Now Reading: Wisconsin Youth Sue State Regulator Over Climate Neglect Amid Flood Crisis
-
01
Wisconsin Youth Sue State Regulator Over Climate Neglect Amid Flood Crisis
Wisconsin Youth Sue State Regulator Over Climate Neglect Amid Flood Crisis

Speedy Summary
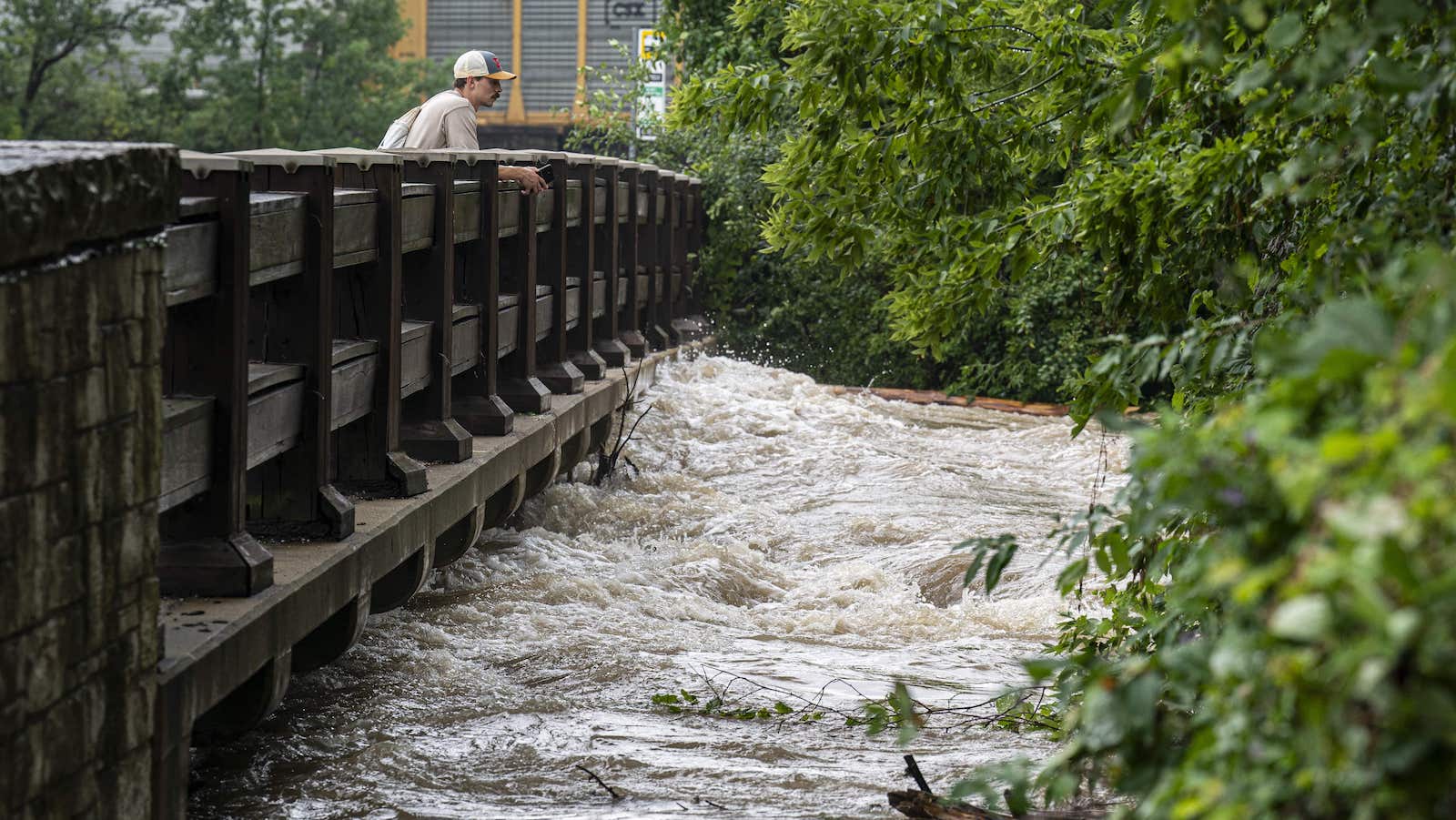
- Event: Southeastern Wisconsin experienced a catastrophic storm on August 9 and 10,dropping up to 13 inches of rain in hours,causing devastating flooding that destroyed over 1,800 homes.
