Now Reading: Curiosity Rover Awaits Next Mission Steps on Sols 4634-4635
-
01
Curiosity Rover Awaits Next Mission Steps on Sols 4634-4635
Curiosity Rover Awaits Next Mission Steps on Sols 4634-4635

Swift Summary
- Mission Details: The Mars Science Laboratory Team received data from weekend activities on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. Downlink assessments were conducted to ensure observations were successful adn the Curiosity rover’s instruments remained functional.
- scientific Objectives: Evaluated targets for analysis with tools like APXS (chemistry), MAHLI (textures), Mastcam (imaging), and ChemCam (laser spectroscopy). A bedrock patch named “Gil” was selected for extensive study after brushing away surface dust.
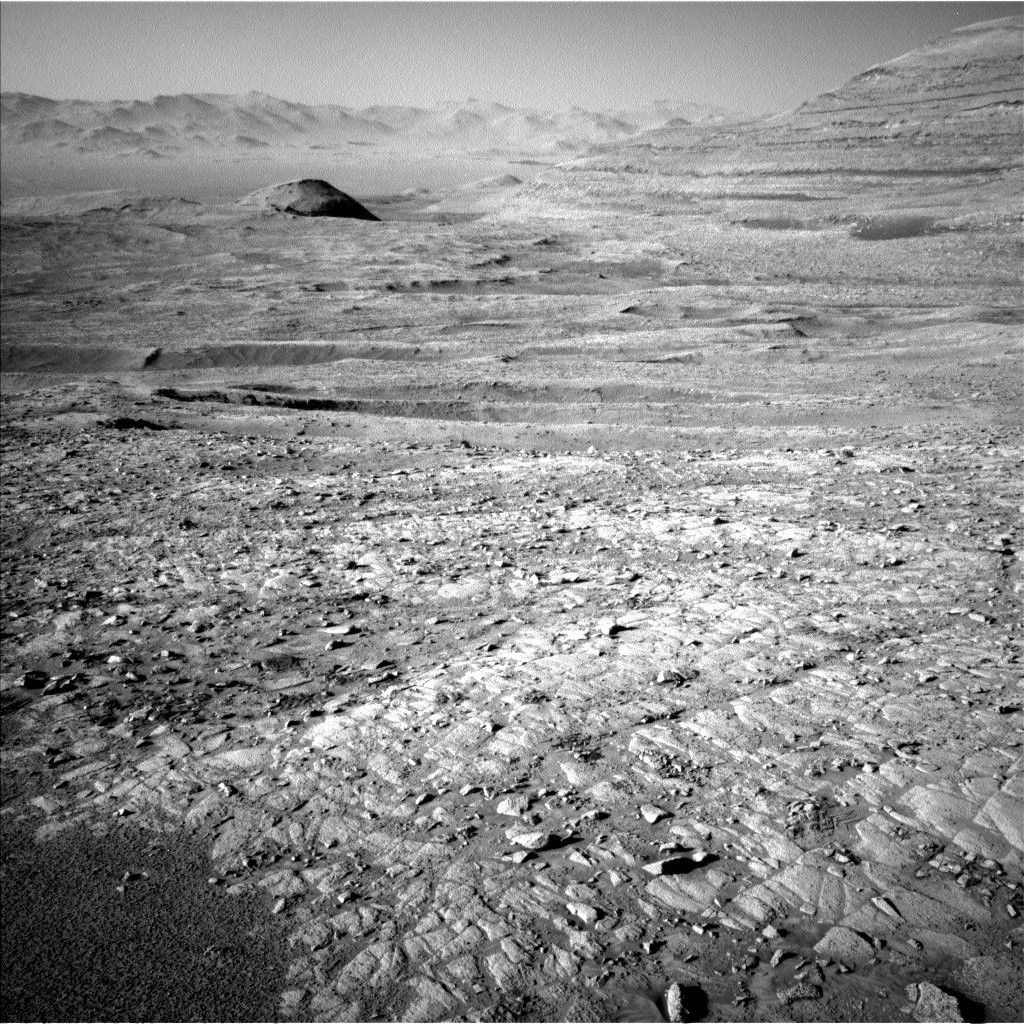
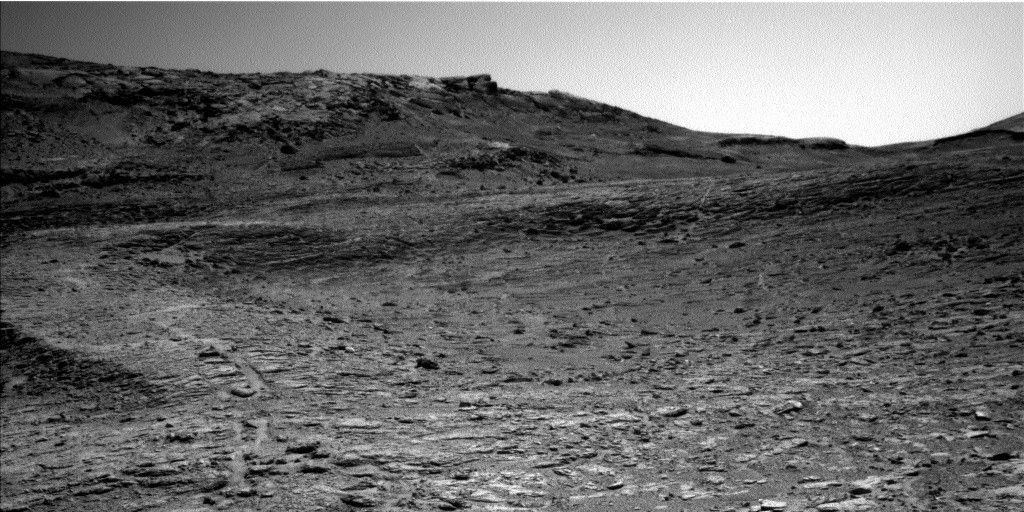
- Terrain Insights: Current exploration focuses on an intermediate zone in boxwork terrain, including ridges (“Río Frío”), sand-filled troughs (“Cusi cusi”), and imaging of distant geological features like Mishe Mokwa butte.
- Atmospheric Monitoring: Conducted dust-devil surveys, suprahorizon movie capture, and observations to analyze atmospheric dust levels before the rover’s next move.
- Drive Plans: Rover scheduled for a drive of approximately 36 meters to reach Río Frío ridge wall. Activities during the drive included capturing ground images with MARDI and employing ChemCam autonomous targeting capabilities at the new location.
- Additional Observations: Early morning Mastcam imaging highlighted structural features; further cloud-altitude monitoring was conducted alongside standard REMS, DAN, and RAD operations.
View associated Image
Read More
Indian Opinion Analysis
India has invested significantly in planetary exploration through its space agency ISRO’s missions to Mars and beyond while engaging as an active participant in global space science research dialogues. The Curiosity rover’s latest detailed findings reflect how robotic exploration is pushing scientific boundaries by analyzing diverse terrains remotely-an approach relevant for India’s ongoing advancements in planetary research efforts like MOM (Mars Orbiter Mission).
the meticulous planning observed here demonstrates how incremental studies can lead to breakthroughs about extraterrestrial environments. For India’s future interplanetary missions such as Chandrayaan or Aditya-L1 programs focusing on lunar or solar studies, similar multidisciplinary methods may enrich their goals.
At a time when atmospheric phenomena affect Earth globally-like rising dust from climate changes-Mars’ atmospheric monitoring outcomes might offer additional perspective useful across nations grappling with similar environmental complexities. This cooperative engagement underscores opportunities where India could align expertise or data-sharing partnerships with NASA towards common objectives benefiting humankind universally amidst spatial advancements.