Now Reading: Human Ancestors May Have Lived in Larger Groups Than Previously Believed
-
01
Human Ancestors May Have Lived in Larger Groups Than Previously Believed
Human Ancestors May Have Lived in Larger Groups Than Previously Believed

Speedy Summary
- Fossilized skull fragments of Homo erectus were discovered off the Javanese coast in Indonesia during a land reclamation project.
- This finding recontextualizes assumptions about ancient H. erectus populations in the region, suggesting they were not isolated from other nearby hominins.
- The fossils are estimated to date back 140,000 years,corresponding to Earth’s penultimate glacial period.
- Researchers found evidence of butchery on turtle and bovid bones, indicating hunting and advanced food utilization techniques similar to modern human behaviors on the Asian mainland.
- Sundaland-formerly a large dry grassland with rivers-provided resources for survival such as water, shellfish, fruits, edible plants, and seeds year-round.
- Study authors theorize interaction or genetic exchange might have occurred between Sundaland’s H. erectus populations and other hominin groups.
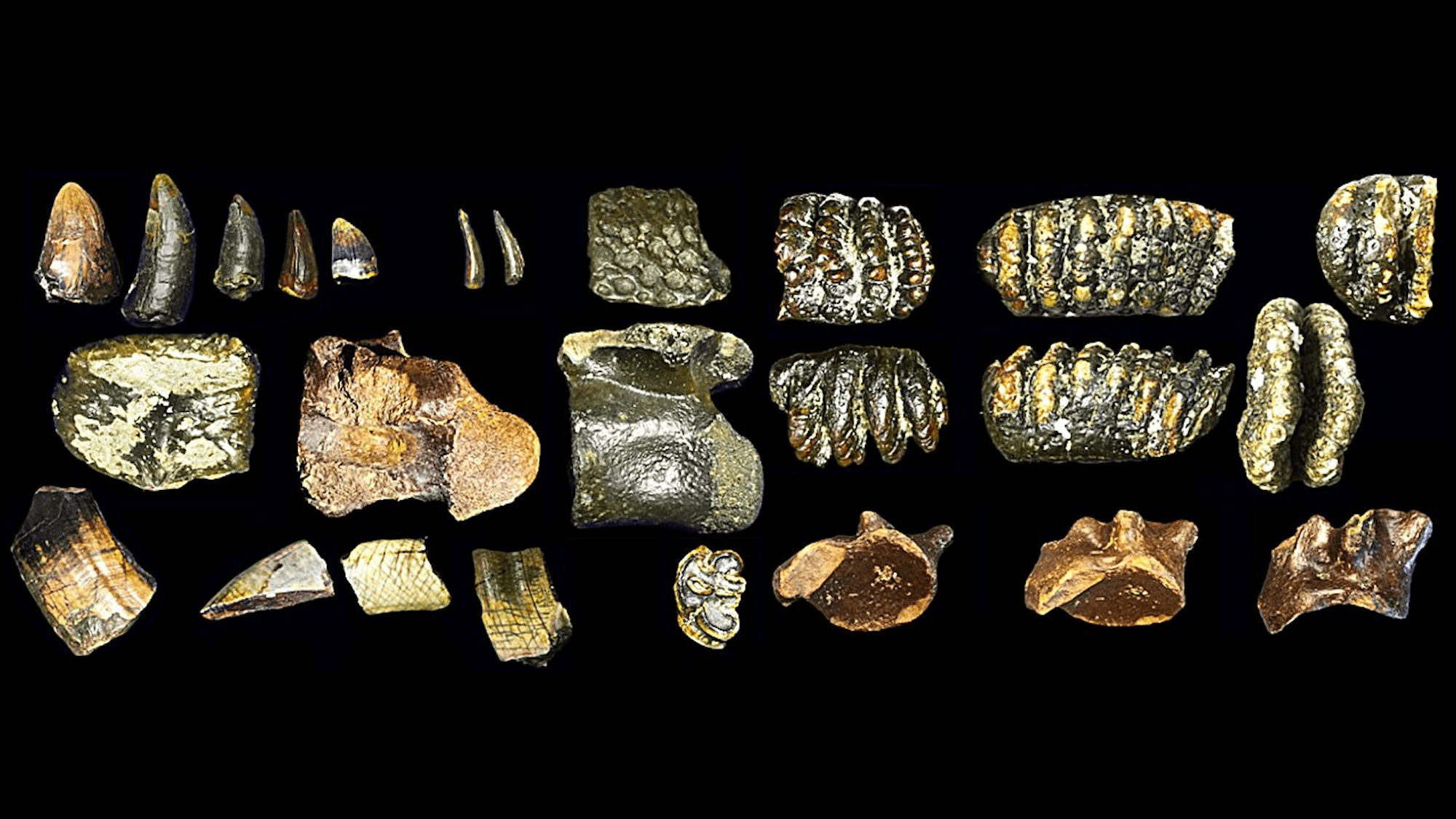
!Fossil fragments
36 fossil fragments from vertebrate animals were documented by researchers.
Credit: Quaternary Environments and Humans
!Java Map
Map depicting Sundaland’s geographic context during lower sea levels.
Credit: Quaternary Environments and Humans
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery of Homo erectus fossils in the Madura Strait presents important implications for understanding early human migration patterns across Southeast Asia. For India-which shares deep historical ties with Sundaland through cultural myths like Lemuria-the study underscores evolving insights into human ancestry in geographically interconnected regions. The evidence of sophisticated butchery practices may point toward shared knowledge transfer or occasional contact among hominin groups across asia-a concept relevant for ongoing research into prehistoric shared ecosystems.
On broader terms, this archaeological breakthrough promotes Indonesian scientific studies that contribute globally to anthropology while encouraging cooperation among neighboring countries like India on ancient knowledge dissemination. With advancing methods now yielding hidden artifacts from submerged landscapes near India’s coasts as well (like Dwarka ruins), this discovery serves as inspiration for further exploration revealing longstanding connections within South Asian history and diverse global contexts.