Now Reading: Hubble Discovers Wandering Massive Black Hole
-
01
Hubble Discovers Wandering Massive Black Hole
Hubble Discovers Wandering Massive Black Hole

Swift Summary:
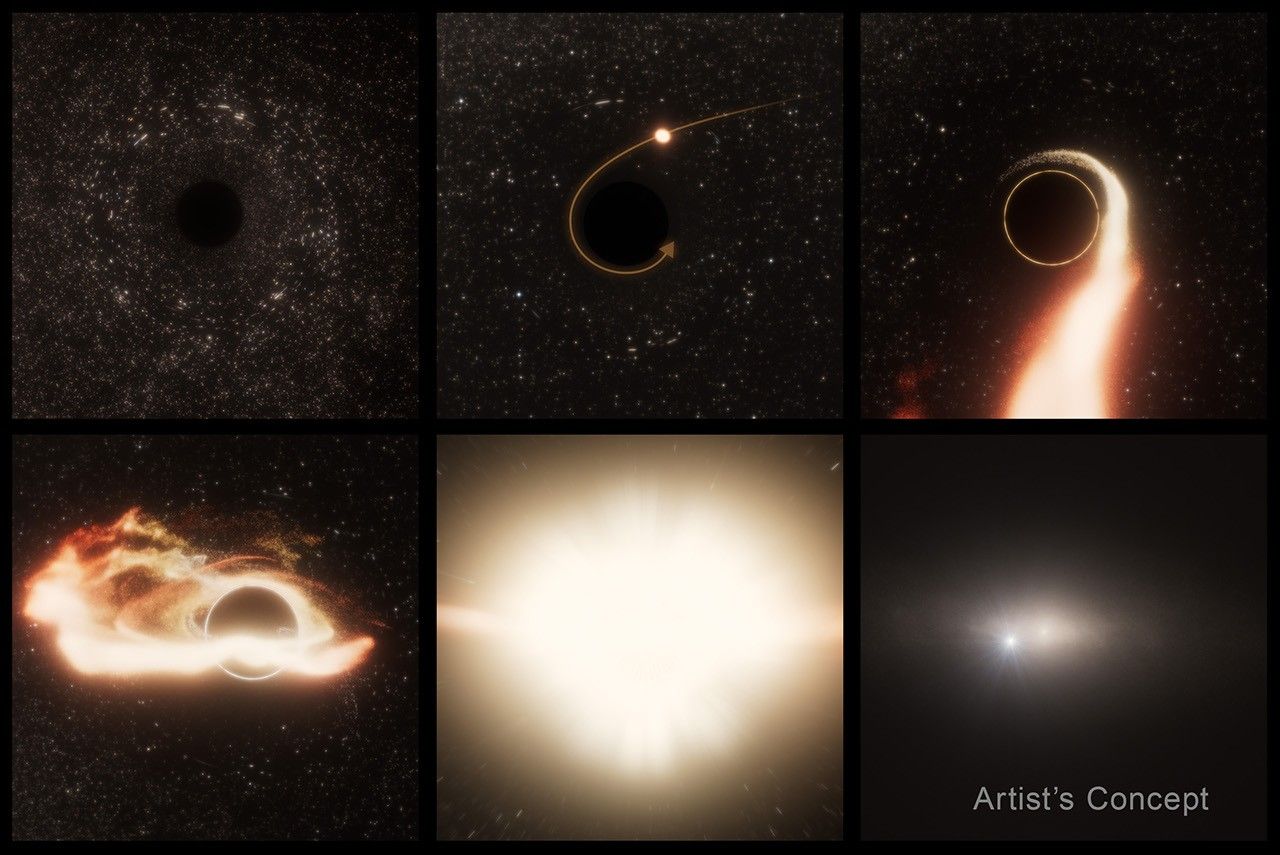
- Astronomers discover “Space jaws”: NASAS Hubble Space Telescope, with support from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory and Very Large Array telescope, detected a tidal disruption event (TDE) caused by a supermassive black hole consuming a star 600 million light-years away.
- Unique finding: This TDE differs from others as the black hole is offset within its host galaxy, rather than being centrally located. it is estimated to have one million times the mass of our Sun.
- Co-existing phenomena: The host galaxy contains another, more massive central black hole (100 million solar masses), making it unusual for two such massive entities to exist in the same galaxy but not be gravitationally bound.
- Detection significance: The event was first observed by ground-based telescopes like Caltech’s Zwicky Transient Facility. Unique flare characteristics confirmed it was caused by a star being shredded and consumed by the wandering black hole.
- Scientific theories explored: This smaller wandering black hole could result from three-body gravitational interactions or as remnants of a galactic merger over one billion years ago, though there has been no evidence yet of such mergers in its host galaxy.
- Future investigations: Upcoming telescopes like Vera C. Rubin Observatory and Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope may aid astronomers in identifying similar offset TDEs.
!Combined Hubble & Chandra Image of Galaxy
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The finding highlights key advancements in observational astronomy and demonstrates how tidal disruption events can reveal hidden phenomena like off-center massive black holes. For India’s space science community-actively expanding capabilities through missions like Aditya-L1-such findings underscore the value of collaborative research involving cutting-edge international telescopes.
From an educational viewpoint, this opens avenues for Indian universities to emphasize interdisciplinary approaches blending astrophysics with theoretical models explaining galactic structures post-mergers. Moreover, upcoming global facilities such as Rubin Observatory align with India’s aspirations toward joining larger transnational projects that focus on transient cosmological events.
India’s growing participation in cooperative missions can build pathways for training researchers to engage with similarly complex astrophysical data analysis while advancing technical instrumentation expertise domestically-a strategic move reflecting on self-reliance paired with global collaboration.