Now Reading: DNA Repair and Mutation: Insights into ADP-Ribosylation in Bacteria and Eukaryotes
-
01
DNA Repair and Mutation: Insights into ADP-Ribosylation in Bacteria and Eukaryotes
DNA Repair and Mutation: Insights into ADP-Ribosylation in Bacteria and Eukaryotes
Swift Summary
- Genome editing advances have introduced Base editors (BEs) that modify DNA chemically without causing double-stranded breaks, reducing risks like chromosomal abnormalities. These edits are programmable by targeting specific DNA sequences.
- Conventional base editing relies on subtractive modifications like deamination or excision of bases; a new approach called “Append Editing” is under exploration, focusing on additive modifications such as ADP-ribosylation of DNA bases.
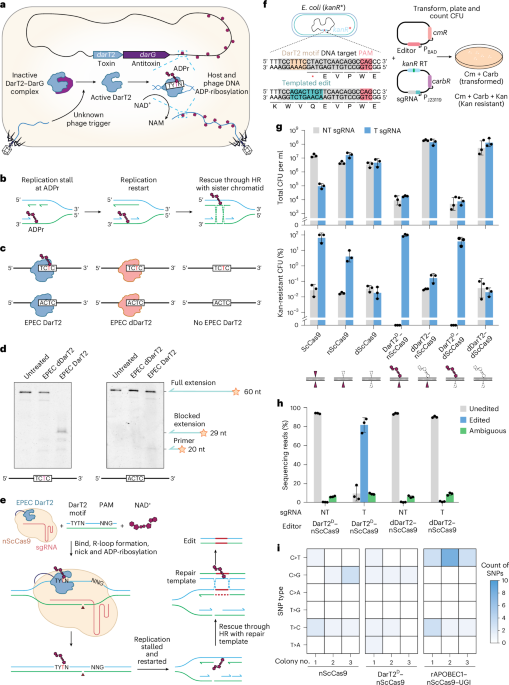
- The study highlights the use of a bacterial toxin protein (DarT2) fused with Cas9 to append ADP-ribosyl groups onto thymine in single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). This “append editing” blocks replication and promotes homologous recombination repair using an external template.
- Experiments in E. coli tested the efficiency of various genome-editing methods including Cas9-centric approaches and Append Editing. Append Editing showed promising results with high accuracy (~97% targeted edits) and minimal toxicity compared to other techniques.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Technological advancements in genome editing are increasingly significant for India due to their applications spanning healthcare, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology research sectors. Append Editing could offer substantial benefits over traditional CRISPR-Cas9-based approaches by enabling precise edits with reduced genetic instability or unintended mutations.
India’s growing investments in biotech R&D position it as a potential leader in leveraging this innovation for customized therapeutic solutions, improved crop resiliency programs (via genetically edited plants), or even tackling genetic disorders prevalent within its population. However, as the technology progresses into clinical applications globally-including trials featuring Base Editors-India must ensure regulatory frameworks capable of addressing ethical concerns while fostering safe implementation.
Advancing partnerships between Indian institutions and global leaders engaged in such transformative research would ensure quicker adoption while aligning domestic priorities with frontier technologies like genome editing.
Read more: Nature Study Link### Quick Summary:
– A study explores the use of targeted DNA ADP-ribosylation for genome editing in bacteria, yeast, and plants.
– This approach relies on homologous recombination to introduce genome edits while avoiding traditional cytotoxic impacts seen with Cas9-based systems.
– The DarT2 enzyme was modified (DarT2DLAA) to reduce cytotoxicity in bacterial cells without compromising editing efficiency.- Efficient edits included replacements,deletions,and insertions of varying lengths primarily in *E. coli* and *Salmonella enterica* without adverse effects on cell viability.
– In eukaryotes like yeast (*Saccharomyces cerevisiae*) and plants, DNA ADP-ribosylation primarily induced base mutagenesis rather than triumphant homologous recombination-based edits.
