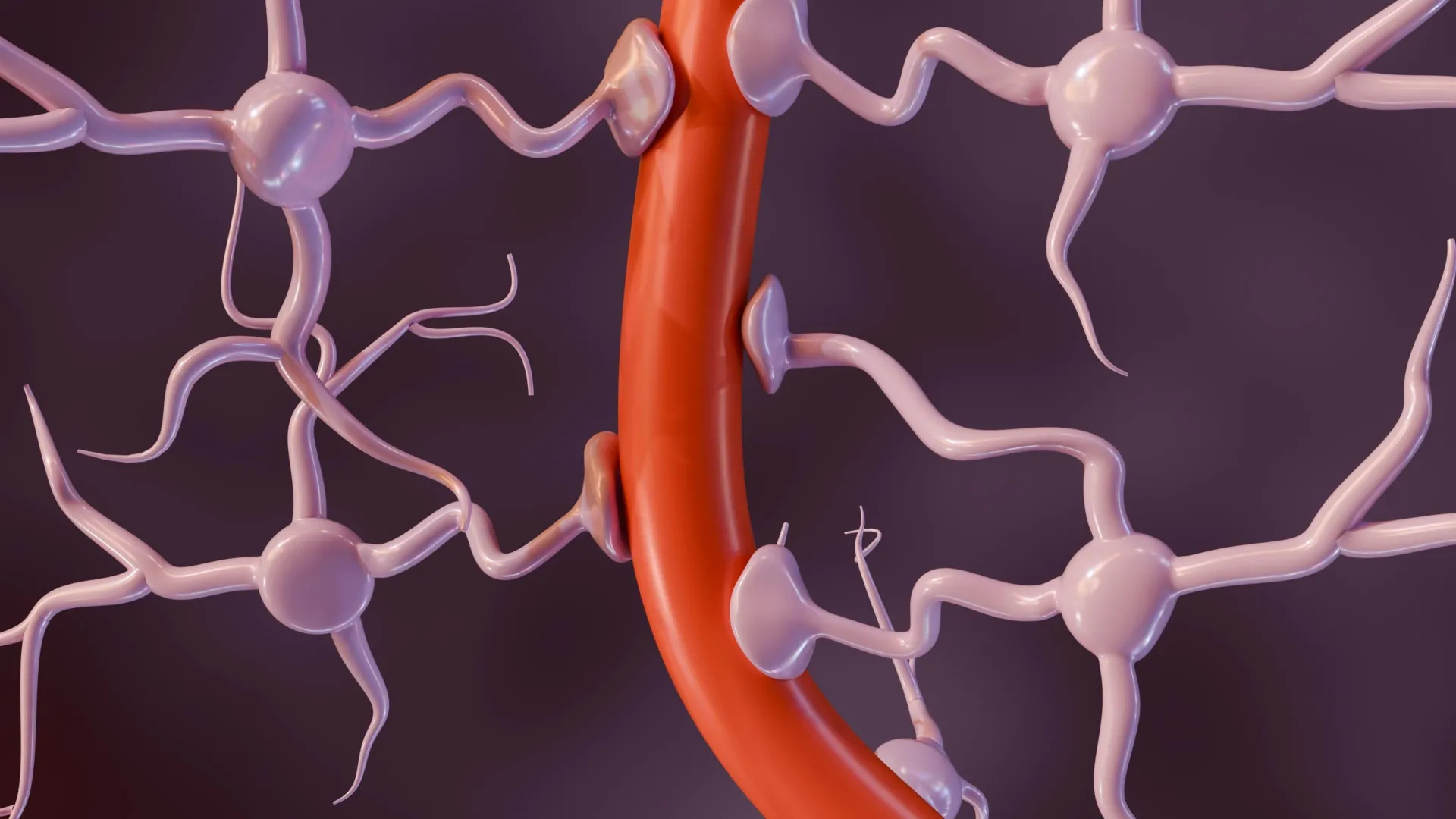
- The research found that genetic risk factors for diseases like Alzheimer’s and stroke primarily affect “guardian” cells forming the blood-brain barrier rather of neurons.
- Using a new technology called MultiVINE-seq, researchers mapped gene activity and chromatin accessibility in these key brain cells across 30 postmortem samples.
- Stroke-related genetic variants weaken blood vessel structures, while Alzheimer’s variants amplify immune signaling, frequently enough overactivating T cells near amyloid plaques.
- A notable finding identifies a common variant near the PTK2B gene as a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s,with existing cancer therapies possibly repurposed for this use.
- The study’s emphasis on brain border-cell vulnerabilities may enable promising drug targets or lifestyle-based interventions to strengthen brain defenses externally without breaching the blood-brain barrier.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study underscores an importent shift in neurological disease research by spotlighting support cells at the junction between the brain and body rather than focusing solely on neurons. Identifying vascular and immune cell dysfunction as contributors to diseases like Alzheimer’s or stroke broadens avenues for both prevention strategies and treatment innovations.
The revelation that structural weakening defines stroke risk while hyperactive inflammation marks Alzheimer’s demonstrates disease-specific mechanisms tied to genetic variations within guardian cells, highlighting opportunities for precision medicine tailored to specific patterns of cellular disruption.
Furthermore, identifying PTK2B gene expression tied directly to T-cell activity opens doors for exploring existing drugs targeting this pathway-potentially accelerating therapeutic timelines through repurposing efforts already underway in oncology.For India specifically-a nation grappling with increasing rates of aging-associated neurological conditions-this evolving understanding has significant implications not just scientifically but socially as well: advancing preventative health initiatives targeting environmental impacts could complement emerging clinical solutions aimed at managing such widespread challenges effectively.