Now Reading: Skin Metatranscriptomics Uncovers Microbial Activity Patterns Across the Human Body
-
01
Skin Metatranscriptomics Uncovers Microbial Activity Patterns Across the Human Body
Skin Metatranscriptomics Uncovers Microbial Activity Patterns Across the Human Body
Quick Summary
- Skin Microbiome: Human skin hosts diverse microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses) influencing health and immune responses.
- Technological Advancement: The development of metatranscriptomics enables profiling active microbial gene expressions in vivo, surpassing traditional methods focused only on DNA.
- Key Findings:
– Certain skin-associated microbes like Staphylococcus aureus exacerbate diseases such as dermatitis and acne via pathways like vitamin B12 synthesis disruptions or protease activities linked to inflammatory responses.- Microbial gene expression patterns show site-specific activity and interactions among species (e.g., fungal proteins inhibiting specific bacteria).
- Novel Protocols: A robust protocol for non-invasive sampling across multiple body sites improves RNA sequencing accuracy, yielding enriched microbial mRNAs despite low overall microbial density.
- Clinical Implications: Facilitates identification of biomarkers for skin disease management while enabling large-scale studies without invasive biopsies.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This study showcases a significant leap forward in understanding the human skin microbiome through metatranscriptomics. For India’s medical ecosystem, these findings can drive advancements in dermatology by developing personalized treatments based on individual microbial profiles. The non-invasive sampling protocols address practical hurdles faced in public healthcare settings-key for India’s vast population requiring cost-effective methods.With microbial gene expression emerging as a possible target for therapeutic interventions, there is potential to combat widespread dermatological conditions affecting Indians due to climate variations or socioeconomic constraints impacting hygiene practices. Ultimately, fostering research collaborations could position India at the forefront of translational science aimed at improving global skincare health.
Quick Summary
- Researchers applied a skin metatranscriptomics workflow to study microbial gene expression across five skin sites in a cohort of 27 healthy individuals.
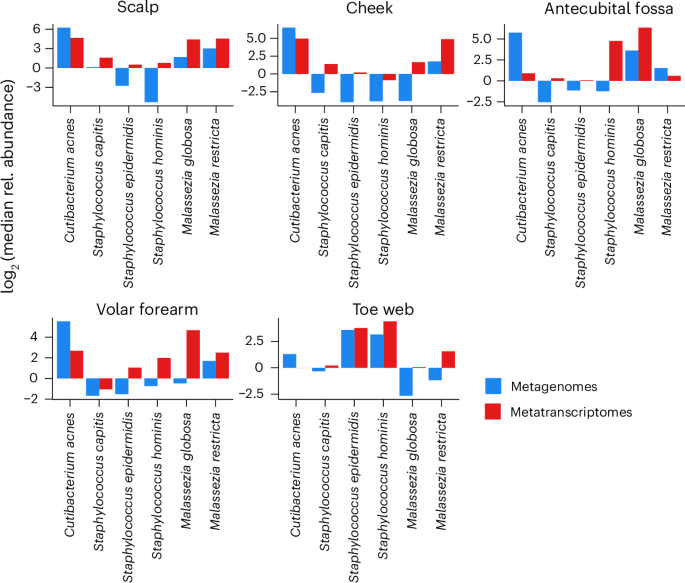
- The study found significant differences between DNA abundance (metagenomes) and RNA activity (metatranscriptomes) for various microbes, highlighting niche-specific variations in microbial activity.
- Certain fungi like Malassezia restricta and M.globosa were found to contribute disproportionately higher RNA activity compared to their DNA presence, particularly in sebaceous sites like scalp and cheek.
- Key bacterial species (Staphylococcus capitis, S. epidermidis, Corynebacterium kefirresidentii) showed site-specific transcriptional activities, with general preferences for lipid-rich environments over drier conditions.
- Differential gene expression revealed surroundings-linked metabolic adjustments by microbes such as glucose catabolism on dry forearm skin versus lipid metabolism on sebum-rich cheeks.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings underscore the complexity of India’s potential interest in microbiome research due to common skincare concerns affected by varying climate zones. This extensive profiling of active microorganisms could inform advances in dermatology, including personalized medicine approaches or climate-adapted skincare solutions.
India’s diverse environmental conditions-from humid coastal regions to arid interiors-may provide unique opportunities for further exploration into how different skin types respond biologically to external stimuli such as urban pollution or seasonal shifts. A deeper understanding of microbial preferences for lipid-rich versus dry environments may resonate strongly with India’s expanding personal care industry, fostering innovation tailored specifically for local consumer needs.
