Now Reading: Assam’s Bodoland Leads as First Tribal Council to Digitise Land Records
-
01
Assam’s Bodoland Leads as First Tribal Council to Digitise Land Records
Assam’s Bodoland Leads as First Tribal Council to Digitise Land Records

Quick Summary
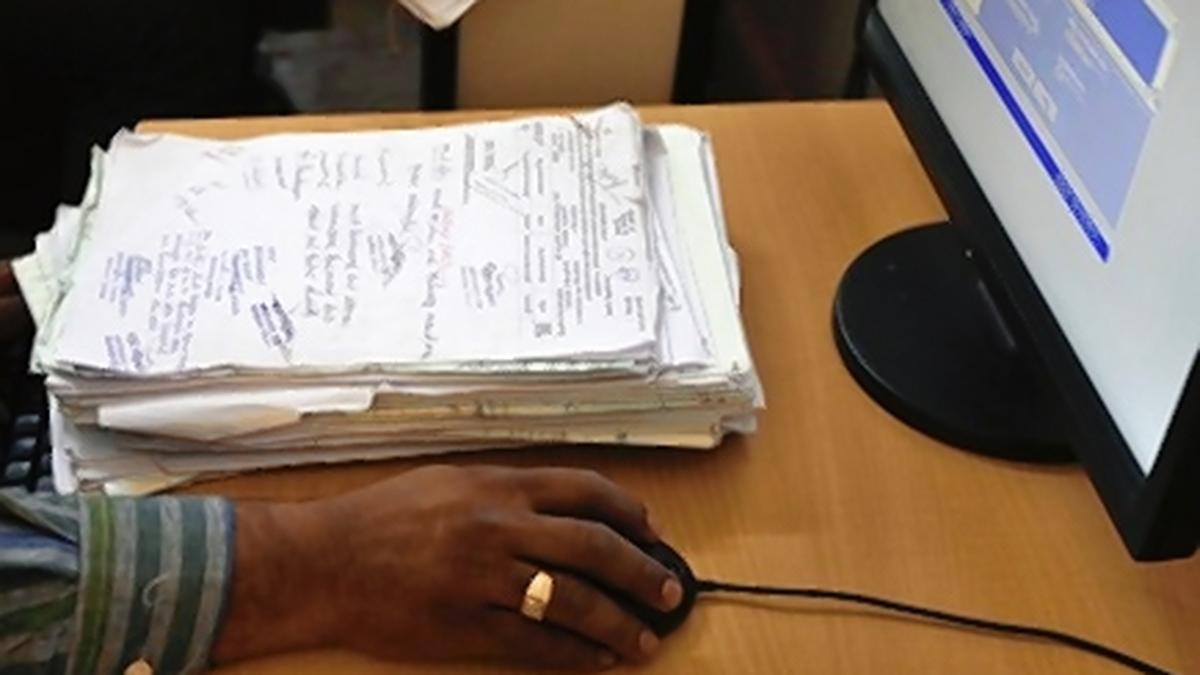
- The Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR) in Assam is the first tribal council under India’s Sixth Schedule to fully digitise its land records.
- Over 15 lakh land documents, including texts and maps, were digitised across BTR’s 8,970 sq.km area.
- This marks a transition from decades of manual record-keeping to a digital system.
- The Sixth Schedule provides special provisions for tribal areas, with 10 such autonomous councils in the north-east region: three each in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram; and one in Tripura.
- Digitisation aligns with the Digital India Mission and aims to improve openness and administrative efficiency.
- BTC Secretary Dhiraj Saud stated that the process began in 2023 with ground-level surveys across districts-Baksa, Chirang, Kokrajhar, Tamulpur, and Udalguri-and included cross-verification of old records using GIS mapping for boundary accuracy.
- Mission Bwismwuthi initiatives have provided land rights this year to 47,000 indigenous families as part of broader land reforms facilitated by digitisation efforts.
- A digital platform now allows efficient access for citizens through kiosks, apps, and web portals while reducing social conflicts related to land disputes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The full digitisation of BTR’s land records is a meaningful achievement both symbolically and administratively. By integrating Geographic Details System (GIS) mapping into a centralised database accessible via modern platforms such as mobile apps and kiosks, this initiative underscores India’s shift toward governance through technology under missions like Digital India.It directly addresses long-standing issues like corruption risks tied to manual recordkeeping processes within tribal council areas.
For local governance structures established under the Sixth Schedule-often hindered by infrastructural challenges-the accomplished implementation serves as an example for how technological adaptation can enhance administrative capacity while preserving customary practices essential to indigenous communities. Moreover, initiatives such as Mission Bwismwuthi demonstrate how targeted reforms intersecting with technological advancements can expand equitable access to resources like secure landownership.
If scaled or replicated across other northeastern councils facing resource constraints or socio-political tensions over community-based ownership rights frameworks; it coudl provide trajectories worth considering regarding self-governance systems’ efficacy evaluation longer time-horizons strengthening ongoing decentralization-policy momentum unravelingly role subnational but critical infrastructure bases .
.Read More