Now Reading: NASA’s X-59 Jet Showcased in Stunning Ground Display
-
01
NASA’s X-59 Jet Showcased in Stunning Ground Display
NASA’s X-59 Jet Showcased in Stunning Ground Display

Swift Summary
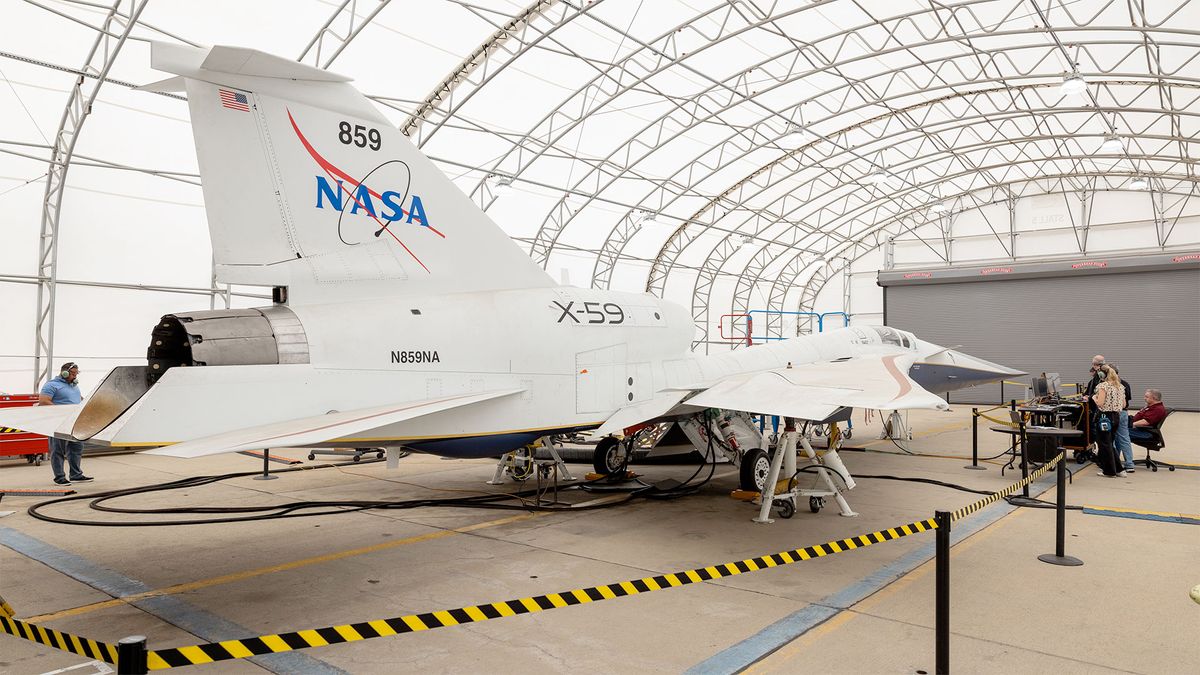
- NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft, developed by Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, aims to reduce noise from sonic booms felt on the ground when traveling at supersonic speeds.
- The aircraft features a long, narrow airframe with canards and has parts sourced from other jets (T-38 cockpit and canopy, F-16 landing gear).
- Powered by a General Electric F-414 engine, it is designed to achieve speeds of up to Mach 1.5 (990 mph), cruising at Mach 1.42 (940 mph) at an altitude of 55,000 feet.
- Engineers recently conducted “aluminum bird” testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in California using the actual aircraft model rather than a simulated metal frame as a cost-saving measure.
- The tests involved simulating flight conditions such as changes in altitude and system failures without activating the engine; pilot inputs and system responses were monitored for functionality.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of NASA’s X-59 signals advancements in supersonic aviation aimed at addressing environmental concerns like noise pollution-a challenge that previously hindered commercial applications of supersonic travel. For India, this may have implications for aerospace engineering collaborations with global innovators or fostering domestic R&D initiatives in enduring aviation technology. As one of the fastest-growing aviation markets globally, India’s alignment with cutting-edge emissions-friendly technologies could enhance its competitiveness while meeting future demands for quieter skies over populated urban centers.