Now Reading: America’s Rarest Songbird Stages an Unlikely Comeback
-
01
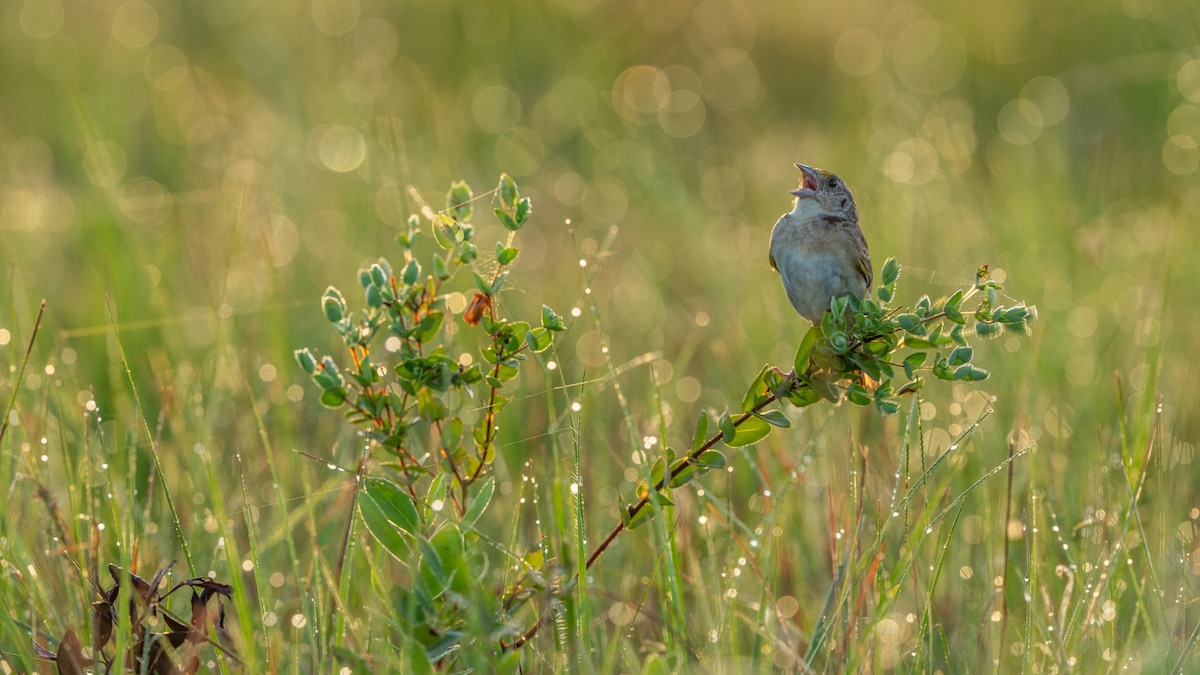
America’s Rarest Songbird Stages an Unlikely Comeback
America’s Rarest Songbird Stages an Unlikely Comeback

### Rapid Summary
– The endangered florida grasshopper sparrow, weighing less than 30 grams, faces threats from habitat loss, floods, predators like snakes and fire ants, as well as human-induced environmental changes.
– Over 90% of its habitat has been destroyed due to advancement, ranching activities, and agriculture.
– Fewer than 200 grasshopper sparrows remain in the wild-a significant enhancement aided by collaborative conservation efforts involving federal agencies (e.g.,U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service), private landowners, military partnerships (e.g.,Avon Park Air force Range),and ecological experts.
– Notable strategies include soil elevation for nesting sites to combat flooding, temporary fencing to block predators, and industrial pressure hot water systems to deter invasive fire ants.
– Conservation methods applied on ranch lands showed success despite initial fears that grazed areas were unfit habitats for the birds; such areas now appear vital ecosystems connecting the last natural populations.
– Captive breeding programs have produced encouraging results as 2019. More than 1,000 birds bred in captivity have been released into protected wild sites like Avon Park Air Force Range and three Lakes Wildlife Management Area.
– Florida’s prairie ecosystem benefits broadly from these conservation efforts-protecting over 180 species while replenishing habitats crucial for local water sources.
### Indian Opinion Analysis
The plight of Florida grasshopper sparrows underlines the global challenge posed by shrinking habitats due to human encroachment. India faces similar biodiversity struggles with endemic species across its own grasslands-from bustards like the Great Indian Bustard to smaller avians facing pressures from agricultural expansion or urban sprawl. Lessons from this case reinforce how multi-stakeholder collaboration is key in reversing ecological decline: partnerships between governments (e.g., wildlife boards), scientists/autonomous researchers, NGOs advocating sustainable ranching or farming practices may yield similar benefits in India’s context.
Captive breeding combined with sustained field conservation offers scalable models that India could incorporate more systematically for critical regional wildlife rescue missions-similar successes might be replicated with species threatened by predator imbalance or invasive organisms if proper resources are prioritized toward preservation projects.What is notable here beyond rescuing an individual bird population is how conservation has ripple effects across ecosystems-for example protecting prairies also safeguards drinking water reserves amidst climate variability shared policy relevance priority shared.