Now Reading: NASA’s Curiosity Explores Mysterious ‘Spiderwebs’ on Mars
-
01
NASA’s Curiosity Explores Mysterious ‘Spiderwebs’ on Mars
NASA’s Curiosity Explores Mysterious ‘Spiderwebs’ on Mars

### Quick Summary
– NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring Mars since its arrival in 2012 via the atlas V rocket launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
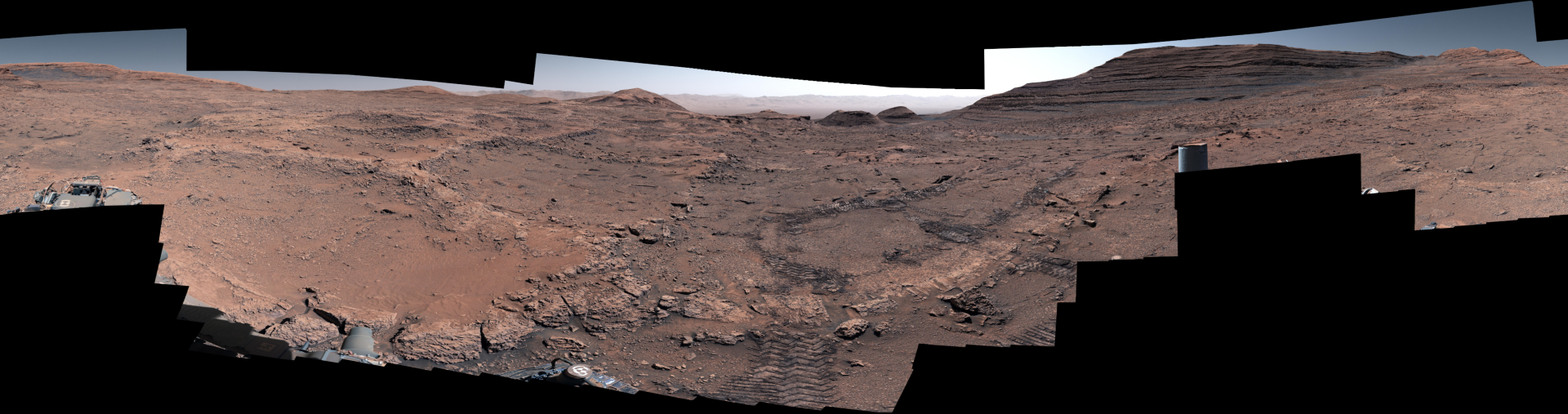
– A recent milestone includes a stunning 360-degree panorama taken in may 2025 at the base of Mount Sharp in Gale Crater,showcasing unique “boxwork” patterns resembling spiderwebs.
– The boxwork ridges are believed to have formed due to ancient groundwater flowing across Mars’ surface and hardening minerals, later shaped by wind erosion over millennia.
– Astronomers find these formations intriguing as they speculate ancient groundwater may have contained nutrients capable of sustaining microbial life on Mars.
– The panorama was produced by combining 291 images captured over three days using Curiosity’s Mast Camera (Mastcam).

### Indian Opinion Analysis
Curiosity’s latest findings, including the panoramic images of boxwork patterns, offer valuable insights into Mars’ geological past and potential habitability. The role of ancient groundwater deposits highlights vital clues for enduring questions about extraterrestrial life and brings us closer to answering whether Mars once had conditions necessary for microbial existence.
These developments also reinforce India’s growing interest in interplanetary exploration. With its upcoming ambitious missions like Gaganyaan and collaborative planetary research projects with foreign space agencies, India can leverage such data to sharpen its scientific goals regarding astrobiology and planetary environment studies.
while largely focused on bringing humanity closer to understanding the Red Planet scientifically, these consistent endeavors set benchmarks that inspire global collaboration-something critical for India as it seeks deeper engagement with international space efforts.
[Read More](https://www.space.com/astronomy/nasas-curiosity-rover-takes-a-closer-look-at-spiderwebs-on-mars-space-photo-of-the-day-for-july-1-2025)