### Indian Opinion Analysis:
this breakthrough demonstrates promising scope for improving genetic modification techniques across various organisms.While successful applications were largely confined to bacterial strains like *E. coli*, the technique’s ability to mitigate cytotoxic effects signifies a step forward in microbial research methodologies that could have industrial or pharmaceutical implications.
From an Indian perspective, this genome-editing approach could be impactful across fields like agriculture and biotechnology. For instance, it may allow Indian researchers to explore safer modifications of food crops or develop bioengineered solutions aligned with affordable medicine production. Though, its limited efficiency in eukaryotic systems poses challenges that require further optimization before wider adoption is feasible.Read more: [Nature Article Link](http://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-025-02802-w)Quick Summary:
- Targeted ADP-ribosylation experiments explored programmable editing mechanisms across yeast, plant, and human cells.
- Mutagenesis predominantly occurred at ADP-ribosylated thymine bases, with biases toward specific base conversions (e.g.,T → A).
- In human cells (HEK293T), editing was significantly higher in the absence of TARG1 protein-a barrier to such modifications. Silencing TARG1 through RNA interference also enabled low-level edits.
- Compared to traditional Cas9-based genome editing, targeted ADP-ribosylation showed lower instances of unwanted indels or deletions.
Read more: Nature Source
indian Opinion Analysis:
This research presents advancements in precise gene editing technologies and the potential for practical applications beyond earlier CRISPR methods by minimizing off-target effects. For India, innovations like these could be transformative in fields including agriculture, biotechnology, and healthcare-addressing challenges such as disease-resistant crops or personalized medicine advancement. However, ethical considerations may arise regarding regulatory frameworks for genetic interventions and preventing misuse of such tools in a highly diverse socio-political landscape like India’s while experts try to standardize broader access inclusively.Read more: Nature Source
Quick Summary:
- researchers explored “append editing,” which uses chemical moieties for precise DNA modifications.
- The bacterial toxin DarT2 was employed to mediate ADP-ribosylation-based thymine editing (ADPr-TAE).
- In bacteria,ADPr-TAE introduced range of DNA edits,including replacements,deletions,and insertions without colony count reductions.
- In eukaryotes like yeast, plants and human cells, this method showed a bias towards unique edits (e.g., T-to-A or T-to-C).
- Comparatively fewer unintended bystander edits were observed versus existing base editors (BEs) using deaminases or glycosylases.
- Distinct pathways in repair mechanisms in eukaryotes were noted compared to homologous recombination in bacteria.
- This method has potential applications like reversing specific genetic mutations otherwise limited by conventional genome-editing tools.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
Append editing represents an innovative addition to the precision genome-editing toolkit. For nations like India with emerging biotechnology sectors and extensive agricultural reliance, this technique could foster breakthroughs such as improving crop resilience or addressing human genetic disorders. The reduced risk of unintended edits underscores its relevance for safe medical advancements. While global ethical concerns about genome editing persist, responsible deployment of ADPr-based methods might strengthen India’s competence both scientifically and economically within genomics research niches.
Read more: Source dataQuick Summary:
- The article discusses innovations in DNA modification techniques, specifically using enzymatic domains derived from host-pathogen interactions (e.g., ADP-ribosylation by DarT2 and related enzymes).
- These enzymes can target nucleotides like thymine and guanine for chemical modifications, potentially enhancing gene editing technologies.
- Applications of these advancements include more efficient genome editing and studying localized DNA repair processes.
- Challenges remain in introducing targeted DNA adducts to study replication-blocking lesions or mutagenesis tied to carcinogenesis.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This technological development in precision genome editing has intriguing implications for India’s biotechnology sector, which is actively contributing to global healthcare research, particularly in genetic studies and cancer biology. If adapted well, these techniques could improve therapeutic interventions and enhance fundamental research outputs related to mutagenesis or disease prevention. Though, ethical considerations around gene manipulation should remain a priority. Opportunities like increased collaboration with international researchers may arise for India’s bioengineering companies or academic setups seeking advanced tools to solve local genetic disorders with precision-targeted solutions.
