Now Reading: Mars Rover Logs Sols 4507-4508: Steady Progress Continues
-
01
Mars Rover Logs Sols 4507-4508: Steady Progress Continues
Mars Rover Logs Sols 4507-4508: Steady Progress Continues

Quick Summary
- Mars science Laboratory Drive Update: The rover completed ~22 meters of driving, short of the expected 30 meters due to a steering command error. The halted drive caused instability, preventing further arm activities.
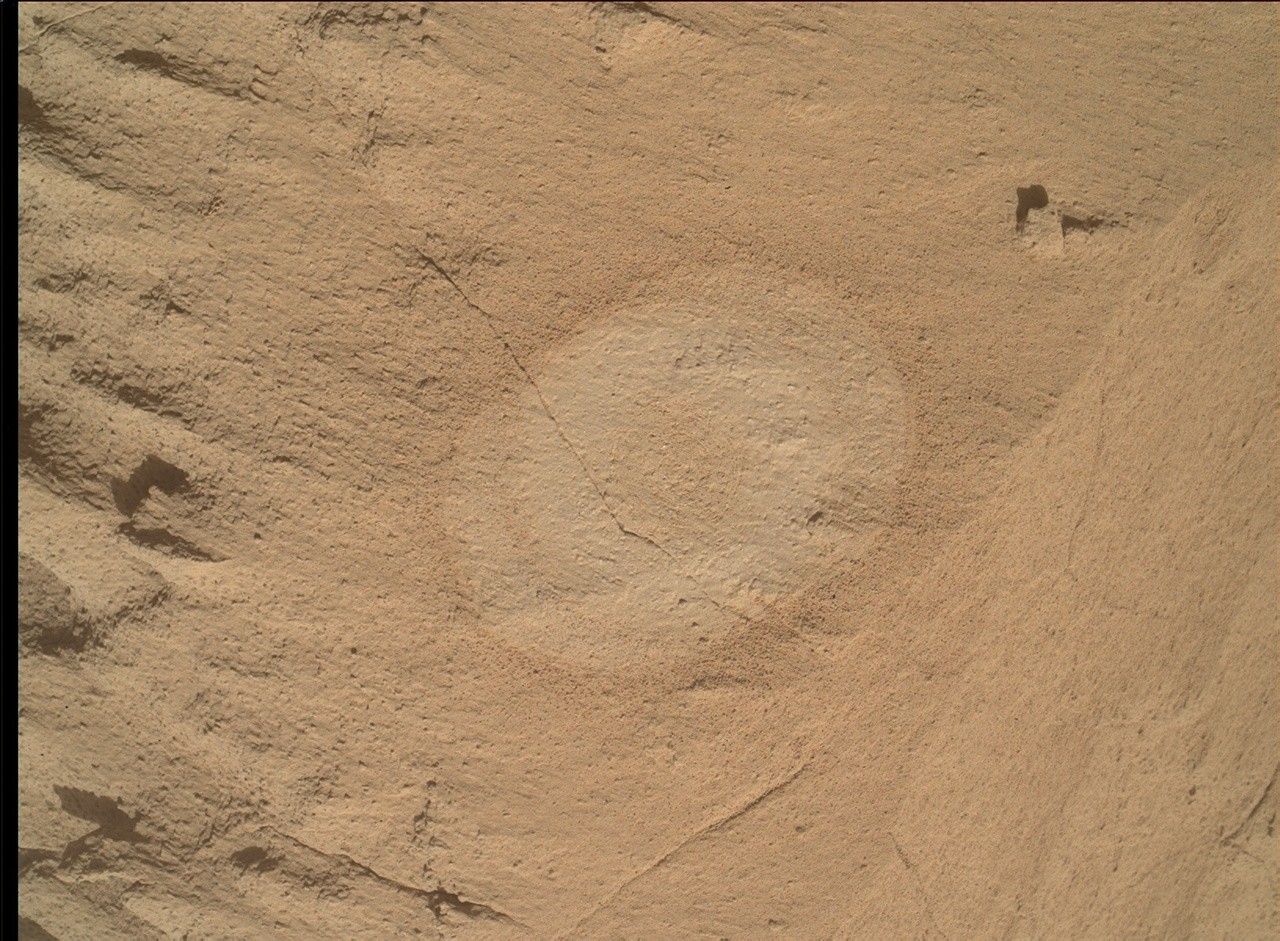
- Terrain Analysis: APXS data shows similar terrain composition recently. Keeping the arm stowed temporarily is expected to conserve power during Martian winter conditions.
- Imaging Progress: Mastcam captured 52 images with themes like “Devil’s gate” ridge and nearby vein networks named “Moonstone Beach.” Imaging was efficiently conducted, increasing rover awake time by only ~2 minutes.
- Chemical and Geological Research: ChemCam planned analyses of workspace veins such as “Jackrabbit Flat” and imaging distant structures like “Condor Peak.” Post-drive aims include reaching boxwork structures in a new valley westward with a projected drive distance of 53 meters.
- Terrain Navigation Test: Post-drive includes testing “Post Traverse Autonav Terrain Observation” (PoTATO) for mapping new terrain.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s growing investments in space exploration align with global advancements led by organizations such as NASA’s Mars missions. This detailed update highlights the complexities involved in operating rovers remotely under constrained conditions like limited power and uneven terrains. For India, which has successfully conducted lunar missions (e.g., Chandrayaan), such efforts underscore potential areas for improvement in robotic navigation technologies required for larger-scale planetary exploration.Moreover, innovations showcased here-like efficient imaging protocols or autonomous navigation systems-offer learning opportunities for expanding India’s Mars ambitions through ISRO’s ongoing Mangalyaan programme.Staying abreast of NASA-led mission updates ensures India remains actively engaged within international collaborative frameworks vital to its scientific objectives.