Now Reading: Report Highlights Ecological Impact of May Shipwreck off Kerala Coast
-
01
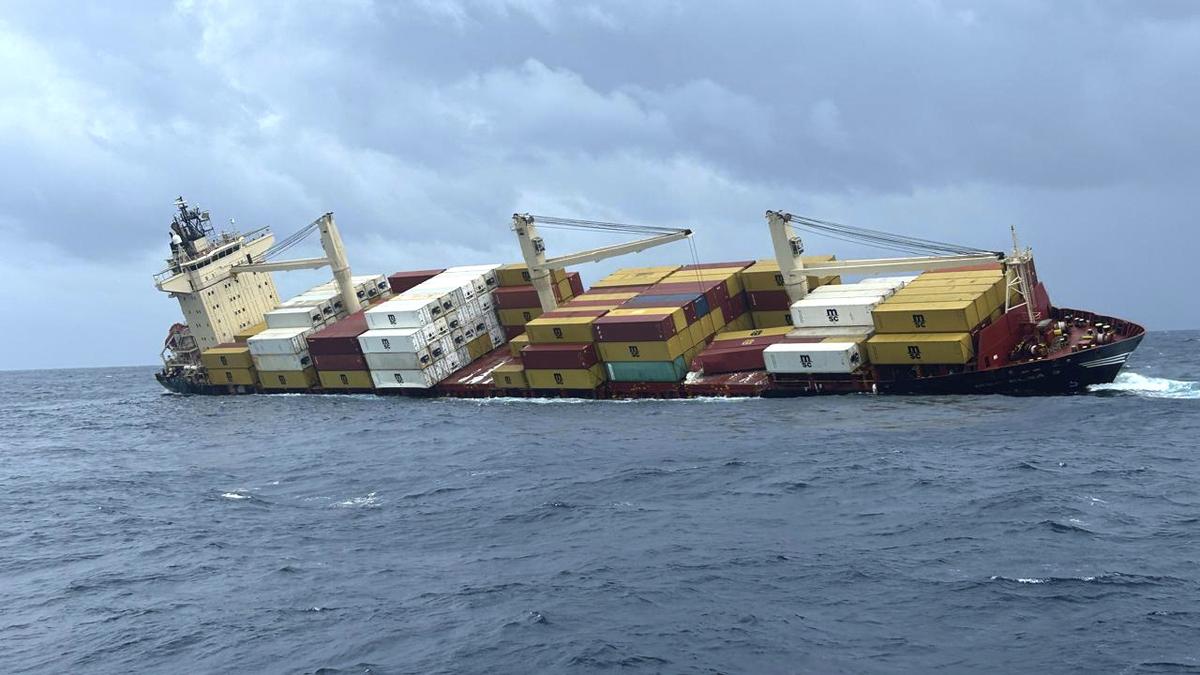
Report Highlights Ecological Impact of May Shipwreck off Kerala Coast
Report Highlights Ecological Impact of May Shipwreck off Kerala Coast

Speedy Summary
- The Liberia-flagged MSC ELSA 3 sank off the Kerala coast, 38 nautical miles into the Arabian Sea, on May 25, 2025.
- The ship was carrying hazardous cargo, including approximately 85 metric tonnes of diesel and 367 metric tonnes of furnace oil, and also at least 13 containers containing hazardous substances like calcium carbide.
- A study by the Center for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE) highlighted significant ecological disruptions in the south-eastern arabian Sea due to the incident.
- Persistent oil leakage from fuel compartments was observed even days after the sinking despite turbulence and ocean currents.
- Analysis revealed high levels of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), such as naphthalene and phenanthrene, indicating human-induced contamination from leaked fuels.Elevated concentrations of heavy metals like nickel and lead were also detected in water and sediments near the wreck site.
- Zooplankton exhibited bioaccumulation of petroleum-derived pollutants, raising concerns about their transfer through marine food chains to fish and eventually humans.
- Marine fauna impacts included a Brown Noddy seabird showing behavioral signs consistent with oil contamination exposure on its plumage near the wreck.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The sinking of MSC ELSA 3 raises serious concerns about maritime safety protocols and environmental safeguards along India’s coastline. Notably, this incident serves as a crucial reminder for stricter monitoring regarding vessels carrying hazardous materials passing through indian waters and enhanced response preparedness for containment efforts during emergencies.The findings point to long-lasting ecological consequences stemming from such accidents-most critically regarding disruptions in marine biodiversity that could cascade across coastal fisheries significant to livelihoods in Kerala’s coastal communities. Furthermore, bioaccumulative toxins entering food chains underline public health risks that demand immediate attention.
Policy responses should potentially involve steps toward creating enforceable international agreements requiring pre-persistent contingency plans or proactive sealing measures for fuel compartments on ships flagged with dangerous goods passing Indian shores to limit future occurrences effectively.
Read More: [Source Link]