For detailed reading: Linkquick Summary
- Extensive base editing experiments and genetic engineering studies were conducted using multiple organisms, including E. coli,S.enterica,yeast (S. cerevisiae), tobacco plants (N. benthamiana), and mammalian cells (such as HEK293T).
- These experiments involved plasmid transformations, genomic DNA isolation, PCR amplification, Sanger sequencing, Nanopore sequencing, and next-generation sequencing techniques to analyze genome edits and assess off-target effects.
- Specific protocols described plasmid construction methods, conversion procedures under various conditions (e.g., temperature or selective media), data collection approaches using BioTek Synergy Neo2 plate readers or illumina iSeq 100 setups, and bioinformatics tools for sequence variant analysis (R libraries, Minimap2 alignments).
Indian Opinion Analysis
the research highlights advanced developments in gene-editing technologies across a wide range of biological systems-expanding our capacity for precision genetics in both fundamental science and applied biotechnology sectors like agriculture or medicine.India has been an active contributor in genomics-related disciplines; thus such methodologies could bolster ongoing efforts in areas like crop improvement (e.g., enhanced yields via genome-edited crops) or biomedical innovations (e.g., disease-resistant cells). However-and critically-the ethical discourse on genetic modification is also vital within the Indian context to ensure sustainable progress considering ecological risks or socio-cultural sensitivities about gene editing’s long-term impacts.
Read moreThe input text does not appear to be newsworthy or related to current events in India that can be summarized for readers of Indian Opinion. It looks like a scientific procedure involving RNA extraction, next-generation sequencing, nanopore sequencing, and statistical analyses related to molecular biology experiments. As the article contains specific technical details aimed at scientific audiences rather than general news consumers, it is unsuitable for creating the requested Quick Summary and Indian Opinion Analysis.
If you have another topic or source text more relevant to Indian affairs or current events, please provide that for an accurate summary and analysis.Quick Summary
- Recent advancements have been reported in DNA base editing technologies, showcasing mechanisms for programmable edits in genetic material.
- The current research involves the use of cytidine deaminase toxins and translesion DNA polymerases, enabling innovative approaches to mitochondrial and genomic editing without relying on traditional CRISPR methods.
- New findings also highlight developments around toxin-antitoxin systems like dartg, which play roles in bacterial defense mechanisms and viral DNA neutralization via ADP-ribosylation processes.
- These studies explore structural bases for effective replication repair pathways and homologous recombination as potential therapeutic tools to address genetic damage.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s scientific and medical industries could benefit significantly from these cutting-edge developments in genome-editing technologies, particularly as the nation progresses in biotechnology and healthcare innovation. Such methods may offer new avenues for addressing inherited diseases or combating viral threats.Strengthening academic collaborations with leading researchers globally could help accelerate domestic expertise while fostering practical applications across agriculture, pharmaceuticals, or precision medicine sectors. Remaining attentive to ethical implications is critical to ensure responsible integration into Indian regulatory frameworks.
read more: PubMed ReferenceQuick Summary
- The raw text provided covers multiple scientific articles focused on DNA cleavage and genome editing techniques using CRISPR/Cas9, cytosine base editors, and similar technologies.
- Key highlights include advancements in base editing tools for A-T to G-C conversions without DNA cleavage, evaluation of off-target effects in genome editing by cytosine base editors, barriers to applying CRISPR systems efficiently in bacteria, and homologous recombination improvements in plant models like tobacco.
