Now Reading: Tracking Cellular Transformations Across Space and Time
-
01
Tracking Cellular Transformations Across Space and Time
Tracking Cellular Transformations Across Space and Time
Quick Summary
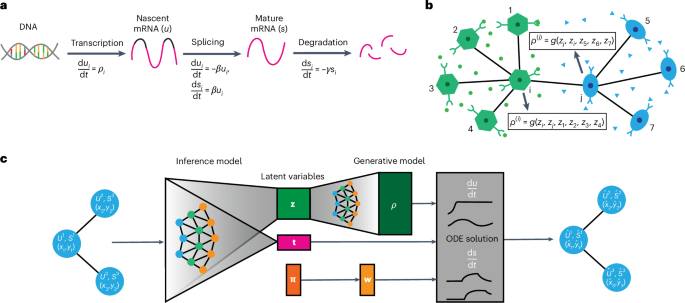
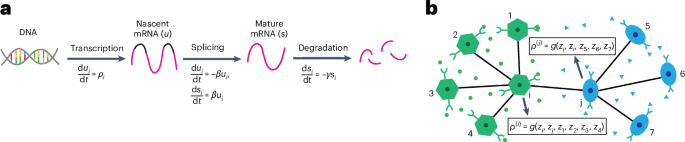
- Article Topic: The research discusses a novel technique integrating spatial transcriptomic data with RNA transcription and splicing dynamics across tissues, enabling the modeling of cell differentiation and migration.
- Highlights: This approach provides insights into physical and chemical interactions between cells during their transition and movement across tissue spaces.
- Publication Details: Published in Nature Biotechnology on 16 July 2025.
- visual Overview: Includes a figure labeled “TopoVelo overview.”
Indian Opinion Analysis
The new methodology outlined in the research represents an important leap in spatial genomic studies, allowing for deeper understanding of cellular behavior within specific tissue environments. By enhancing the ability to map how cells differentiate and migrate, this tool may advance fields like regenerative medicine or cancer research globally-including potential applications for India’s ongoing efforts to understand genetic diseases prevalent among its diverse population. Neutral observation suggests that such breakthroughs coudl open pathways for Indian researchers to focus on disease-specific applications tailored to local healthcare challenges while also contributing intellectual capital to global scientific advancements.