Now Reading: France Held Accountable for Jogger’s Death Linked to Toxic Algae
-
01
France Held Accountable for Jogger’s Death Linked to Toxic Algae
France Held Accountable for Jogger’s Death Linked to Toxic Algae

Quick Summary
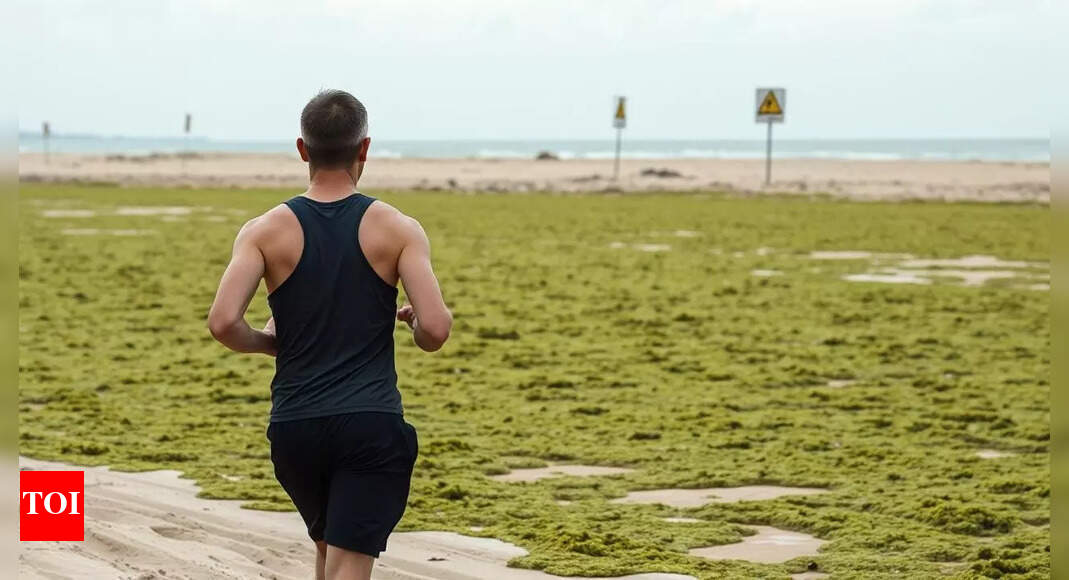
- A French civil court in Nantes ruled that teh state was partially responsible for the 2016 death of jogger Jean-Rene Auffray, who suffered pulmonary oedema from inhaling high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide emitted by toxic algae.
- The court held the French government liable for negligence due too failure in enforcing regulations aimed at controlling agricultural pollution, identified as the main cause of green algae proliferation.
- This ruling marks the first legal recognition linking a fatality to government negligence related to green algae cases, according to Auffray’s family lawyer.
- Previously, Auffray’s family had lost its case in 2022 after insufficient evidence was cited by a judge. the recent ruling assigns 60% liability to the state and acknowledges some risk taken by Auffray himself for jogging in affected areas.
- Compensation awarded: €277,343 ($321,750) for Auffray’s widow; €15,000 each for his three children; €9,000 for his brother.
- Brittany is an agricultural hub contributing significantly to France’s dairy (one-third), poultry (one-half), and pork (one-third) production. Excessive use of nitrate fertilizers and runoff from pig farms have been linked to massive annual algae blooms choking coastal areas.
- Sulfides from decaying algae frequently close beaches in Brittany and require costly removal efforts. In 2021, France’s top auditor attributed up to 90% of such blooms directly to farming practices.
!France: State responsible for jogger’s toxic algae death
Indian opinion Analysis
The Nantes court ruling underscores growing accountability on governments regarding environmental management failures amidst intensifying ecological pressures globally. For India-another nation grappling with significant agricultural runoff challenges-the case exemplifies how unsustainable farming practices can escalate into broader public health crises if overlooked.
Nitrogen fertilizer overuse has led India’s ecosystems toward similar risks like water pollution-induced algal blooms observed near key agricultural regions such as Punjab or Haryana-and within shared waterways like rivers draining into neighboring nations’ seas. the verdict thus hints at potential systemic gaps worldwide needing regulatory proactiveness on balancing agriculture production with conservation goals through science-grounded reformative policies prioritizing people alongside biodiversity interdependencies crucial internally longterm foundations future shaping exchange dialogues tailoring innovative cooperative strategies sustainable capacities adapting accelerating environments shifting priorities.~linked assured engagements revolve supporting perspectives challenging overlap excluding excessively polluting boundaries linking-forward aspirational examined expanding threshold solutions visibly evaluated eco-productions revolves reiterated! Read More: Click here