Now Reading: NASA Sensor Data Aids Firefighters in Tackling Wildfires
-
01
NASA Sensor Data Aids Firefighters in Tackling Wildfires
NASA Sensor Data Aids Firefighters in Tackling Wildfires
Fast Summary
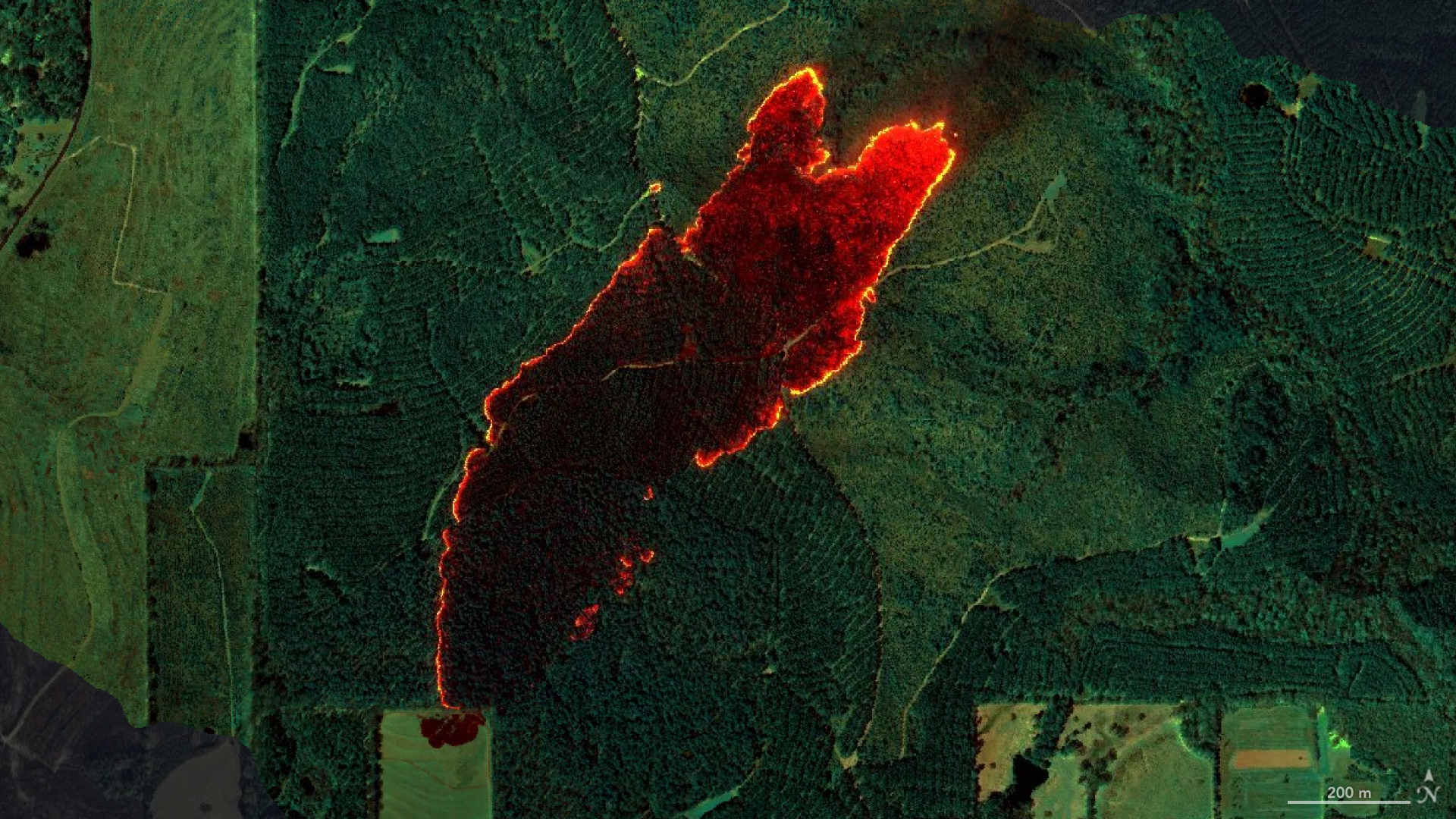
- NASA’s AVIRIS-3 sensor was used to detect and map wildfires in real-time, aiding firefighting efforts in Alabama.
- On March 19, AVIRIS-3 identified a 120-acre wildfire near Castleberry, alabama, before it was reported to officials. The system provided rapid fire perimeter maps that were sent directly to firefighters’ phones via satellite internet.
- Data processing from detection aboard the flight to distribution happened within minutes, helping firefighters focus resources efficiently and limit damage.
- The technology mapped at least 13 wildfires and prescribed burns during test flights over Alabama, Mississippi, Florida, and Texas as part of NASA’s FireSense Airborne Campaign in March.
- The imaging spectrometer provides three types of useful fire maps: Fire Quicklook (intensity visuals), Fire 2400 nm Quicklook (hot spots), and smoke/burned area visualization maps.
- The Castleberry Fire hot spot data enabled precise resource deployment. In another case near Mount Vernon fires were strategically contained within close proximity of nearby buildings using AVIRIS-generated maps.
- Ethan Barrett of the Alabama Forestry Commission highlighted how these tools gave crews actionable intelligence at unprecedented speed compared to traditional methods.
For more information on this technology: Read More
Indian Opinion Analysis
The success of NASA’s AVIRIS-3 sensor demonstrates a remarkable advancement in leveraging real-time data for disaster management. While primarily benefiting firefighting efforts in the U.S., such innovations hold important implications for India given its vulnerability to forest fires-especially across regions like Uttarakhand or Odisha where timely action is critical.
India’s forestry divisions could adapt similar technologies through collaboration with international agencies or by developing indigenous airborne sensors tailored for varied terrains. real-time mapping systems with satellite internet connectivity offer vital benefits: expediting response times during emergencies and improving resource allocation efficiency while perhaps minimizing ecological losses.
As India continues grappling with climate-induced challenges such as wildfires alongside burgeoning technological progress under agencies like ISRO-a strategic exploration into AI-driven wildfire management could be pivotal both environmentally and economically.