Now Reading: Advanced Method Uncovers Gene Transfer in Microbial Communities
-
01
Advanced Method Uncovers Gene Transfer in Microbial Communities
Advanced Method Uncovers Gene Transfer in Microbial Communities
Quick Summary:
- Category: Research Briefing
- Publication Date: 28 March 2025
- Source Journal: Nature Biotechnology
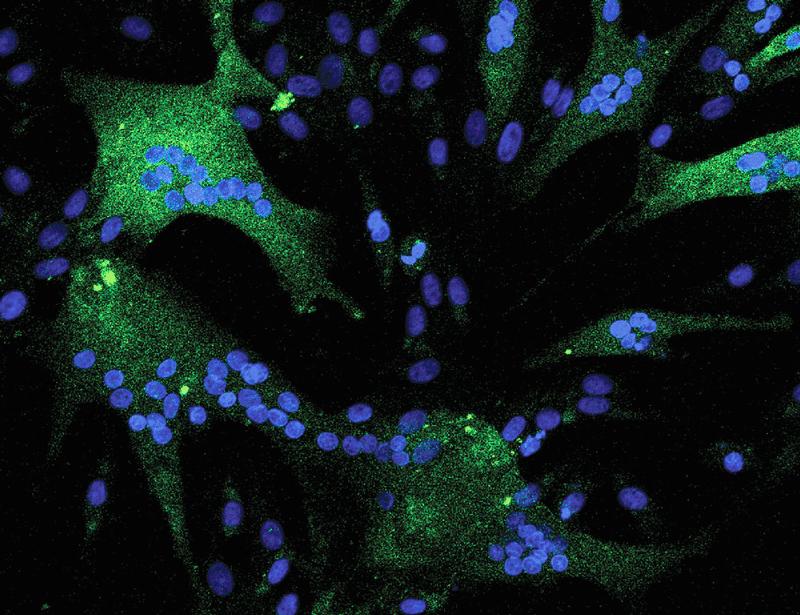
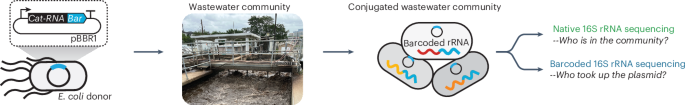
- Researchers developed a synthetic biology tool, RAM (RNA-based Analytic Metric), which incorporates barcodes into RNA to trace gene transfer during DNA exchange among microbes.
- Applied in wastewater microbial communities,RAM utilizes high-throughput sequencing to identify microorganisms involved in gene transfer activities.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The development of RAM as a high-resolution tool for tracking horizontal gene transfer coudl have significant implications for India’s scientific community and environmental policy. Wastewater management systems are a key focus area for sustainability in densely populated regions like India, where contamination can lead to public health risks and ecosystem imbalance.
If adopted by Indian research institutions, this method could enhance microbial studies within urban sewage systems or industrial waste setups-ultimately aiding pathogen control efforts and bioengineering applications aimed at improving treatment processes.
Neutral yet significant advancements like these represent opportunities that align well with India’s broader goals of leveraging biotechnology in addressing pressing environmental challenges while fostering global partnerships in scientific research.