Now Reading: New Protein Breakthrough Targets RASG12D Mutation in Tumors
-
01
New Protein Breakthrough Targets RASG12D Mutation in Tumors
New Protein Breakthrough Targets RASG12D Mutation in Tumors
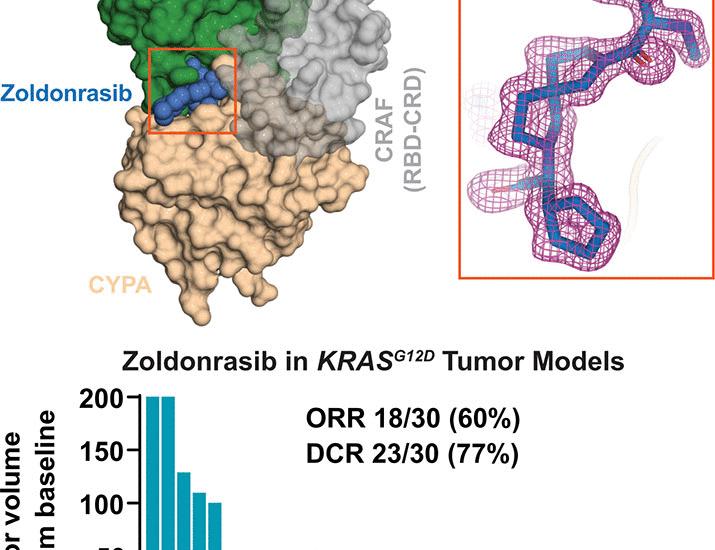
Rapid Summary
- Mutant RAS proteins are among the most prominent contributors to human cancer.
- The glycine-to-aspartic acid mutation at codon 12 (G12D) is identified as the most common variant of RAS mutations.
- Mutation-selective covalent inhibitors have been developed to specifically target these mutant proteins while sparing healthy tissue.
- these inhibitors offer the potential for sustained treatment benefits for cancer patients by focusing on mutated RAS proteins.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research around mutation-selective covalent inhibitors targeting mutant RAS proteins represents a notable advancement in precision oncology. For India, where cancer prevalence is increasing, such targeted therapies could mark a transformative step toward more effective treatments and reduced side effects for patients suffering from aggressive forms of cancer driven by these mutations. However, broader accessibility and affordability of such advanced therapeutics must remain key priorities to ensure equitable healthcare in India’s diverse socio-economic landscape.