Now Reading: Exploring the Unknown: Insights from Sols 4493-4494
-
01
Exploring the Unknown: Insights from Sols 4493-4494
Exploring the Unknown: Insights from Sols 4493-4494

quick Summary
- The Mars Science Laboratory Mission team conducted Earth planning for sols 4493-4494 on March 26, 2025.
- Curiosity rover skipped contact science due to its “field geologist” pose, enabling more remote sensing opportunities.
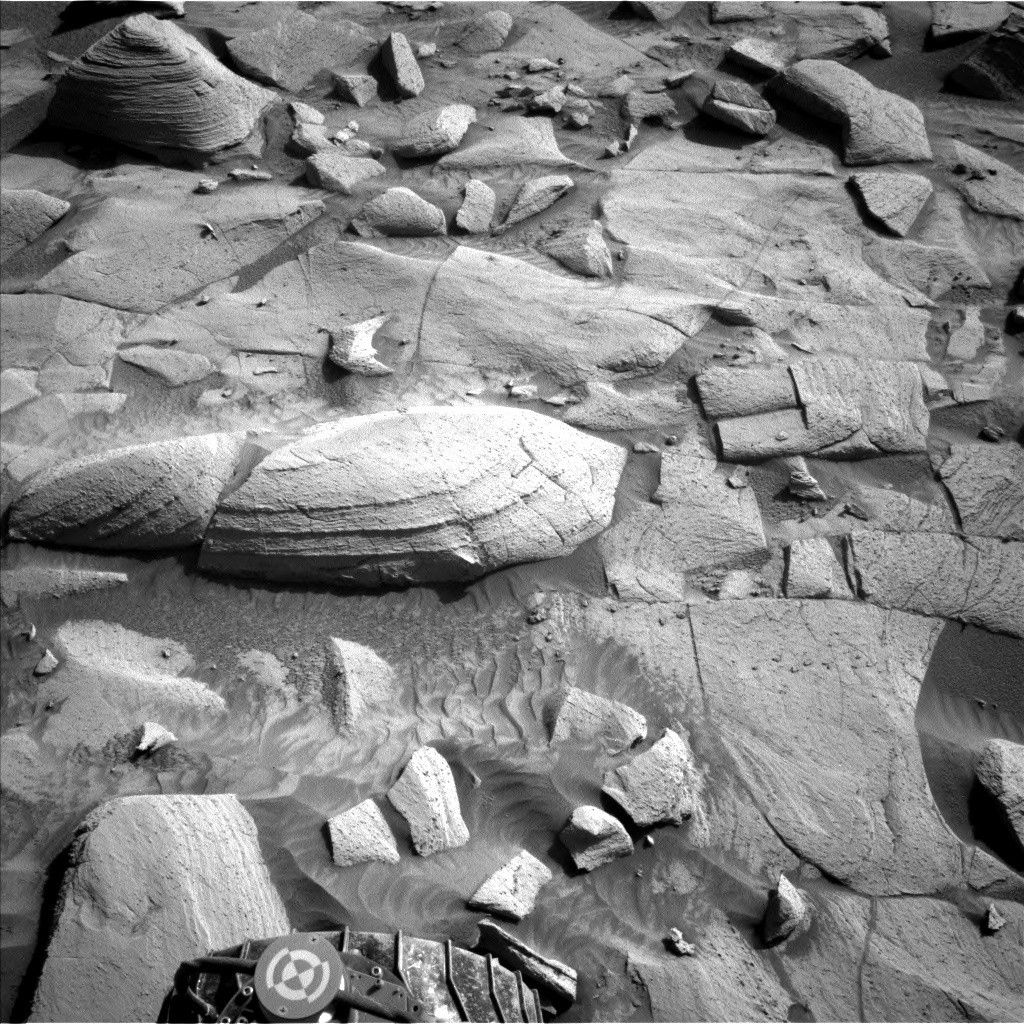
- Day one included targeted remote sensing like suprahorizon cloud observation and a dust-devil survey. Geology-focused analysis covered bedrock targets (“Observatory Trail”) and features like “Point Loma,” “Black Butte,” and boxwork structures.
- ChemCam examined targets such as “Cholla” using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) alongside distant observations of Texoli butte and other geological formations.
- On day two, untargeted remote sensing featured an extended dust-devil movie, atmospheric dust tracking using Mastcam tau observations, and autonomous LIBS selection by ChemCam via AEGIS.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s burgeoning interest in space exploration aligns well with advancements such as NASA’s Mars missions. Remote operations demonstrate how complex autonomy in planetary rovers can advance scientific understanding with limited direct human intervention-a model perhaps useful for India’s own lunar or Martian ambitions. Notably, technologies like LIBS spectroscopy contribute valuable environmental data that could refine resource utilization strategies for future missions by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). While ISRO has focused mainly on Chandrayaan lunar projects recently, international efforts like Curiosity emphasize the collaborative need in studying broader cosmic phenomena such as planetary atmospheres or surface dynamics.