Now Reading: Reviving Miniature Cas9 for Advanced Genome and Epigenome Editing
-
01
Reviving Miniature Cas9 for Advanced Genome and Epigenome Editing
Reviving Miniature Cas9 for Advanced Genome and Epigenome Editing
Quick Summary
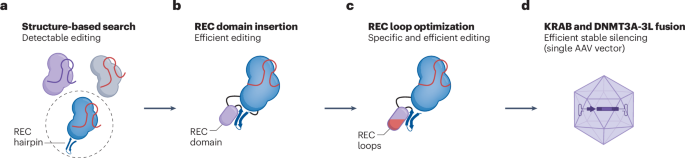
- A new form of the CRISPR-Cas9 system has been developed, leveraging its ancestral protein called IscB.
- This engineered version is smaller in size and effective as a DNA-targeting tool for mammalian genome editing.
- It utilizes adeno-associated virus (AAV) delivery mechanisms and adds functionalities for epigenome editing and gene silencing.
For full details: Nature Biotechnology
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of this streamlined CRISPR technology represents an critically important leap in genetic engineering, with potential applications in biotechnology, healthcare, and agriculture. For India,this advancement aligns well with growing investments in science-driven solutions. The reduced size of the tool may facilitate easier delivery systems-useful in tackling genetic disorders or enhancing crop yields through precise modifications. To capitalize on such innovations sustainably, policies bolstering research infrastructure should support these next-generation technologies. Ultimately, international collaborations could also help integrate such developments into India’s agricultural and medical frameworks.
!pubmed reference | Article reference
Quick Summary
- A research article titled “Resurrecting a miniature Cas9 ancestor for genome and epigenome editing” has been published in Nature Biotechnology on June 3, 2025.
- Authors G.L. Butterfield and C.A. Gersbach explore the potential of using a reconstructed version of Cas9-a key gene-editing tool-for genome and epigenome modifications.
- The study focuses on creating a smaller, more efficient form of Cas9, improving its adaptability for therapeutic applications.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02707-8.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The advancement in genome-editing technologies represented by this study may have significant implications for India’s biotechnology landscape, which already plays a growing role globally. A smaller and more adaptable version of CRISPR-Cas9 could aid in developing cost-effective treatments targeting genetic disorders prevalent in India while reducing access barriers due to affordability constraints. Additionally, this breakthrough aligns with the government’s push toward strengthening research infrastructure under programs like “Made-in-Biotech India.” However, ethical considerations surrounding human genome modifications will need careful deliberation in policy frameworks before clinical applications are introduced.
























