Now Reading: Devoted Partners: Male Hornbills Cater to Mates with Utmost Care
-
01
Devoted Partners: Male Hornbills Cater to Mates with Utmost Care
Devoted Partners: Male Hornbills Cater to Mates with Utmost Care

Rapid Summary
- Hornbill Nesting Habits: Hornbills, native to Southeast Asia and Africa, mate for life and have a unique nesting process where females are sealed into tree cavities with only a small opening left for feeding and cleaning.
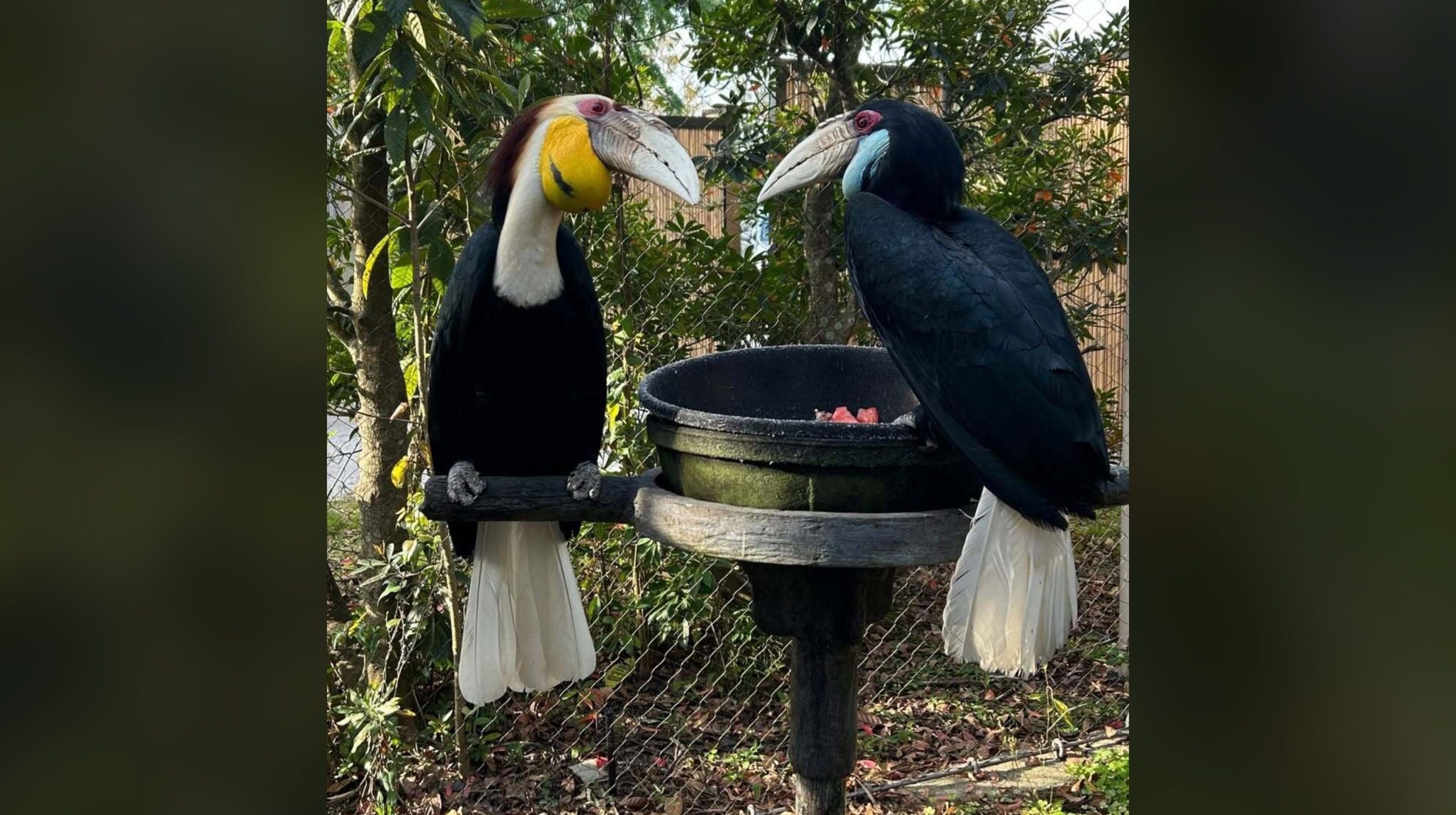
- Nesting Materials: At Jacksonville Zoo, hornbill pair Humphrey and Bacall discarded pre-provided materials like pine shavings and showed individual preference in selecting nesting material.
- Sealed Female Role: The female lays eggs inside the sealed nest while the male feeds her through a slit. She keeps the cavity clean by defecating through this opening.This process lasts 111-137 days until chicks hatch.
- Matchmaking Success: Humphrey and Bacall were paired at Jacksonville Zoo earlier this year using careful steps like introducing them via side-by-side enclosures before placing them together. They bonded quicker than usual despite hornbills sometiems taking years to form strong bonds.
!Hornbill couple sitting near their chosen nest
Indian Opinion Analysis
The mating patterns of hornbills reflect deep ecological meaning sence these birds contribute to forest regeneration by dispersing seeds during feeding. Insight into their complex behaviors can aid India’s conservation efforts, given that many hornbill species are critically threatened due to habitat loss in South asia. Zoos like Jacksonville setting an example of assisting these endangered creatures may inspire enhanced protective measures for India’s iconic Great Hornbill species found in regions such as Western Ghats or Arunachal Pradesh.
Such studies underline human obligation toward wildlife preservation by understanding nuanced ecological behavior-critical as India continues balancing advancement alongside biodiversity preservation.