Now Reading: Advancing Mitochondrial DNA Editing with Base Excision Repair
-
01
Advancing Mitochondrial DNA Editing with Base Excision Repair
Advancing Mitochondrial DNA Editing with Base Excision Repair
Quick Summary
- Targeted deep sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, and genome sequencing datasets have been made available publicly through specific BioProjects hosted by the National Center for Biotechnology Details.
- De novo Single Nucleotide Variants (SNVs) were identified using a toolkit called BEIDOU integrated with SNV data from dbSNP version 151.
- Researchers used custom Perl and Shell scripts to calculate base substitution frequencies; these codes are accessible on GitHub at YangLab/CFBI.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The availability of comprehensive genomic, transcriptomic, and targeted data alongside computational resources like BEIDOU for identifying mutations underscores the growing openness in scientific research globally. While no explicit mention is made of india in this dataset provisioning process, it holds important potential for Indian researchers working on genomics-based solutions across healthcare and agriculture sectors. Access to pre-analyzed SNV databases coupled with calculation toolkits can shorten research timelines and enrich India’s contribution to global genomics innovations. Investment in training Indian scientists and expanding infrastructure might allow deeper participation in such open-platform collaborations.
Read more: NCBI BioProjects PRJNA1223321, GitHub YangLab/CFBI.Quick Summary:
- The article examines advancements in mitochondrial and nuclear DNA editing technologies using base editors.
- Several studies referenced include development of CRISPR-free and compact zinc finger base editors, programmable deaminases, and novel methods enhancing editing fidelity across diverse contexts.
- research highlights include improvements in compatibility for target sequences, reductions in off-target effects, and applications in cells and mice.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The breakthroughs outlined represent significant strides in genetic research with potential implications for global human health challenges such as hereditary diseases. For India, where healthcare access still faces inequalities across populations, these advancements suggest possibilities for implementing precision medicine therapeutics tailored to endemic genetic disorders. However, it also raises concerns about ethical considerations surrounding genome editing technologies that require regulated policies to prevent misuse while ensuring equity for all citizens.Read more: [source link]Quick Summary:
- The article presents advancements in the understanding and application of zinc finger architecture and toxin-derived cytidine deaminases for efficient base editing in human cells.
- Research highlights the structural basis for sequence-specific DNA deamination mechanisms,focusing on enzymes like DddA,APOBEC3,and EXOG.
- Studies also analyze posttranslational modifications affecting DNA repair pathways such as base excision repair (BER).
- Progress has been made in high-throughput assays tracking enzyme activities related to DNA mismatch repair processes.
- The findings are significant for improving CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing precision and minimizing mutation risks during biological repairs.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The advancements described represent potential breakthroughs not just globally but also with implications for India’s scientific community. Efficient genomic editing holds promise for accelerating research in agriculture, bioengineering, disease treatment innovations (including rare genetic conditions), and personalized medicine-objectives aligned with India’s long-term goals of achieving global competitiveness in biotechnology. While ethical considerations around gene-editing persist globally, it is imperative that Indian institutions proactively engage with international regulatory frameworks to integrate these technologies responsibly into public health initiatives.
For further details: articleQuick Summary
- The article outlines advancements in mitochondrial DNA manipulation, particularly through CRISPR-free base editors and other tools.
- Various studies introduced techniques like mitoBEs and CyDENT for precision editing of mitochondrial DNA, addressing mutations involved in diseases.
- Base-editing innovations have expanded targeting scopes but raised concerns about unintended nuclear off-target effects.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings represent progress in genetic editing technology with significant implications for medicine,including the treatment of hereditary conditions linked to mitochondrial dysfunction. For India, these technologies could bolster it’s growing biotech sector while addressing genetic disorders prevalent in the population. Ethical safeguards must be prioritized due to unresolved issues like off-target mutations, ensuring responsible integration into diagnostic and therapeutic platforms nationwide.
Read more: PubMed CentralIt seems like the text provided does not contain any structured content about a specific event,issue,or development related to India that can be summarized or analyzed in the required format. The content mostly appears to include references and citations from academic research.