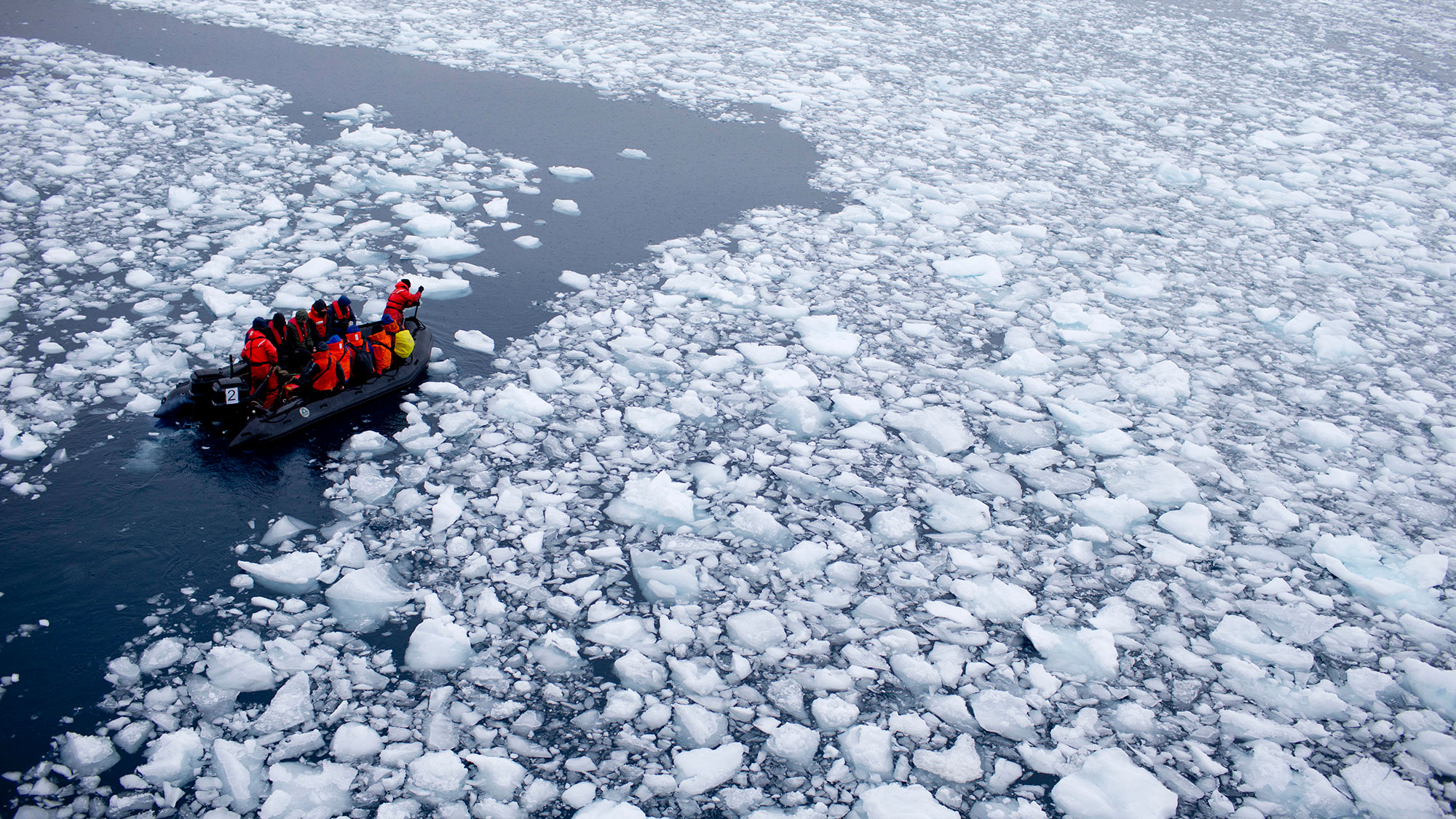
- Climate Context: The event is described as a “1,000-year flood,” highlighting climate change’s role in intensifying extreme weather events.
- Legal Action: Fifteen youth plaintiffs, including Indigenous members, have filed a lawsuit against Wisconsin’s Public Service Commission. They seek accountability for failing to consider climate change impacts while approving fossil fuel projects.
