Now Reading: Rare Mineral Discovery on Asteroid Ryugu Reshapes Its History
-
01
Rare Mineral Discovery on Asteroid Ryugu Reshapes Its History
Rare Mineral Discovery on Asteroid Ryugu Reshapes Its History

Quick Summary
- Discovery: Researchers identified the mineral djerfisherite in dust grains from asteroid Ryugu. This mineral is typically associated with high-temperature environments (exceeding 662°F or 350°C) in the inner solar system but was found on a colder outer solar system body.
- Mineral Origin: Djerfisherite is an iron-nickel sulfide containing potassium,often observed in enstatite chondrites formed during extreme conditions billions of years ago. Ryugu’s composition suggests a cooler and wetter origin instead.
- Mystery and Implications: Scientists hypothesize that djerfisherite either came from an impact involving enstatite chondrite or formed under unexpected localized high-temperature conditions on Ryugu. Evidence supporting either theory remains incomplete due too a lack of isotopic data.
- Importance: The finding challenges previous assumptions about primitive asteroids being homogeneous and raises questions about mixing materials during early solar system evolution.
- Next steps: Further analysis will investigate whether this instance is unique or indicative of broader trends, potentially altering understanding of chemical processes in asteroid formation.
Image Descriptions:
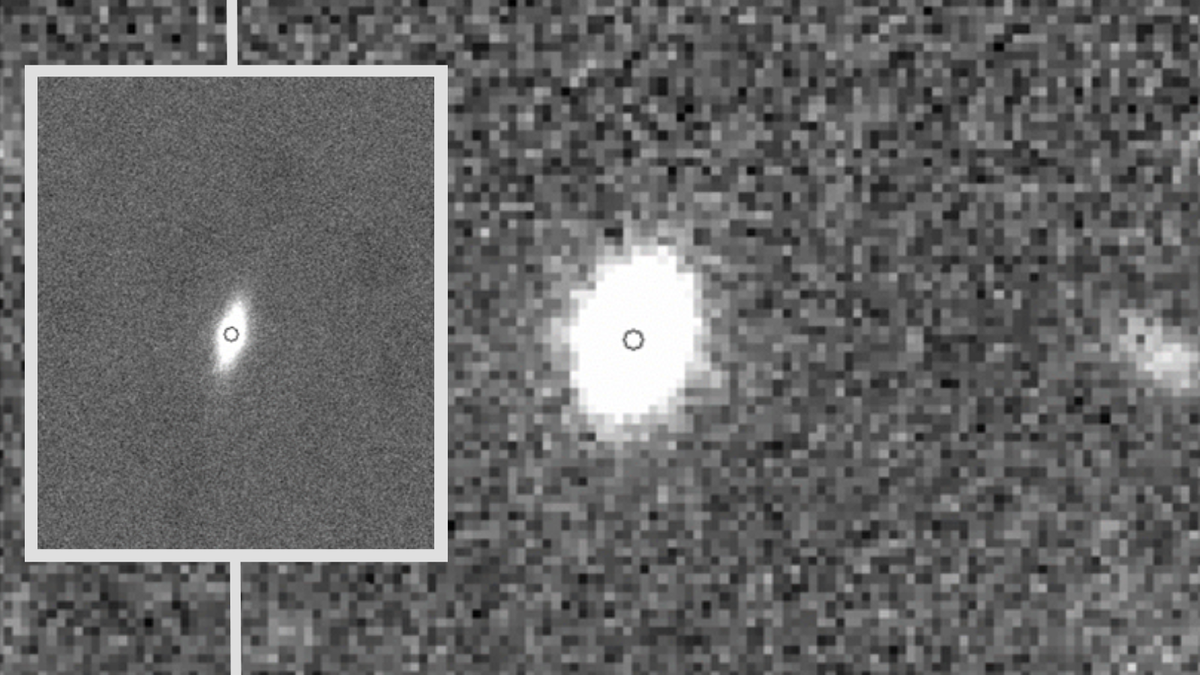
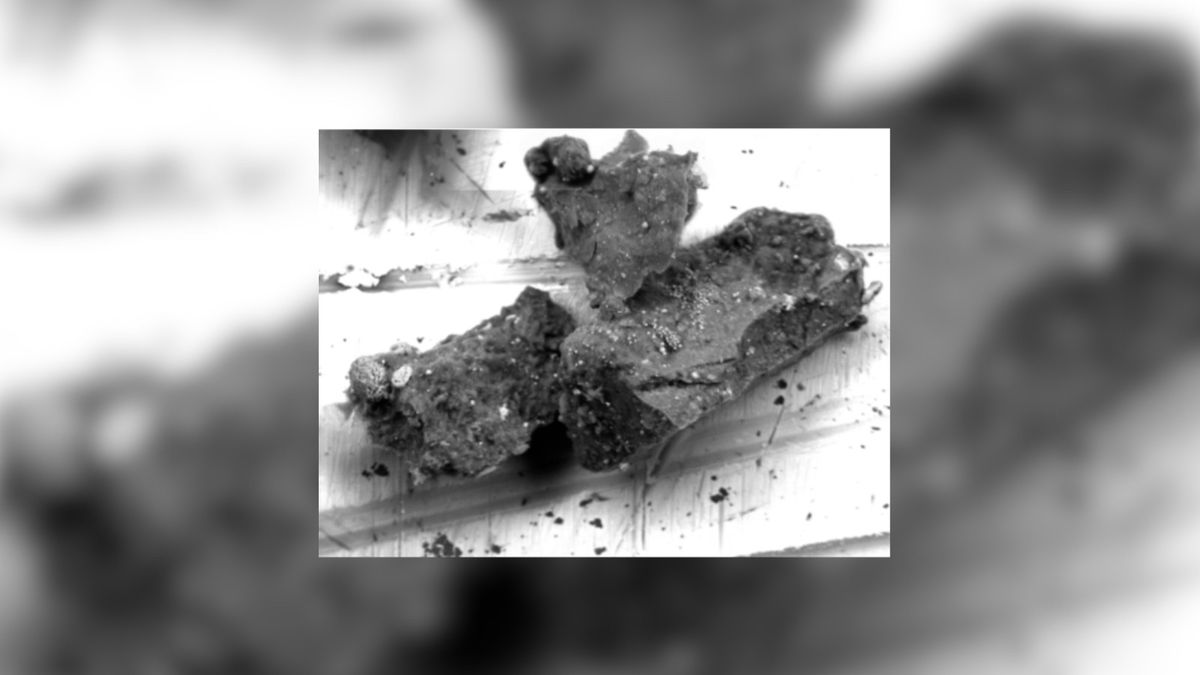
- Scanning electron microscope image showcasing the dust grain containing djerfisherite (Credit: Hiroshima University/Masaaki Miyahara).
- A visual representation of asteroid Ryugu against a dark background (Credit: DARTS archive/Meli Thev via Wikimedia Commons).
Indian Opinion Analysis
This discovery redefines aspects of planetary science by shedding light on complexities previously unaccounted for in asteroid formation theories.It demonstrates how seemingly contrasting materials-high-temperature minerals like djerfisherite-can exist within objects assumed to have undergone low-temperature evolution, hinting at either material transport across vast regions or unexpectedly diverse localized conditions.
For India’s scientific community, which has made strides in space exploration through missions like chandrayaan and upcoming interplanetary ventures such as Aditya-L1, these findings underscore the importance of international collaborations similar to Japan’s Hayabusa2 mission for advancing planetary research capabilities further.
The progress also stresses the need for sophisticated tools capable of analyzing extraterrestrial samples effectively-a frontier that India could aim to achieve as it continues investing strategically under its space research programs.
By engaging globally with discoveries like these, India can refine its own methodologies while contributing meaningfully toward broadening our collective understanding regarding early solar system phenomena and chemical evolution processes essential to cosmic history.