Now Reading: Targeting a cell surface RNA-binding protein driving acute myeloid leukemia
-
01
Targeting a cell surface RNA-binding protein driving acute myeloid leukemia
Targeting a cell surface RNA-binding protein driving acute myeloid leukemia
- Research Briefing
- Published:
(2025)Cite this article
Subjects
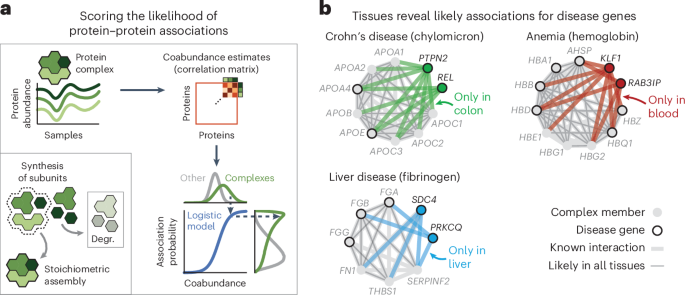
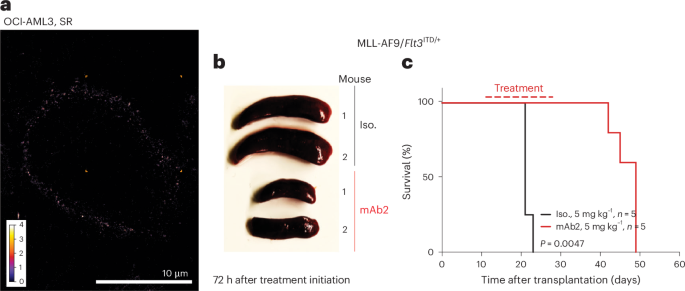
How modifications to RNA molecules and the proteins they interact with on the cell surface contribute to cancer is largely unknown. Preclinical evidence indicates that cell surface nucleophosmin (NPM1, an RNA-binding protein) is a novel druggable biomarker in acute myeloid leukemia, with potential implications for improving detection and immunotherapy strategies for several cancer types.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
195,33 € per year
only 16,28 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

References
-
Box, J. K. et al. Nucleophosmin: from structure and function to disease development. BMC Mol. Biol. 17, 19 (2016). A review article that summarizes the biology of NPM1 and its relevance in disease.
-
Perr, J. et al. RNA-binding proteins and glycoRNAs form domains on the cell surface for cell-penetrating peptide entry. Cell 188, 1878–1895.e25 (2025). This paper reports our characterization of cell surface RBPs and their role in regulating cell entry of cell-penetrating peptides.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This is a summary of: George, B. M. et al. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia models by targeting a cell surface RNA-binding protein. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02648-2 (2025).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Targeting a cell surface RNA-binding protein driving acute myeloid leukemia.
Nat Biotechnol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02695-9
-
Published:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02695-9