Now Reading: New Frog Species in Meghalaya Named After Iconic Khasi Dish
-
01
New Frog Species in Meghalaya Named After Iconic Khasi Dish
New Frog Species in Meghalaya Named After Iconic Khasi Dish

Speedy Summary
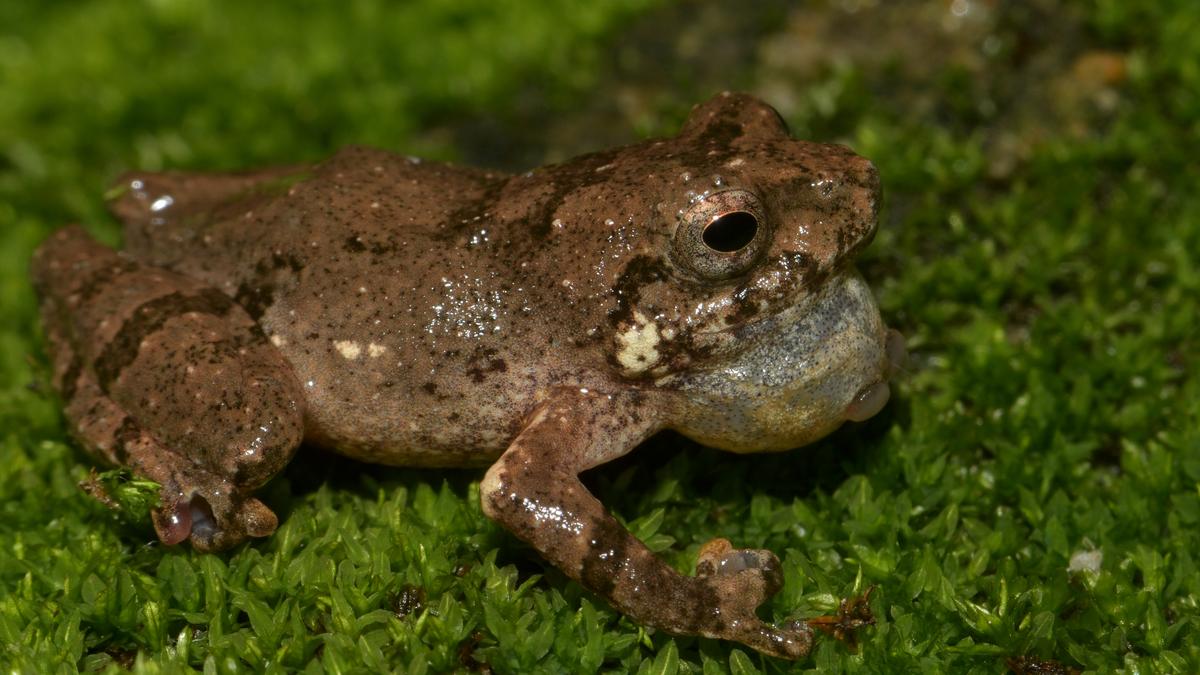
- Species Finding: Two new species of direct-developing frogs, Raorchestes jadoh and Raorchestes jakoid, have been recorded in Meghalaya by a team of researchers.
- Naming Inspiration: The names are inspired by Khasi culture – “Jadoh,” a traditional rice-and-meat dish, and “Jakoid,” the Khasi word for ‘frog.’
- key Features: Direct-developing frogs bypass the tadpole stage and hatch as froglets. These new species exhibit unique morphological traits, calls, and DNA sequences that place them within the Raorchestes genus.
- Locations Found:
– Raorchestes jadoh: Langtor village in Eastern West Khasi Hills district at an altitude of 1,655 meters.
– Raorchestes jakoid: Lawbah village in East Khasi Hills district at an elevation of 815 meters.
- Habitat Observations: Found near human settlements, indicating adaptive ecological traits; however, their habitats are vulnerable to landscape changes.
- Research Techniques Used: Genetic analysis combined with acoustic observations confirmed these frogs as distinct from other known species.
- Meaning for Meghalaya Amphibians: Meghalaya hosts approximately 70 amphibian species; discoveries since 2000 highlight its biodiversity’s importance.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery of two new frog species uniquely tied to indigenous Khasi culture underscores the deep relationship between biodiversity and cultural heritage. Naming them after local traditions not only celebrates community identity but also fosters pride and conservation awareness among locals-a key strategy in sustaining ecological efforts.These findings highlight how rapid landscape changes threaten even adaptable amphibians like R. jadoh and R. jakoid. The use of advanced scientific methods alongside fieldwork showcases India’s growing contribution to global biodiversity studies. With northeastern India being a hotspot for amphibian diversity-20 new records since 2000-it is crucial to align advancement plans with environmentally conscious actions.
This research reinforces how preserving fragile ecosystems like Meghalaya benefits both science and local communities alike while offering invaluable insight into lesser-studied animal groups critical for ecological balance.
Read more: The Hindu