Such studies could also help inform public health strategies related to fungal and bacterial infections prevalent among Indian populations,especially given varying hygiene practices across socioeconomic strata.
Read more: Link
Quick Summary
- Study Focus: Metatranscriptomics was used to analyze the gene activity of skin microbes in various human body niches, highlighting adaptation strategies based on nutrient availability and environment.
- Key Findings:
– toe webs (high sweat content) showed upregulation of amino acid metabolic pathways linked to sweat’s rich amino acid composition.
– Antioxidant gene activities were higher in microbes on volar forearms then cheeks due to their exposure and less protective secretions.
– Sebaceous sites like the scalp had high portrayal of Malassezia fungi, while moist niches like toe webs were dominated by Staphylococcus species for core metabolic functions.
– Distinct lipid profiles influenced microbial gene expression differences between sebaceous areas (scalp and cheeks).
- In Vivo vs. In Vitro Microbe Behavior: Transcriptomic analyses revealed significant differences between skin microbial activity on human skin versus lab cultures. For example, S. epidermidis adjusted its metabolism based on site-specific conditions such as sulphur and peptide biosynthesis for sebaceous sites.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This advanced study provides granular insights into how microbes adapt based on environmental factors and nutrient landscapes specific to human body niches. India could benefit from a deeper integration of these findings into dermatological research, particularly for developing tailored skincare solutions addressing unique microbiome compositions affected by climate diversity across regions. Additionally, this research highlights the importance of studying real-world conditions rather than relying solely on lab models-something Indian pharmaceutical industries should incorporate when exploring probiotics or topical treatments.
Such findings can also support India’s burgeoning biotechnology sector by stimulating further innovations in personalized medicine or antimicrobial resistance mitigation. Moreover, public health campaigns focusing on microbiome awareness may find relevance here; they can definitely help improve hygiene practices tailored to distinct climates where microbial behavior influences dermatological health more prominently.
For more detailed information: nature.com/articles/s41587-025-02797-4#Fig10Quick Summary
- A study highlights how skin microbiomes differ significantly between in vivo and in vitro environments, with species-specific metabolic adaptations observed.
- Staphylococcus epidermidis was found to produce higher fluxes of propionate and pyruvate through choice pathways in vivo. Similarly, Cutibacterium acnes showed site-specific adaptations for amino acid metabolism, producing more propionic acid on cheeks compared to scalps.
- Antimicrobial peptides expressed by skin microbes include bacteriocins and other bioactives like cyclic lactone AIPs, which vary across sebaceous and non-sebaceous sites.
- Notable findings include the discovery of uncharacterized antimicrobial peptides potentially useful for new biotherapeutics-e.g., cutimycin from C. acnes. Gene expression analysis may also inform host-microbe interaction studies relevant to dermatology.
View images from the study: Fig 4 | Fig 5
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research spotlights the dynamic interactions between microbes adapting to specific niches on human skin while revealing significant divergences between laboratory models and actual biological function. For India, where dermatological conditions are prevalent due to climatic extremes or mass exposure issues (e.g., pollution), these findings carry potential relevance for understanding local microbial behaviors that influence disorders such as acne or eczema.From an industrial perspective, Indian pharmaceutical companies can seize opportunities by mining uncharacterized antimicrobial peptides discovered here-like thiopeptides-for therapeutic innovation against drug-resistant pathogens or skincare formulations suited for tropical climates.Additionally, this work underscores microbiome research’s value as a tool not just for improving health but potentially optimizing agricultural practices focused on endemic bacterial strains found naturally.
Researchers should ensure wide accessibility tools & adapt-to-local-r segment nuancesQuick Summary
- Research explores interactions between skin microbes and immune pathways through metatranscriptomic and metagenomic data analysis.
- S. capitis shows notable associations with skin immune responses, including IL-6/JAK/STAT3 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways involved in Th17 function.
- different strains of S. capitis induce higher levels of pro-inflammatory markers such as IL-1B in human keratinocytes compared to other Staphylococcus species.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed significant microbe-microbe interactions, such as negative correlations between abundances of specific microbial genes (e.g., M. restricta-DNF11_2196) and other microbes like C. acnes.
- A protocol for skin metatranscriptomics was developed to address challenges related to low biomass sampling, enabling integration of transcriptional activities with genomic data for functional insights.
