Now Reading: Hidden Fat Could Harm Your Heart, Even with Regular Exercise
-
01
Hidden Fat Could Harm Your Heart, Even with Regular Exercise
Hidden Fat Could Harm Your Heart, Even with Regular Exercise
Swift Summary:
- A new study links excessive visceral fat (hidden fat surrounding organs) with faster aging of the heart, a major risk factor for heart disease.
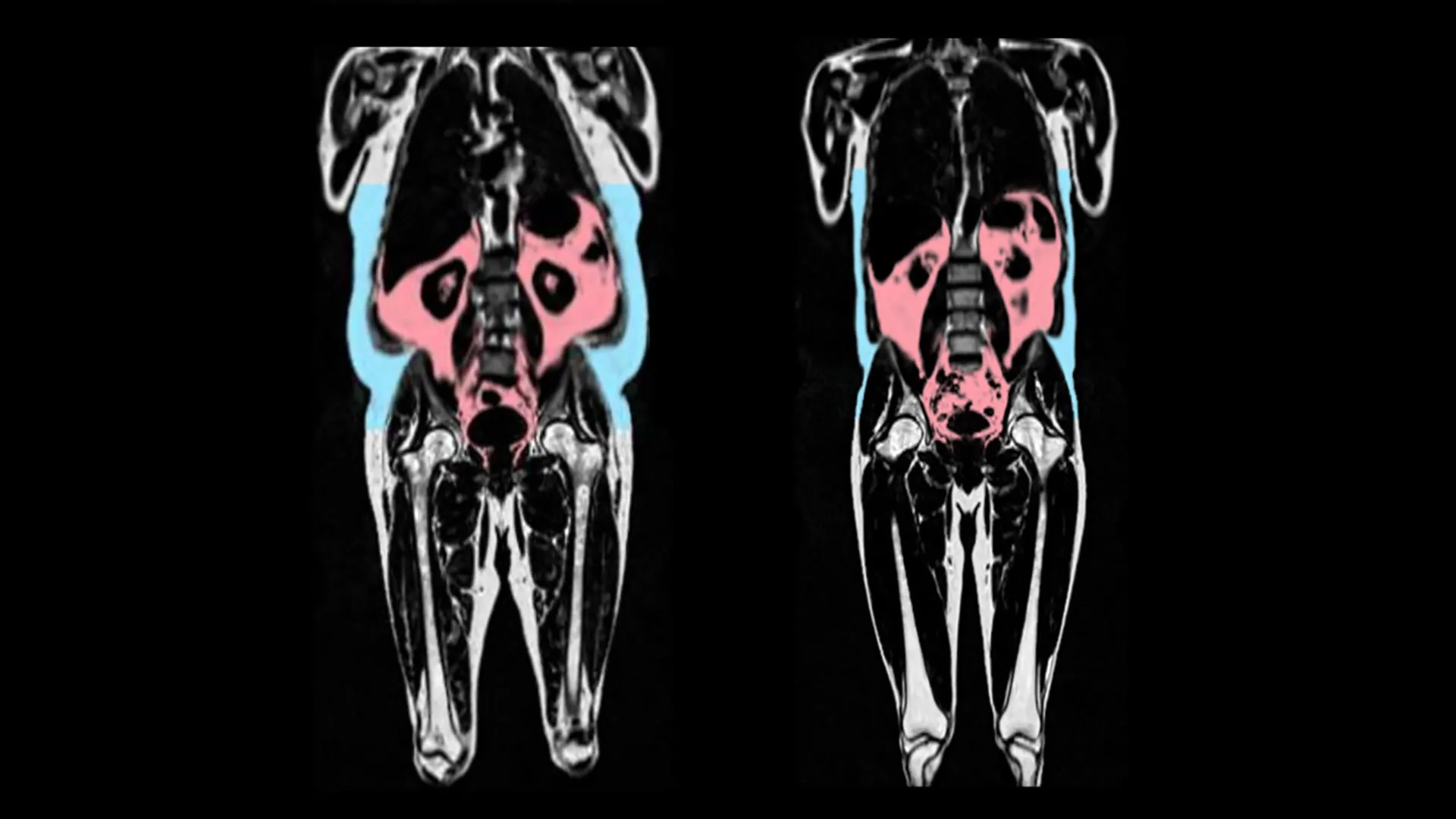
- The research was conducted by the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences,UK,and analyzed data from 21,241 participants in the UK Biobank using AI imaging.
- Notable findings include:
– Visceral adipose tissue is associated with increased inflammation and faster heart aging.
– Male-type fat distribution (“apple” shape) accelerates early aging in men.
– Female-type fat distribution (“pear” shape) around hips and thighs appears protective against heart aging in women.
– Higher oestrogen levels in premenopausal women may slow down heart aging due to hormonal influence.
- Prof. Declan O’Regan highlighted that BMI alone is not a reliable predictor of heart age; where fat is stored is crucial.
- Recommendations emphasize lifestyle changes like healthier diets and physical activity to reduce harmful visceral fat.
- Future studies aim to explore drug therapies targeting negative effects of visceral fat, including GLP-1 inhibitors (e.g., Ozempic).
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This study underscores an evolving understanding of how different types of body fat can impact health outcomes-insights relevant for both global public health strategies and India’s growing burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). In India, rising obesity rates coupled with genetic predispositions toward abdominal weight gain make these findings particularly pertinent.
Public health narratives should incorporate evidence distinguishing unhealthy “visceral” vs. safer peripheral fat accumulation while emphasizing nuanced tools over general measures like BMI to assess risks comprehensively. Awareness campaigns advocating dietary reforms and regular physical activity could effectively target reductions in hidden harmful fats among urban populations prone to sedentary lifestyles.
For Indian medical research stakeholders,this could inspire future localized investigations into gender-driven differences or hormonal influences on CVD risk-and potential applications for preventive care through hormone-based or GLP-1 therapies tailored for Indian demographic realities.