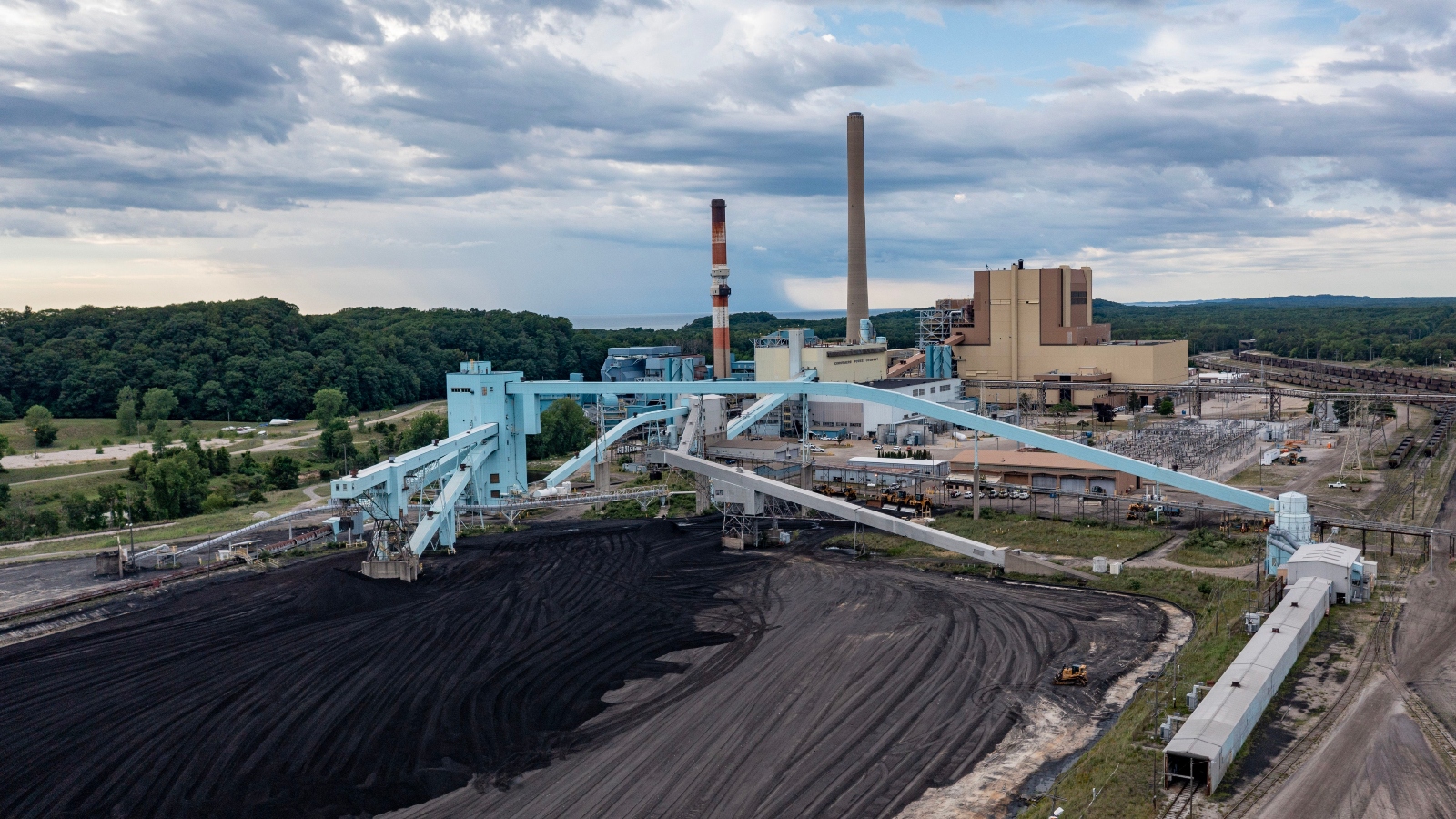
- Key Arguments: The plaintiffs argue that laws blocking renewable energy mandates and excluding pollution considerations violate their constitutional rights. Indigenous youth highlighted the environmental damage affecting sacred practices like wild rice harvesting and fishing.
- Regional Energy Profile: About three-fourths of Wisconsin’s electricity comes from fossil fuels-lagging in renewable energy adoption compared to some states like South Dakota with over 75% renewables.
- legal Context and Precedent: Advocates reference triumphant climate litigation precedents like Held v. Montana, asserting constitutional rights to “a clean and healthful habitat.”
- Response & Outlook: A state spokesman declined comment on the lawsuit while recovery efforts for flood damages continue.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This lawsuit underscores growing global challenges around balancing economic activity with urgent environmental sustainability goals. Climate litigation led by youth aligns with international trends where courts are increasingly seen as potential avenues for addressing systemic environmental concerns governments struggle-or refuse-to act upon effectively.
For india, such developments offer lessons about integrating thorough climate frameworks into decision-making processes. As existing legal battles underscore gaps between policy enforcement and sustainable practices (e.g., pollution control or renewable targets), India must evaluate its preparedness against externalities magnified by extreme weather events-rising floods being one example witnessed domestically every monsoon season.
While specificity of state constitutions plays a key role in cases like this-and differs fundamentally from India’s unified judiciary-the symbolic precedent adds momentum toward embedding ecological safeguards into governance structures globally. These lawsuits also highlight how marginalized communities face disproportionate impacts from changing climates-a factor closely relevant amidst India’s still-unfolding debates on balancing development with equitable access to resources.