Now Reading: 160-Million-Year-Old Fungus Fossils Discovered in China
-
01
160-Million-Year-Old Fungus Fossils Discovered in China
160-Million-Year-Old Fungus Fossils Discovered in China
Quick Summary
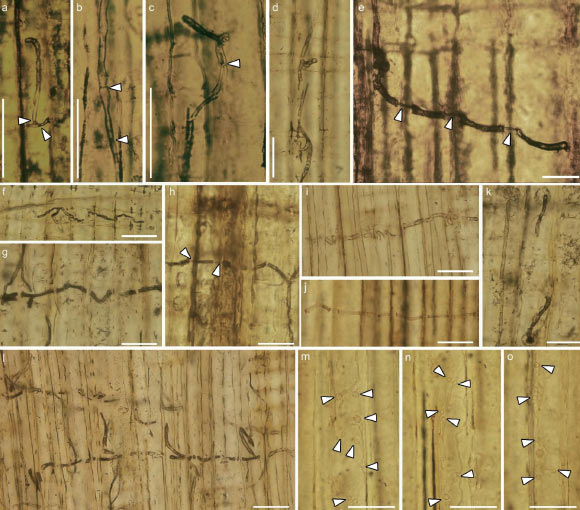
- Fossilized blue-stain fungi were discovered in 160-million-year-old petrified conifer wood of Xenoxylon phyllocladoides from the Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation in northeastern China.
- This extends the earliest fossil record of blue-stain fungi by approximately 80 million years, surpassing a previous record from the Cretaceous period found in South Africa.
- Blue-stain fungi are wood-colonizing organisms that cause sapwood discoloration but lack enzymatic abilities to decompose wood structures, instead penetrating mechanically through cell walls using specialized “penetration pegs.”
- The study suggests these fungi co-evolved ecological associations with wood-boring insects during the Jurassic period, predating modern bark beetles (Scolytinae) as spore dispersal vectors. Possible option insect dispersal agents existed during this time.
- Research highlights pigmentation as a defining trait of both ancient and modern blue-stain fungal groups and provides insights into their evolutionary history and ecological systems involving plants and insects during the Jurassic era.
Image:
!Blue-stain fungus
Caption: Blue-stain fungus in wood tissues of Xenoxylon phyllocladoides from western Liaoning province,China. Image credit: Tian et al., doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaf160.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This discovery represents significant progress in understanding fungal evolution and demonstrates their role in early ecological systems involving trees and insects dating back to the Jurassic period. Insights into such primordial interactions could contribute to broader scientific initiatives aimed at tracing climate shifts, plant health dynamics, or patterns related to species interdependence over geologic timescales.
For India-a nation with vast forest ecosystems susceptible to pest infestations-the observations about how fungal-insect associations can accelerate tree mortality may hold relevance for forest conservation strategies today. Such research underscores interspecies correlations across eras that might inform measures against environmental stresses caused by invasive species or pathogens.
The extension of fossil records further highlights how ancient discoveries continue reshaping knowledge boundaries within paleontology-offering India’s academic institutions studying biodiversity fresh benchmarks for interdisciplinary studies between botany, geology, and entomology.