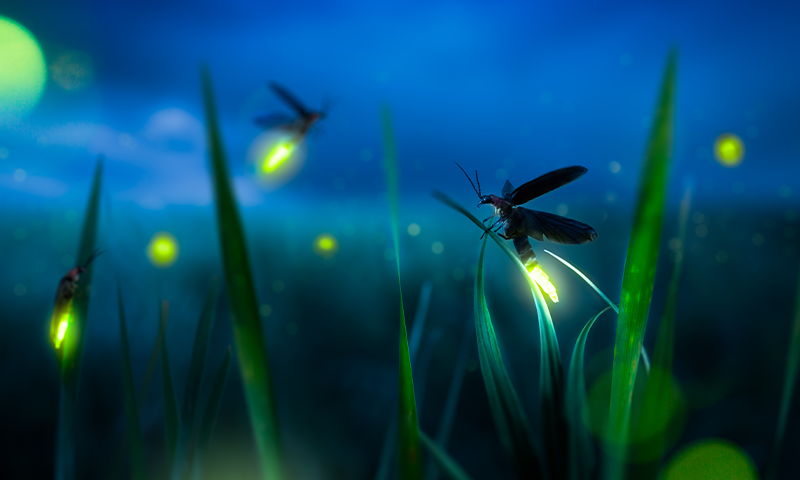
Now Reading: Unraveling the Mathematical Secrets of Fireflies
-
01
Unraveling the Mathematical Secrets of Fireflies
Unraveling the Mathematical Secrets of Fireflies

Fast Summary
- Firefly species exhibit a rare synchrony in their flashing behavior,with only a few species globally engaging in this phenomenon.
- Synchronization occurs for short periods annually and has been extensively studied at parks like Great Smoky Mountains and Congaree National Parks.
- Orit Peleg, a biophysicist from the University of Colorado Boulder, studies firefly synchrony to understand biological and mathematical models of coupled oscillators.
- Past research traced synchronization theories back to Kuramoto’s work on coupled oscillators (1975) and integrate-and-fire models. Both explore how individual cycles interact towards collective patterns.
- Male fireflies synchronize flashes predominantly as part of mating strategies. Population density substantially influences synchrony success rates. Females generally remain stationary but respond to males’ synchronized signals.
- Peleg’s team employs cameras to record 3D movements during peak firefly periods, generating experimental data that investigates mechanisms such as visual cues aiding synchronization.
- “Chimera states,” where some individuals lock phases while others act asynchronously, have been observed in swarms but remain debated among scientists due to insufficient empirical evidence.
- Fireflies are increasingly threatened by habitat loss, light pollution, and pesticides-possibly diminishing population densities required for these synchronous behaviors.
indian Opinion Analysis
The study of synchronized blinking behaviors in fireflies deepens understanding not only of biological systems but also broader phenomena such as electron movement or cardiac rhythms. While this research is global in orientation-such as focusing on swamps like Congaree-it holds potential meaning for biodiversity approaches applicable across nations including India.
India hosts diverse insect populations under varying ecological niches similar to Southeast asia’s tropical conditions where early studies originated. Insights into synchronization may advance conservation management strategies addressing pollination systems or climate resilience methods critical locally.
Ecological threats noted (habitat destruction/pollutants) underline parallels with challenges faced by India’s native wildlife-highlighting possible cascading reproductive vulnerabilities within ecosystems reliant upon particular densities/behaviors triggering survival cycles here to.This lens boosts reasonings adaptable ecosystem debts Read Full-Traverse ➡️