If you have a specific news article related to India or intend for me to work on some other provided input that includes relevant details, feel free to share it! I’ll be happy to assist.Quick Summary:
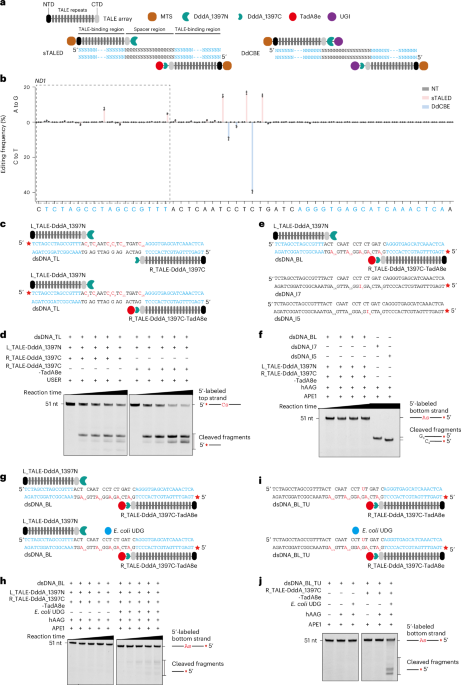
- A research study develops advanced editing techniques for mitochondrial DNA using precision base editors.
- The study introduces various methods to achieve targeted A-to-G and C-to-T conversion efficiencies in mitochondrial DNA sequences with reduced off-target effects.
- Researchers employed TALED (TALE-derived editor) technology alongside improvements such as engineered variants like sTALED, mTALED, and edTALED-GSVG to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
- Tests were conducted in 293FT cells targeting specific mitochondrial sites (ND1, ND4, ND5.3).
- Funding was provided by Chinese government-supported programs including the National Key Research Program and several Shanghai-based institutions.
- Authors disclosed competing interests related to CorrectSequence Therapeutics but emphasized scientific neutrality.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This research reflects advancements in gene-editing technologies that may have significant implications for biomedical fields globally. India could benefit from further collaboration on similar cutting-edge studies wich address genetic diseases or improve therapeutic approaches domestically.As gene-editing tech spreads worldwide-factoring ethical considerations-it promises healthcare advances for complex disorders presently tough to treat. However,balancing access costs with equity will require careful policy adaptation within the Indian context while ensuring regulatory frameworks align rapidly evolving global norms.
Read more: Google Scholar LinkQuick Summary:
- Research centered on TALEDs for mitochondrial DNA editing presented by Yuhang Fan et al. highlights advancements in adenine base editing (A-to-G) efficiency in specific cells.
- Heatmaps detail A-to-G editing frequencies and single-nucleotide substitutions induced by engineered editors in cellular experiments like A549 and U2OS.
- The study explores nuclear genome-wide mutations, cellular toxicity, and narrowed editing windows for effective targeting of sites like ND5.1 and ND1.
- Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test or Welch’s t-test based on experiment designs.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The research on mitochondrial DNA editing introduces cutting-edge technologies that could redefine approaches to genetic disorders globally, including India where genetic diseases are a significant healthcare concern due to the diverse population genetics. this innovation might eventually lead to customized treatments addressing inherited conditions caused by mitochondrial mutations. India’s robust capacity for scientific research provides an prospect for local adaptation of such advancements which could enhance public health outcomes while contributing to global knowledge-sharing initiatives.
Read more: Springer Nature ArticleQuick Summary
- The article discusses advancements in adenine base editing for mitochondrial DNA by leveraging base excision repair mechanisms.
- Published in Nature Biotechnology on March 25, 2025, the research represents a breakthrough in genome editing technology.
- Researchers focused on efficient and precise modifications of mitochondrial DNA, which could have implications for treating genetic disorders.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This innovation in mitochondrial DNA editing marks a significant leap forward in genetic biotechnology. For India, such advancements hold potential applications in addressing hereditary diseases prevalent within the country and enhancing health outcomes through precision medicine strategies. Though, it is indeed essential to balance scientific progress with ethical considerations and robust regulatory frameworks to ensure safe applications of this technology within India’s diverse medical landscape.