Now Reading: Scientists Decode Brain Cell Clumps and Find a Way to Eliminate Them
-
01
Scientists Decode Brain Cell Clumps and Find a Way to Eliminate Them
Scientists Decode Brain Cell Clumps and Find a Way to Eliminate Them
Rapid Summary
- Researchers at teh University at Buffalo have uncovered how harmful RNA clusters contribute to neurological disorders like HuntingtonS disease and ALS.
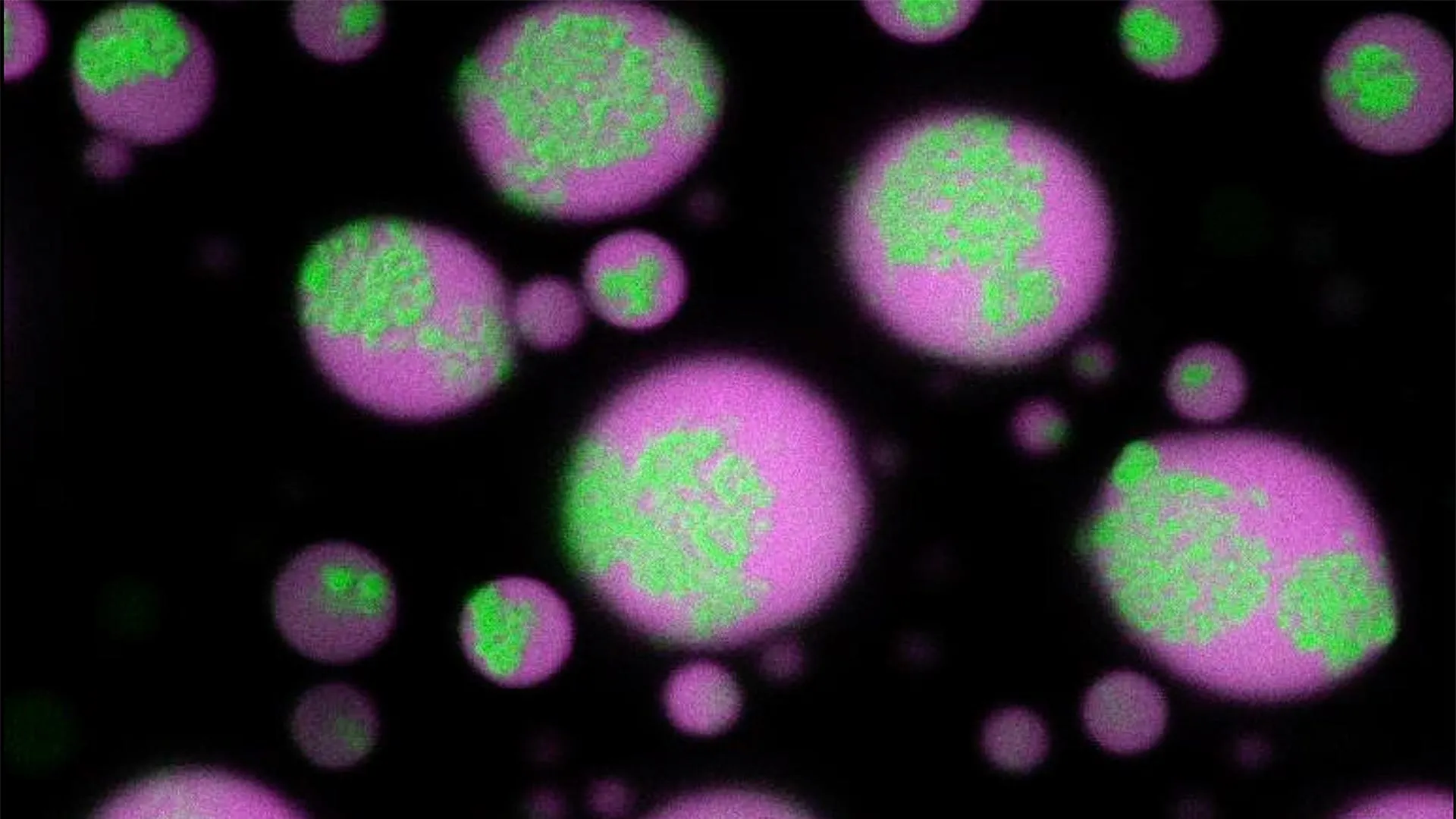
- RNA clusters form within biomolecular condensates, which are liquid-like droplets made from RNA, DNA, and proteins found inside cells.
- The study revealed that repeat rnas clump together over time within these condensates, creating solid cores surrounded by fluid shells. These clusters are persistent even after their host dissolves.
- Using an engineered strand of RNA called antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), researchers demonstrated a method to prevent and disassemble these clusters.
- ASOs bind specifically to repeat RNAs with complementary sequences, effectively breaking down RNA aggregates.Their efficacy depends on precise sequence matching.
- The research also discovered that introducing an RNA-binding protein known as G3BP1 can inhibit cluster formation by disrupting RNA interactions within condensates.
- This study provides new perspectives on addressing neurodegenerative disorders perhaps linked with misfolded or aggregated RNAs.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This groundbreaking research advances our understanding of both the mechanisms responsible for pathological RNA clustering in neurodegenerative diseases and viable strategies for reversing or preventing such formations. Given India’s increasing prevalence of diseases like ALS due to demographics transitioning toward older populations, the insights from this study could lead scientists closer to effective treatments targeting molecular pathways common in these debilitating conditions.
Additionally, innovations such as engineered antisense oligonucleotides present opportunities for India’s biopharma sector to invest in cutting-edge therapeutic technologies. With a growing reputation in affordable medicine innovation globally, Indian firms could play a pivotal role in developing accessible applications based on this revelation while tapping into international collaborations.
The neutral tone here emphasizes both potential applications domestically (healthcare advancements) and globally (research partnerships)-underscoring how knowledge-generation benefits not just scientific communities but human health universally without polarizing perspectives.