Now Reading: Hubble Captures Star Explosion, Aiding Cosmic Mapping
-
01
Hubble Captures Star Explosion, Aiding Cosmic Mapping
Hubble Captures Star Explosion, Aiding Cosmic Mapping

quick Summary:
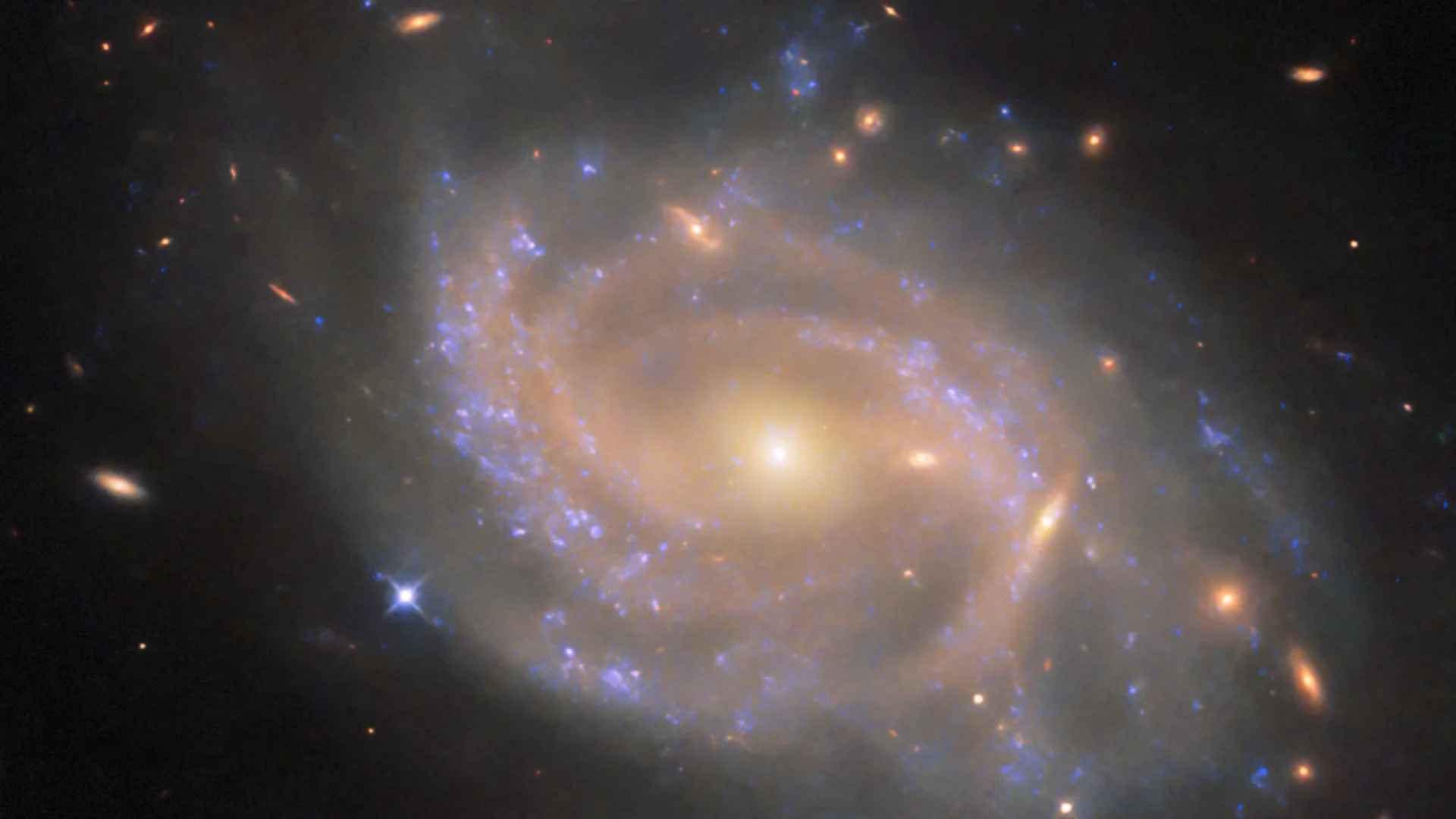
- NGC 3285B is a spiral galaxy located 137 million light-years from Earth in teh Hydra constellation, which spans the largest area among the 88 constellations.
- The galaxy is part of the Hydra I cluster, one of the largest nearby galaxy clusters containing hundreds to thousands of galaxies bound by gravity.
- The Hydra I cluster’s center features two massive elliptical galaxies, each around 150,000 light-years across-50% larger than the Milky Way.
- NGC 3285B lies on the outskirts of this cluster and became notable due to hosting a Type Ia supernova in 2023 named SN 2023xqm.
- Type Ia supernovae occur when a white dwarf detonates, producing nuclear fusion and briefly shining about five billion times brighter than our Sun.
- Hubble targeted NGC 3285B as part of research observing 100 Type Ia supernovae to study their signatures in ultraviolet, optical, and near-infrared wavelengths. This aims to refine distance measurement techniques crucial for understanding cosmic scales.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s growing emphasis on space exploration aligns smoothly with such groundbreaking studies by NASA/ESA leveraging tools like Hubble Space Telescope. Observations like those involving NGC 3285B advance humanity’s understanding of universal phenomena such as galaxy formations and accurate cosmic distance measurements-essential data for developing space technologies globally including india’s ambitious projects like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan missions.
The focus on refining methods for measuring distances more precisely could indirectly benefit scientific collaborations or observational techniques within India’s burgeoning astronomy sector (e.g., ISRO or academic programs). This underscores prospects for increased international partnerships aiming at decoding mysteries beyond Earth-a vision india enthusiastically supports given its recognition in global astronomy advancements.