- Notable applications mentioned involve protein structure prediction with AlphaFold technology and protective mechanisms against toxic DNA ADP-ribosylation.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s rapidly growing biotechnology sector could immensely benefit from the advancements described here. Improved genome editing methodologies such as CRISPR/Cas9 have significant implications for agriculture (e.g., enhanced crop yields), medicine (such as precision therapies), and industrial applications (biomanufacturing). With Indian scientists actively contributing to global research,these breakthroughs could empower domestic innovation if integrated effectively through educational investments and supportive policies prioritizing ethical use. However, careful management of off-target effects is crucial for ensuring safety while applying these technologies broadly across diverse ecosystems.Read more: Nature ArticleQuick Summary:
- The raw text input contains references and citations related to advancements in genetic engineering and genome editing technologies, particularly involving CRISPR-Cas9 systems and other tools aimed at optimizing DNA alterations.
- studies discussed include innovations such as base editors for mammalian cells, strategies targeting double-strand break repair mechanisms, and development of gene-editing toolkits for bacteria like E. coli.
- These articles illustrate current progress in genome editing through enabling higher precision, minimizing off-target effects, and unlocking new potential applications across cellular models.
- Technological milestones mentioned range from engineered glycosylase-based tools to deaminase-free genomic platforms.
Indian Opinion analysis:
The developments in genome-editing technologies showcased provide transformative insights that could have lasting implications globally. For India, a country with burgeoning interests in biotechnology research and pharmaceutical innovation, such advancements may fuel local initiatives studying human diseases or agricultural improvements via genetically modified organisms. Though, ethical considerations tied to genetic manipulation remain critically important deterrents for broader realization.
These can also amplify India’s self-reliance under its “Make-in-India” ethos by collaborating on indigenous research using global findings. Striking balanced regulation while leveraging technological benefits demands integration into the Indian policy framework with streamlined supervision over bioethics committees attachedयुक्त Does currently . Analysises permirQuick Summary:
- The article includes references to various scientific studies, primarily centered around advances in CRISPR/Cas gene-editing technologies.
- CRISPR tools are highlighted for their role in genetic modifications through RNA-guided DNA integration techniques and base editing advancements.
- Research studies focus on optimizing efficiency in bacterial environments, stem cells, and developing programmable base-editing capabilities targeting particular genetic sequences.
- Specific enzymes like uracil-N-glycosylase variants have been mentioned for enabling certain types of edits (e.g., T-to-G or T-to-C conversions).
- Deep mentions of how cellular factors influence outcomes in prime editing capabilities were noted.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s robust scientific ecosystem could benefit immensely by incorporating these advanced CRISPR-related findings into its ongoing biotechnology research. With strategic investments, it can boost sectors such as agriculture (genetic resilience against pests), healthcare (gene therapy solutions for inherited diseases), and environmental conservation. While the adoption of gene-editing tools promises transformative impacts, ethical considerations-particularly relating to its regulation-will require rigorous oversight. india’s gradual move toward adopting global biotechnological trends needs an informed dialog among policymakers to balance innovation with societal impacts.
Read More: pubmed Central referenceQuick Summary
- The article discussed scientific studies on molecular mechanisms, including ADP-ribosylation of guanine bases and immune evasion by modified phage DNA.
- Research advances highlight 7-deazaguanine modifications in bacteriophages that protect their DNA from host system attacks.
- DNA modification strategies interfere with CRISPR-Cas systems,affecting bacterial immunity to pathogen attacks.
- Applications include understanding bacterial mutations and implications for therapeutic genetic tools like CRISPR.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The highlighted research underscores essential developments in microbial and phage biology,particularly concerning immune evasion mechanisms and genetic protection strategies. These findings have potential implications for India’s biotechnology sector, where areas such as genetic engineering and antibiotics resistance studies are gaining momentum. By leveraging these insights,India could enhance its capabilities in genomic medicine or agricultural microbiology innovations aimed at improving food security through pest-resistant crops or advanced therapeutic tools like precision gene editing technologies.
Read moreIt appears the provided input is primarily a list of references and citations rather than raw text for a news article about India. Unfortunately, there doesn’t seem to be any substantive content or context about an India-related topic in this input to produce a write-up under the Quick Summary and Indian Opinion Analysis sections.
