Now Reading: SpaceX Launches European Reentry Capsule on Bandwagon-3 Mission
-
01
SpaceX Launches European Reentry Capsule on Bandwagon-3 Mission
SpaceX Launches European Reentry Capsule on Bandwagon-3 Mission

Swift Summary
- Launch Details: SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket launched the Bandwagon-3 mission on April 21,2025,at 8:48 p.m. EDT from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
- Payloads:
– Phoenix 1: A European-built reentry capsule by German company Atmos Space Cargo aimed to test its inflatable heat shield technology, with plans for future space logistics applications.
– Additional satellites: South Korea’s Agency for Defense Advancement launched the 425Sat-3 and Tomorrow Companies Inc. deployed their satellite for weather forecasting.
- Past meaning: Phoenix 1 marks the first reentry mission conducted by a European company and is set to splash down in the Atlantic Ocean after one orbit around Earth.
- SpaceX Programs: Bandwagon missions are part of SpaceX’s rideshare initiatives alongside their larger Transporter program, which has completed thirteen missions since its debut in January 2021.
Images:
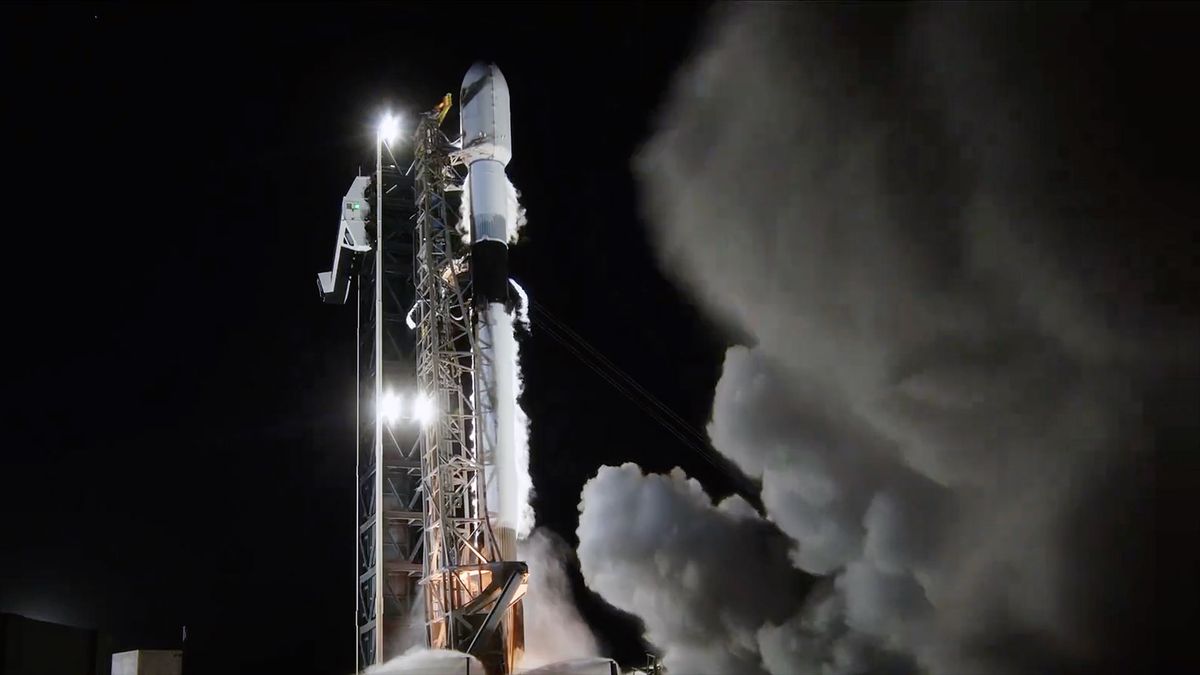
!Image of Falcon rocket launching
A white and black rocket gives off a large plume as it lifts off from launch pad (Image credit: SpaceX)
!Image of rocket stage landing
The first stage returning after launching payload at night (Image credit: SpaceX)
Indian Opinion Analysis
The successful deployment of Phoenix 1 underscores evolving space capabilities outside traditional government-led programs.Germany’s venture into reusable technology positions Europe as a growing player in global space logistics-echoing advancements made by countries like India through ISRO’s reusable transport tests. As nations pursue microgravity research and cargo retrieval from orbit, this could pave new avenues for interconnected international partnerships.
for India, this reaffirms the trajectory set by private-public collaboration, such as recent strides with homegrown space startups like Skyroot Aerospace or Agnikul cosmos facilitating cost-efficient launches. Potential knowledge exchange between emerging private entities internationally may elevate India’s prospects across orbital manufacturing or defense collaborations-a vital area amid rapid geopolitical shifts globally.
India will need sustained focus on indigenous innovation while leveraging policy frameworks to challenge existing leaders like NASA/SpaceX through competitiveness rather than hierarchy-based systems alone!