Now Reading: Hubble Discovers White Dwarf Merger Remnant 130 Light-Years Away
-
01
Hubble Discovers White Dwarf Merger Remnant 130 Light-Years Away
Hubble Discovers White Dwarf Merger Remnant 130 Light-Years Away

Quick Summary
- Astronomers using NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope data found atmospheric carbon in ultramassive white dwarf WD 0525+526.
- Located 130 light-years away in the constellation Auriga,it has a mass 20% larger than the Sun and is considered unusual.
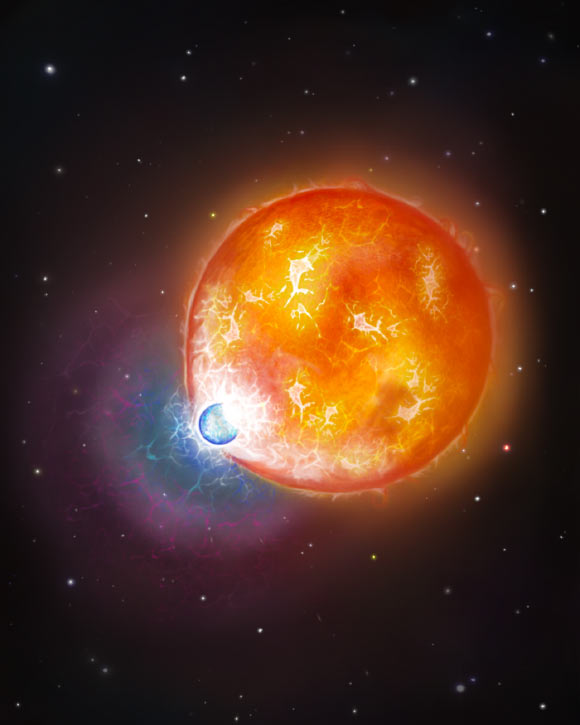
- This white dwarf is believed to be a merger remnant from two stars combining, based on its lower-than-usual hydrogen and helium envelope thickness and faint atmospheric carbon signatures.
- Hydrogen and helium layers are approximately ten-billion times thinner than typical white dwarfs due to the presumed merger event burning them off.
- The star’s surface contains considerably less carbon than other merger remnants previously studied, suggesting it is indeed much earlier in its post-merger evolution cycle while being nearly four times hotter than the sun.
- A process called semi-convection has been identified as responsible for small traces of carbon reaching the surface despite normal convection being inactive due to high temperatures.
- Research provides insights into binary star system evolution, including phenomena like supernova explosions, which may result from such mergers.
- Findings published in Nature Astronomy, emphasizing ultraviolet observations as key for detecting these stellar phenomena.
Image Credit: Snehalata Sahu / University of Warwick – Illustration depicting past merger between white dwarf & subgiant star.
indian Opinion Analysis
India’s space research community may draw inspiration from this discovery regarding ultraviolet spectroscopic capabilities-currently accessible mainly through advanced instruments like Hubble Space Telescope outside Earth’s atmosphere. With growing investment in astronomy (e.g., astro-sat programs), Indian scientists could focus on similar observations essential for understanding stellar growth at advanced phases-including mergers influencing cosmic events such as supernovae or neutron stars formation.
The study highlights how technology-driven breakthroughs transform essential science knowledge about rare phenomena like ultramassive remnants after stellar mergers. Such research contributes critical input into astrophysical theory globally while encouraging India’s role within collaborative scientific missions harnessing cutting-edge exploration tools.