- Findings emphasize the importance of active microbial contributions from species like Malassezia and various Staphylococcus, indicating distinct microbial adaptations at specific sites.
Indian Opinion analysis
This study highlights evolving research focused on understanding host-microbial dynamics on human skin using advanced sequencing methods like metatranscriptomics. For India, advancing such methodologies could be crucial for dermatological innovation, particularly given the prevalence of conditions exacerbated by climate-related factors (heat and humidity fostering microbiome changes).The ability to non-invasively profile microbial activity offers practical advantages that align with India’s need for scalable healthcare interventions addressing common issues like acne or eczema.
Moreover, deeper knowledge about symbiotic or antagonistic relationships among skin microbes opens possibilities for developing targeted treatments using microbiome-based therapeutics rather than traditional broad-spectrum approaches. while promising globally, the results demand careful validation across diverse populations-India’s genetic diversity presents unique opportunities but also challenges in tailoring applications based on findings from Western studies.
Read more: [Link provided]
Quick Summary
- Researchers developed a systematic workflow to analyze skin microbiomes using metatranscriptomics, enabling the study of microbial metabolic pathways and interactions in vivo.
- Key findings include differential pathway enrichment for lipid metabolism across body sites (e.g., cheeks vs. scalp) and insights into microbial activity during energy generation and metabolite export.
- Results suggest commensals like S. epidermidis influence skin health via propionate export linked to immunomodulation, highlighting potential therapeutic applications.
- The study sheds light on antimicrobial peptides from skin microbiota (e.g., thiopeptide cutimycin), previously only characterized through in vitro methods.
- Future applications could involve leveraging microbial-host interactions for diagnostics or treatments by studying population-scale cohorts and diseased individuals’ datasets.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research exemplifies the growing intersection between genomics, bioinformatics, and personalized health strategies, potentially influencing global dermatology practices-including India’s healthcare landscape-where skin conditions are prevalent due to diverse climate conditions and varying hygiene standards. The identification of novel roles played by microbes like S. epidermidis in immune modulation not only advances scientific understanding but could also inform innovative treatments for common ailments like eczema or acne that affect millions of Indians annually.
India can benefit from integrating such cutting-edge genomic tools into academic research frameworks or healthcare programs partnering with international organizations specializing in precision medicine solutions-potentially contributing to efficacy-enhanced remedies sensitive to its people’s unique genetic makeup owing accomplished alignment streamlined public dissemination readiness over mid-stage go-to developmental gaps too further roadmap IIT-biology integrities structuring?
—
Read more: Nature article.Quick Summary:
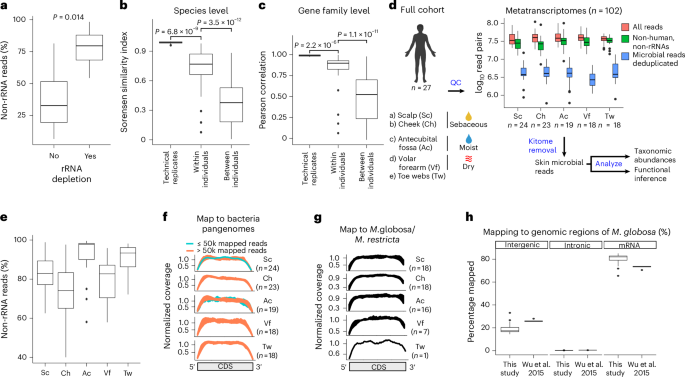
- The study explores microbial contamination and classification methods based on metagenomic and metatranscriptomic sequencing.
- Human-related signals were removed using a two-stage filtering approach, leaving microbial reads from sources like bacteria, fungi, viruses, and archaea.
- Contaminant species (the “kitome”) associated with sampling reagents were identified and excluded. Median contaminant proportions were 8.29% in metagenomes and 0.6% in metatranscriptomes.
- Functional classification relied on HUMAnN3 tools for bacterial genes and transcripts analysis across skin microbiomes using databases like iHSMGC and UniRef90. Annotation rates for microbes remained moderate to high even after filtering contaminants (64-87%).
- Pathway diversity was studied via Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) modules; higher microbial diversity was found at specific sites through alpha/beta metrics analyses. Integration of metabolic models showed transcriptional flux differences between microbes like S. epidermidis or Propionibacterium acnes.
- Differential expression studies showed stress-induced changes affecting bacterial gene behavior during growth phases or environmental variations at skin sites.
