Now Reading: Why India Should Embrace Open Ecosystems
-
01
Why India Should Embrace Open Ecosystems
Why India Should Embrace Open Ecosystems

Speedy Summary:
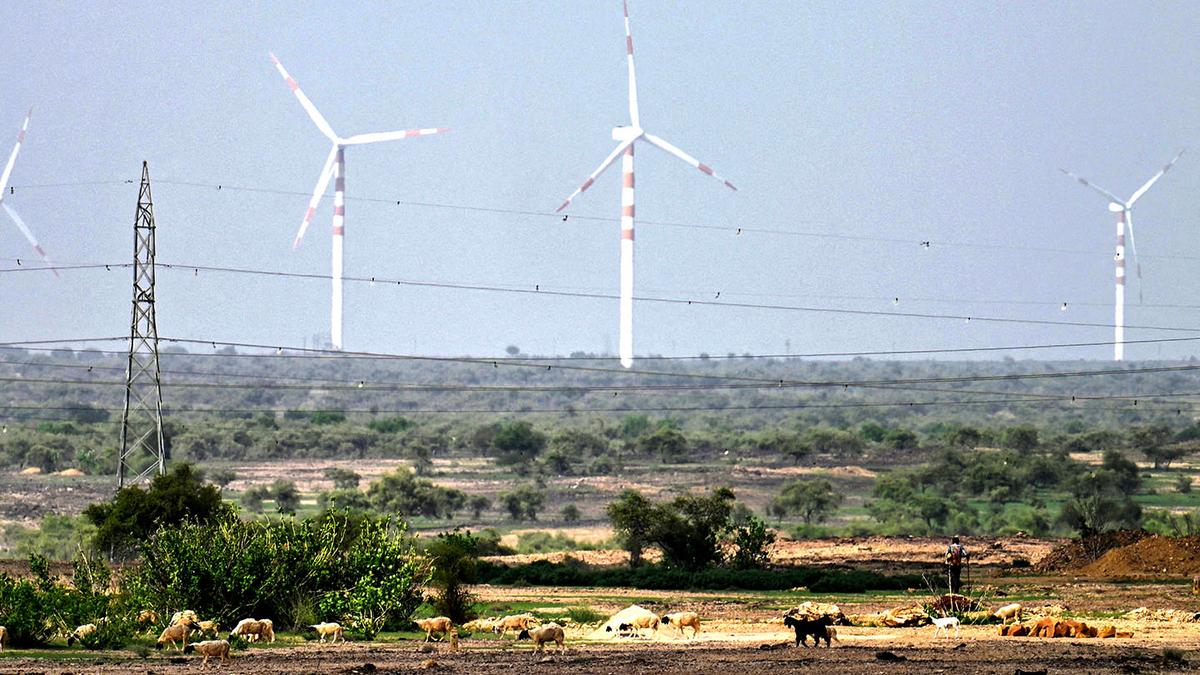
- Deserts occupy nearly one-third of Earth’s land surface and are resilient, diverse ecosystems home to unique plants, animals, and human cultures. They have historically supported early civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley.
- In India, natural open ecosystems like deserts, grasslands, savannas, and scrublands are often misclassified as “wastelands” on official maps due to colonial inherited policies.thes misclassifications lead to needless transformations through afforestation or industrial conversions.
- India’s deserts host rare species like the Great Indian Bustard and serve critical ecological functions such as deep soil carbon storage. Millions of pastoralist communities also depend on these spaces for grazing while stewarding biodiversity.
- Current efforts turning open spaces into monoculture plantations or fenced zones harm ecological balance and livelihoods of pastoralists dependent on these areas for their survival.
- Advocates call for policies promoting restoration based on native vegetation conservation methods like rotational grazing and indigenous knowledge rather then greenwashing projects focused solely on tree planting in drylands.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s approach to classifying open ecosystems-deserts included-as unproductive “wastelands” reflects a need for reevaluating colonial policy legacies that disregard ecological diversity and cultural interdependence with nature. The change efforts often overlook how these biomes sustain unique biodiversity alongside traditional livelihoods rooted in centuries-old adaptive practices by local communities such as pastoralists.
Promoting sustainable restoration techniques grounded in indigenous knowledge can definitely help address land degradation without compromising native ecosystem dynamics or human well-being derived from them-highlighting an opportunity for growth aligned with conservation priorities rather than mono-focused interventions like large-scale plantation projects.
The broader policy challenge lies in balancing national aspirations with ecosystem stewardship principles through recognition frameworks rewarding soil carbon preservation while nurturing community participation that safeguards resources including desert equilibrium mechanisms biologically designed sustaining harsh climates but systems collapsing links between ruined fragile states depended resilience over millenia proven adaptive past climates pioneering societal foundations actively shaped complex innovations pivotal towards survival strategies longer-term planning environmental equity future sustainability.
Read more: The Hindu