Now Reading: Is Mars Truly Red? A Physicist Breaks It Down
-
01
Is Mars Truly Red? A Physicist Breaks It Down
Is Mars Truly Red? A Physicist Breaks It Down

Quick Summary
- mars has been historically labeled the “red planet” due to its reddish appearance, a result of iron oxide (similar to rust) covering its rocks and dust.
- While primarily appearing red, photos from rovers reveal variations in color like rusty brown and tan. The ice caps at the poles appear white due to frozen water and carbon dioxide (dry ice).
- Ultraviolet light causes dry ice on Mars’ poles to evaporate during sunlight exposure, influencing seasonal changes.
- Observations in non-visible spectrums such as infrared, ultraviolet, and others provide diverse insights into Martian surface features and atmospheric conditions.
- Scientists aim to uncover answers regarding Mars’ formation history, volcanic activity duration, atmosphere origin, and potential presence of liquid water in the past.
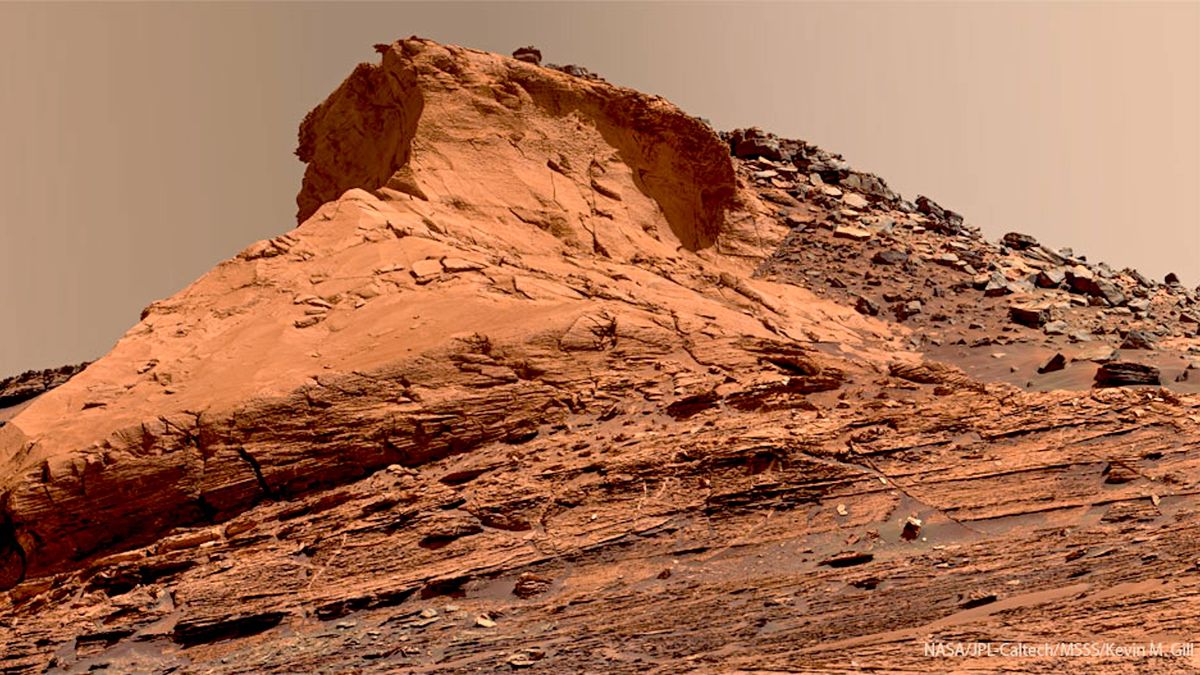
!Siccar Point photographed by NASA’s Curiosity rover
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS; Processing & License: Kevin M. Gill
!Mars’ rusty colors captured via Viking lander
Image credit: NASA/JPL
!Visible vs infrared photo comparison of Mars from Hubble Telescope
Image credit: NASA/Cornell University/NASA-JPL
!UV view taken by MAVEN spacecraft revealing unique perspectives on Mars
Image credit: NASA/LASP/CU Boulder
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s growing ambitions in space exploration-highlighted through missions such as Mangalyaan-align closely with global efforts that study celestial bodies including Mars. Research into planetary surfaces like Mars not only deepens scientific knowledge but also aids technological development with practical applications across sectors.
For India specifically:
- Advances in observational technologies seen here may inspire ISRO’s future planetary missions.
- Insights about non-visible spectrums are notably valuable for enhancing payload capabilities within upcoming lunar or Martian probes.
- Investigating volatile processes such as surface-seasonal shifts coudl help Indian scientists refine Earth-focused climate models.
These endeavors promote collaborative frameworks globally while paving pathways for long-term interplanetary exploration goals relevant for both science and societal progress.