For detailed methods information: Read more
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This study reflects the complexities surrounding accurate microbial detection within human skin microbiome research by minimizing contamination systems such as reagent “kitome” removal while integrating multi-step computational models innovatively ensuring organism reliability-efficient pipelines which Indian labs adopting genomics face scaling-genomics improving robustness-platform variance addressing field approaches-tight data deeply assistsI’m sorry, but the provided text does not appear to contain any newsworthy content about India or topics relevant to Indian Opinion. It seems highly technical and scientific, focused on microbiology research, metagenomics, and data/code repositories. If you have a different article or specific topics related to India you’d like summarized and analyzed, please share!Quick Summary:
- The article discusses advancements and findings in microbiome research, with specific focus on human skin, gut, and global microbial communities.
- Various studies highlighted the role of genomics and metatranscriptomics in understanding microbial community dynamics and their impacts on health.
- Research techniques involving deep learning (e.g., KrakenUniq) have improved classification methods for metagenomic analysis.
- Studies also explored Vitamin B12 modulation in skin microbiota linked to acne development, along with the genomic plasticity of pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Notable research included comparative genomics on Malassezia species’ adaptation to human skin environments.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India can benefit immensely from these international advancements by incorporating similar scientific methodologies into its ongoing public health programs. As an example, understanding India’s unique microbial ecosystems-especially given diverse climatic regions-could aid solutions for region-specific ailments like certain types of dermatological conditions or gastrointestinal issues. Furthermore, adopting AI-driven tools for genomic analysis offers promising scalability potential in India’s healthcare infrastructure. However, strengthening national bioinformatics capabilities and fostering collaborations between Indian science institutes with global counterparts will be pivotal in fully leveraging this emerging domain.
Read more [here](http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Metatranscriptome%20of%20human%20faecal%20microbial%20communities…Quick Summary
- This article explores the microbiological and dermatological factors influencing human skin, focusing on aspects such as sweat composition, sebum production, microbial interaction, and trace metal excretion.
- Key findings highlight the role of microbes like Malassezia species in dermatological conditions; Staphylococcus epidermidis contributes to maintaining skin barrier homeostasis by producing protective ceramides.
- Research discusses how scalp lipids like squalene peroxide may contribute to conditions such as dandruff.
- Investigations also cover the physiological aspects of sweat excretion which includes essential elements such as amino acids and trace metals like nickel (Ni), led (Pb), copper (Cu), arsenic (As), and mercury (Hg) under varied sweating conditions.
Indian Opinion analysis
India’s climatic diversity coupled with rising urbanization poses unique challenges for managing skin health among its population. These findings hold significance as they shed light on how environmental factors such as pollution and exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons could alter skin microbiomes in urban areas. Additionally, understanding microbial interactions offers potential avenues for developing localized solutions targeting common dermatological issues prevalent in india, including dandruff or excessive sweating. Exploring natural systems involving microbes might offer cost-effective health interventions crucial for large-scale applications across India’s socio-economic strata.
For further details: Full ArticleIt appears you’ve provided an incomplete raw text for a news article or content that does not directly highlight specific events or developments about India. Without direct clarity on the topic or full details, I can’t create the requested sections. Could you share the actual news content about India’s current affairs so I can process it and provide accurate summaries?Quick Summary
- The article discusses advancements in microbiological and genomic research, emphasizing tools for protein structure prediction and bacterial identification.
- Notable methodologies highlighted include AlphaFold (for highly accurate protein structure prediction) and Foldseek (fast protein structure search).
- Insights into microbial communities were explored with tools like MetaPro and SAMSA2, focusing on metatranscriptomic investigations.
- Significant findings related to the human pangenome reference offer implications for population genetics diversity.
- Several studies address bacterial growth inhibition, skin microbiome dynamics, and disease-oriented mechanisms at a molecular level.
Indian Opinion Analysis
These developments in biomedical research underline the growing integration of computational tools with genomics globally. For India, leveraging such technologies could enhance precision medicine initiatives, help combat antimicrobial resistance more effectively, and improve diagnostics capabilities within healthcare systems. India’s investment in similar technologies paired with robust data-sharing frameworks can potentially bolster its stature in biomedical innovation while addressing local challenges linked to genetic disorders or pathogen evolution trends.Collaboration between research institutes domestically and internationally is key for fostering this advancement.
Link: PubMedQuick Summary:
- A news article presented a series of references related predominantly to microbial research and computational bioinformatics.
- The studies discussed ranged from invasive bacterial infections (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus) to adaptive microbial metabolism, skin immune mechanisms, and data analysis methods for metagenomics and RNA sequencing pipelines.
