Now Reading: Scientists Unveil Mystery of Giant Planet Orbiting Tiny Star
-
01
Scientists Unveil Mystery of Giant Planet Orbiting Tiny Star
Scientists Unveil Mystery of Giant Planet Orbiting Tiny Star

Rapid Summary
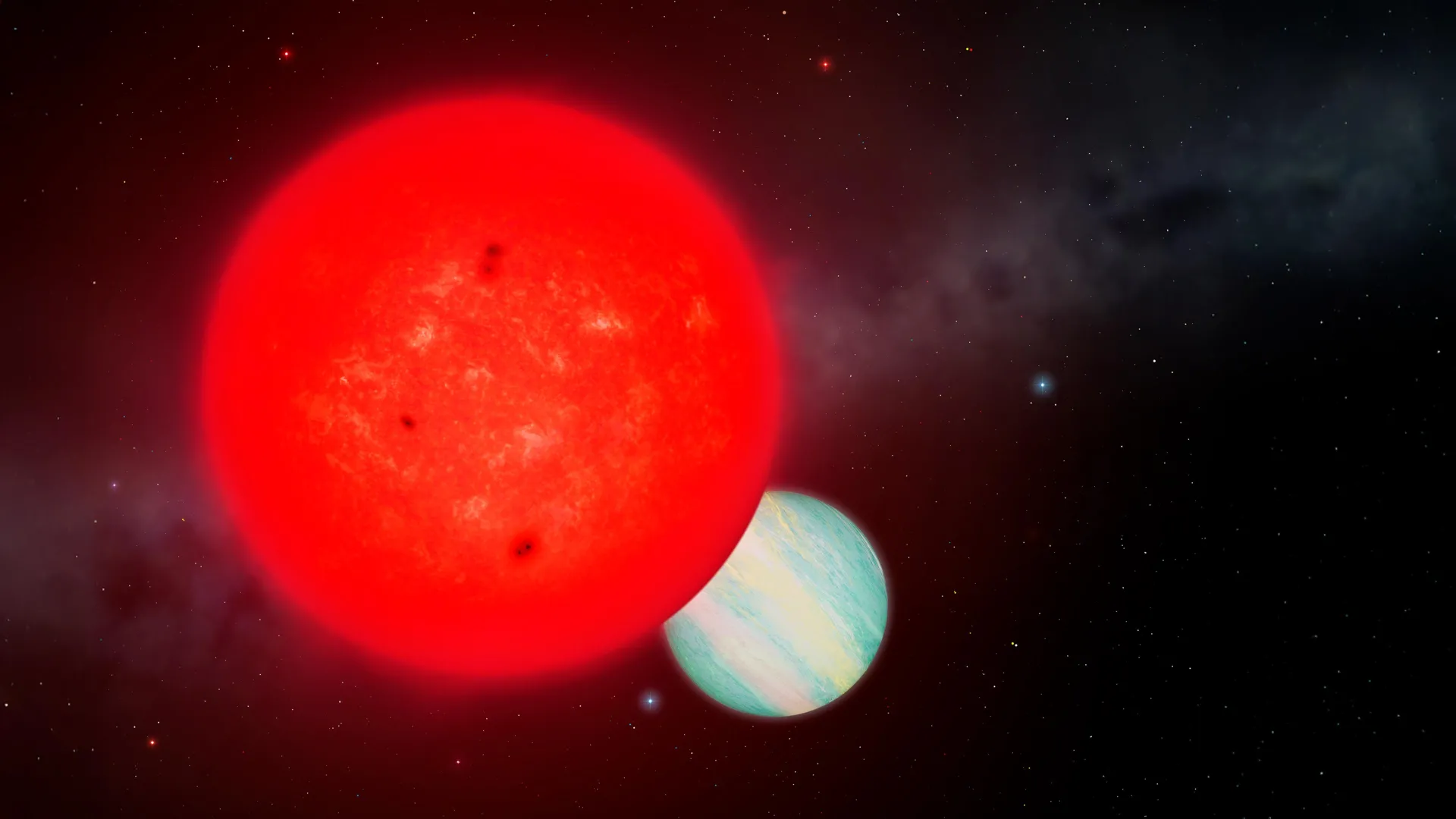
- Discovery: A Saturn-sized giant planet, TOI-6894b, has been detected orbiting a red dwarf star (TOI-6894).
- Host Star Characteristics: TOI-6894 is a red dwarf with only 20% the mass of the Sun adn a radius 40% smaller than any previously known host of transiting giant planets.
- Detection Methods: Initial identification was made using NASA’s TESS data, followed by detailed observation campaigns from ground-based telescopes affiliated with SPECULOOS and TRAPPIST projects led by the University of Liège.
- Planet Details: TOI-6894b has half the mass of Saturn and completes an orbital period in just over three days. It challenges previous assumptions about planet formation around low-mass stars.
- Implications for Planetary Science: The discovery questions existing models which suggest small stars lack sufficient material to form or retain giant planets. Experts believe similar discoveries could reshape understanding of planetary diversity in our galaxy.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The detection of TOI-6894b presents groundbreaking implications for planetary science, particularly concerning how planets form around low-mass stars like red dwarfs, which are among the most common stellar types in our galaxy. For India’s growing space exploration ambitions-embodied through missions such as Chandrayaan and Aditya-L1-the findings underscore the importance of fundamental space research collaborations globally.
India might benefit strategically by prioritizing research initiatives that explore exoplanet diversity or forming partnerships involving advanced observational infrastructure like SPECULOOS and TRAPPIST telescopes abroad. The discovery also highlights emerging gaps in theoretical models that Indian academic institutions could tackle alongside international peers through deeper computational studies and simulations.
Understanding cosmic anomalies such as TOI-6894b enhances humanity’s grasp over worldwide phenomena-a scientific endeavor that aligns well with India’s vision for expanding its role as both an explorer and contributor within global astronomy efforts.