Now Reading: Scientists Develop Light-Controlled RNA Editor for Precise Gene Regulation
-
01
Scientists Develop Light-Controlled RNA Editor for Precise Gene Regulation
Scientists Develop Light-Controlled RNA Editor for Precise Gene Regulation
Quick Summary
- Category: Research Briefing
- Publication Date: 31 March 2025
- Source Journal: Nature Biotechnology
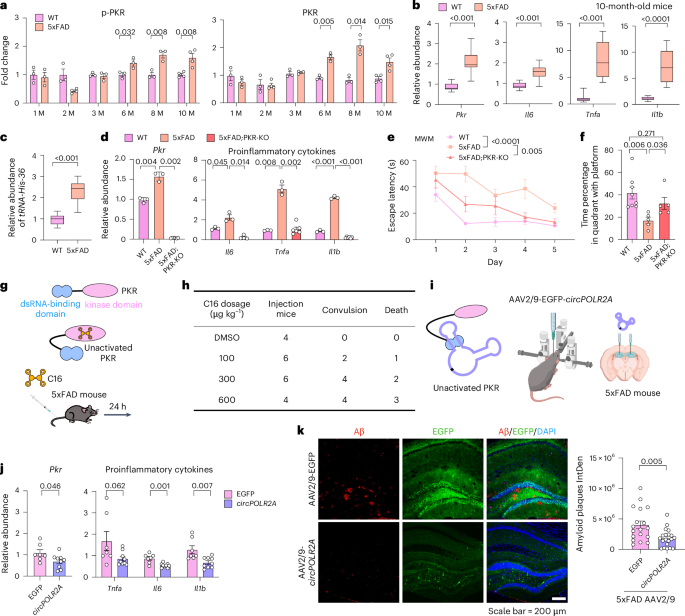
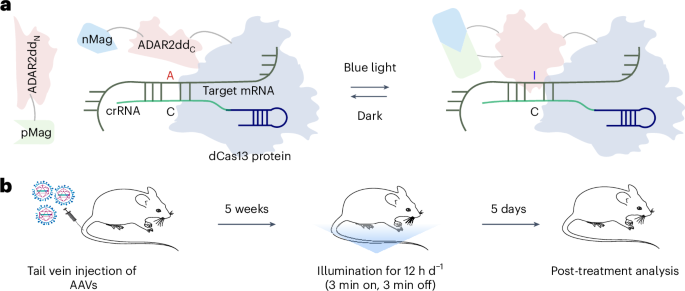
- Key Highlight: A novel photoactivatable RNA base editor has been developed to enable tunable and reversible regulation of gene expression, addressing safety and efficacy challenges in gene therapy.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The advancement in RNA editing,especially the advancement of a photoactivatable base editor,opens new avenues for precision medicine globally. for India-a country with growing investment in biotechnology-such innovations could bolster efforts in tackling complex genetic conditions and chronic diseases. Leveraging this technology might accelerate india’s capacity to deliver safer gene therapies while aligning with ongoing Make-in-India initiatives targeting cutting-edge medical innovation. However, affordability and accessibility remain critical concerns that must be addressed to ensure equitable application within India’s diverse healthcare landscape.
Image:
!Read More