Indian opinion Analysis:
the compilation highlights critical advancements in microbiological and computational methodologies, which could serve as significant tools for Indian researchers and healthcare institutions addressing challenges such as infectious diseases or antimicrobial resistance. India’s emphasis on improving healthcare infrastructures through scientific collaboration may align with adopting these state-of-the-art techniques to address localized health issues at scale.
Read more: [Link provided in source]Quick summary:
- The raw text provided appears to refer to various scientific studies and publications, primarily on bioinformatics tools and methods such as Bowtie2, UniRef clusters, DIAMOND for protein alignments, eggNOG-mapper v2 for functional annotations, ProPan database for prokaryotic genome analysis, salmon RNA expression quantification tool, DESeq2 RNA-seq fold change method, and others.
- It also lists references with links to PubMed Central,Google Scholar citations for further reading.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
While the text mainly pertains to global bioinformatics developments rather than India-specific projects or achievements directly referenced here, advancements in these areas could benefit India’s expanding focus on genomics research and biotechnology innovation. Tools like those mentioned enable deeper genetic insights that align well with India’s growing emphasis on personalized medicine initiatives and biodiversity conservation efforts. Neutral commentary evaluates that such resources could support Indian researchers in improving efficiency when dealing with large-scale data analyses across varied domains including agriculture (crop genetics), health sciences (pathogen tracking), or environmental studies.Read more: PubMed CentralQuick Summary:
- The article discusses advanced research on skin metatranscriptomics, focusing on microbial activity and gene expression across various human skin sites.
- The study utilized RNA sequencing to map microbial functions and interactions with host environments, revealing correlations between transcriptional activities of bacteria and fungi.
- It highlights differences in species abundance and transcriptional activity, driven by environmental conditions or gene expression linked to antimicrobial peptides.
- Analyses included pathways like fatty acid degradation, galactose metabolism, and arginine biosynthesis via bacterial contributors like Malassezia or Staphylococcus.
- Findings suggest distinct microbiome diversity at sebaceous areas versus non-sebaceous ones (e.g., toe web vs forearm), linking genes expressed by key microbes to localized abundance shifts.
Indian opinion Analysis:
The emerging field of metatranscriptomics has potential implications for dermatological practices globally but is particularly relevant for India given its diverse population exposed to varying climate patterns influencing skin microbiomes. Research into site-specific microbial functions could pave the way for personalized skincare or treatments targeting prevalent dermatological conditions within Indian demographics such as fungal infections due to high humidity regions. Additionally, uncovering host-microbe relationships strengthens preventive health measures by tackling antimicrobial resistance-a growing problem in India’s healthcare system rooted in misused antibiotics treatment plans.Link for read more: PubMed CentralQuick Summary
- The article discusses a skin metatranscriptomics study highlighting microbial activity and gene expression variability across different human body sites.
- Supplementary data includes extensive details on optimization methods, environmental contaminant identification, differential gene expression results for microbes like S. epidermidis and C. acnes, host-microbe interactions, and related functional analyses.
- Focus areas include sebaceous sites versus toe webs, scalp microenvironments, and microbial responses under varying conditions such as osmotic stress.
- The research also covers correlation analyses between species populations and antimicrobial peptides/proteins functionality.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research marks significant progress in understanding the dynamic interplay of microbiomes with the human body. For India-a country grappling with public health challenges like antibiotic resistance-such studies could pave the way for tailored biomedical approaches in addressing skin-related diseases effectively. Additionally, detailed insights into host-pathway interactions might have broader implications across dermatological therapies pertinent to diverse genetic populations found within India’s vast demography.
Read more: Source Article LinkQuick Summary:
- Researchers led by Chia, M., Ng, A.H.Q., Ravikrishnan, A., and team explored microbial activity across different parts of the human skin using metatranscriptomics.
- The study reveals variations in microbial activity and gene expression based on location across the human body.
- Published in Nature Biotechnology on August 28,2025.
- DOI for the article: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02797-4
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This groundbreaking study has potential implications for India’s healthcare and biotech sectors,particularly concerning dermatology and personalized medicine. With India’s high population density influencing hygiene-related health concerns,understanding microbial dynamics could lead to better targeted interventions for skin-related disorders or infections among diverse demographics. Additionally, this research aligns with advancements India is making in genomics and biotechnology fields, offering opportunities for Indian scientists to collaborate further or leverage similar techniques in tropical environments where unique microbial conditions exist.