Now Reading: AP CM Initiates Satellite Survey to Boost Farmers’ Income
-
01
AP CM Initiates Satellite Survey to Boost Farmers’ Income
AP CM Initiates Satellite Survey to Boost Farmers’ Income

Speedy Summary
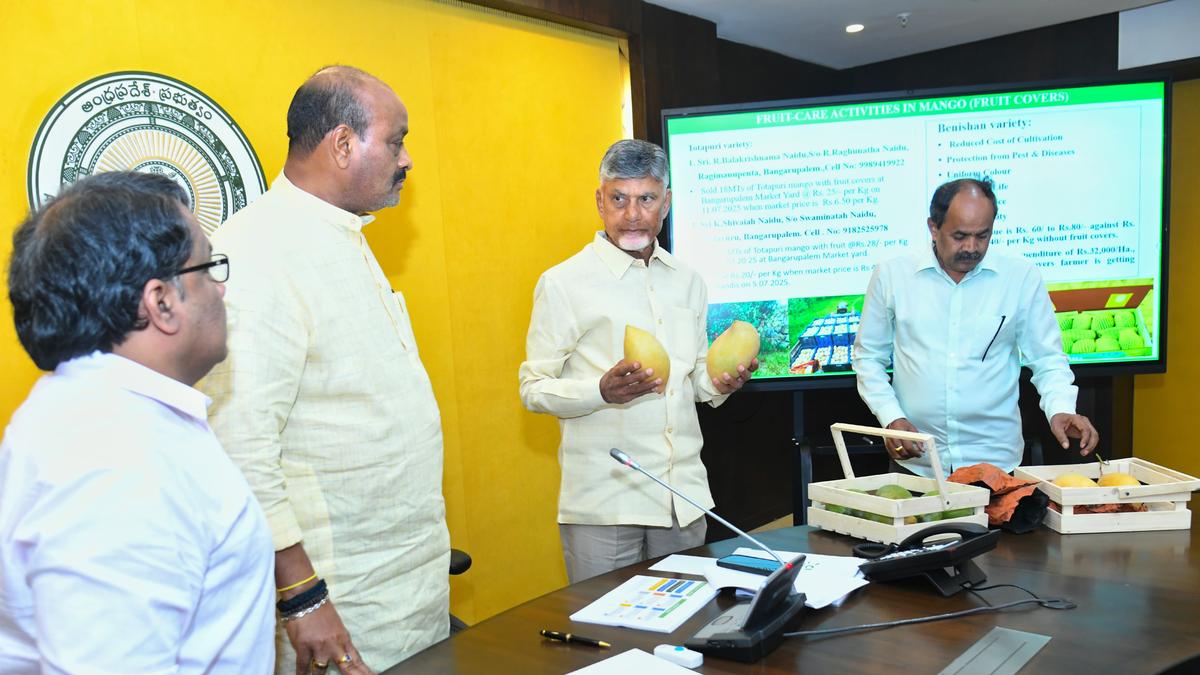
- Satellite Survey: Andhra Pradesh CM N. Chandrababu Naidu directed officials to conduct a satellite-based survey of crop patterns statewide for improved agricultural planning, following accomplished trials in East Godavari district.
- Crop Clustering: Farmers will be guided to cultivate similar crops in clusters to enhance profitability. Field-level data verification is essential.
- Technological Integration: Advanced tools like AI, drones, and satellite data will be utilized for real-time monitoring of crop health (using 42 parameters) and improving productivity across sectors.
- water Resource Management: Groundwater recharge structures are targeted at achieving 1,000 tmc ft storage; canal desilting and inter-departmental coordination were mandated.
- AI Chatbot & Awareness Campaigns: AI chatbots will assist farmers with crop planning while campaigns will address issues like excessive pesticide use affecting soil health and causing diseases such as cancer. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) was recommended as an alternative approach.
- Organic Certification Partnership with Tata Group: Organic certification efforts aim to increase farmer income and enable exports globally (to countries like Japan, Taiwan).Certified produce can access over 130 markets worldwide.
- Coconut Industry Highlighted: Mr. Naidu appreciated ‘Coco Munj’ companyS coconut-based product innovations alongside other growth-oriented agriculture interventions.
Indian Opinion analysis
Andhra Pradesh’s proactive emphasis on using advanced technologies like artificial intelligence,drones,and satellite data exemplifies how agriculture can evolve into a science-backed system that prioritizes efficiency over tradition amid growing environmental challenges such as climate change or shrinking groundwater resources.The decision to incorporate organic certification linked to international export opportunities demonstrates forward-thinking economic vision by broadening market access for sustainably grown crops-a move likely intended not only for higher farmer incomes but also environmental conservation through reduced chemical dependency.
Addressing systemic challenges such as soil degradation from fertilizer misuse highlights the government’s responsibility toward long-term sustainability goals while balancing immediate yield demands of Indian farms.
However,realizing these substantial plans would require diligent execution-notably integrating high-tech solutions where infrastructural gaps exist-and continuous field-level training programs given farmers’ varied familiarity with digital tools.
Mr. Naidu’s encouragement of clustering crops also underlines the need for rural economies localized around cooperation and shared expertise among farming groups-potentially increasing resilience during uncertain weather cycles or global commodity volatility concerns ahead.
Read More Here: Source