If you can provide specific details or an actual news article text relevant to India, I will gladly assist with crafting the requested write-up!Quick Summary
- No specific news or factual details regarding India’s developments were mentioned in the raw text provided. The content focuses on various references related to scientific research articles, methodologies, and tools within fields such as genome editing, bioinformatics, and computational biology.
- The list includes prominent resources like SAMtools for sequence alignment/map formats, CRISPR/Cas systems for genome engineering, and software aids like MAFFT for sequence alignment.
Indian Opinion analysis
Without explicit mention of Indian involvement or implications in the source text provided, understanding its relevance would require assessing India’s position in biotech research globally. india has a burgeoning biotechnology industry with significant focus on genetics research aligned with tools mentioned above. enhanced adoption of these technologies could bolster advancements in healthcare breakthroughs such as genetic disorder treatment or agricultural innovation through genome editing.Neutral observability around usage efficiency might benefit collaborative efforts domestically while expanding global partnerships within scientific communities.
For more details: PubMed CentralQuick Summary
- A collaborative research effort has led to advancements in base-editing technologies for DNA repair and genetic engineering.
- The study highlights several innovations, including improved genome editing tools targeting specific gene sequences across organisms like E. coli, yeast, plants, and human cells.
- Funding contributions came from multiple institutions globally, with key grants from organizations like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and European Research Council (ERC).
- ethical guidelines declared competing interests from researchers affiliated with biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
Indian Opinion analysis
The progression in base-editing technology as outlined in this research is a critical breakthrough for genetic medicine,offering promising applications for treating diseases like spinal muscular atrophy as mentioned within the study context. For India specifically, advancements such as these may pave pathways for future biotechnological collaborations or therapeutic developments benefiting large populations suffering from genetic disorders. India’s substantial expertise in biotechnology could synergize with global efforts to adapt these innovations locally and inexpensively-a step further toward improving healthcare accessibility while also contributing to global science initiatives.Read more: Nature ArticleQuick Summary
- Researchers explore targeted DNA ADP-ribosylation for genome editing in bacteria and eukaryotes, advancing methods to induce precise genetic changes.
- Data reveals correlations between mutation frequencies mediated by Cas9 variants and predicted indel formation.
- Techniques assess off-target effects by generating orthogonal R-loops via modified gene editors like dSaCas9.
- Experiments underline the importance of ensuring high-specificity editing to minimize unintended mutations.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of more advanced genome-editing technologies has scientific and ethical implications for India, a country with burgeoning research in biotechnology and agriculture. Enhanced genome editing can aid advancements in medicine, crop improvement, or disease resistance but requires stringent oversight on accuracy to prevent risks associated with off-target effects. As India invests heavily in genomic research for innovation-driven growth,breakthroughs such as ADP-ribosylation-based mutation technologies highlight the importance of integrating science with regulation to ensure safe adoption without societal or environmental compromises.
read More: Nature Article
quick Summary
- Article discusses targeted DNA ADP-ribosylation,a biochemical process triggering templated repair mechanisms in bacteria and base mutagenesis in eukaryotes.
- Published in Nature Biotechnology on September 4, 2025.
- Research integrates cellular repair pathways and could have implications for genetic engineering tools.
- Authors include Gupta, D., Patinios, C., bassett, H.V.,among others.
- Research was received on October 29, 2024; accepted on July 31, 2025.
Citation details:
DOI – https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02802-w
Read More
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study offers promising advances in genetic modification by leveraging natural repair mechanisms. For India’s biotechnology sector-a burgeoning field striving for innovation-these findings could be transformative.With potential applications ranging from agricultural improvements to healthcare innovations like gene therapies, such breakthroughs align with India’s growth goals as a global player in scientific research.
Moreover, facilitating collaborations for adapting this method locally may enhance India’s technical capacities. Though, careful regulation will be key to prevent misuse or ethical concerns related to genetic modifications within Indian contexts.