Now Reading: AI Advances Unlock Insights into Yellowstone Wolves
-
01
AI Advances Unlock Insights into Yellowstone Wolves
AI Advances Unlock Insights into Yellowstone Wolves

Quick Summary
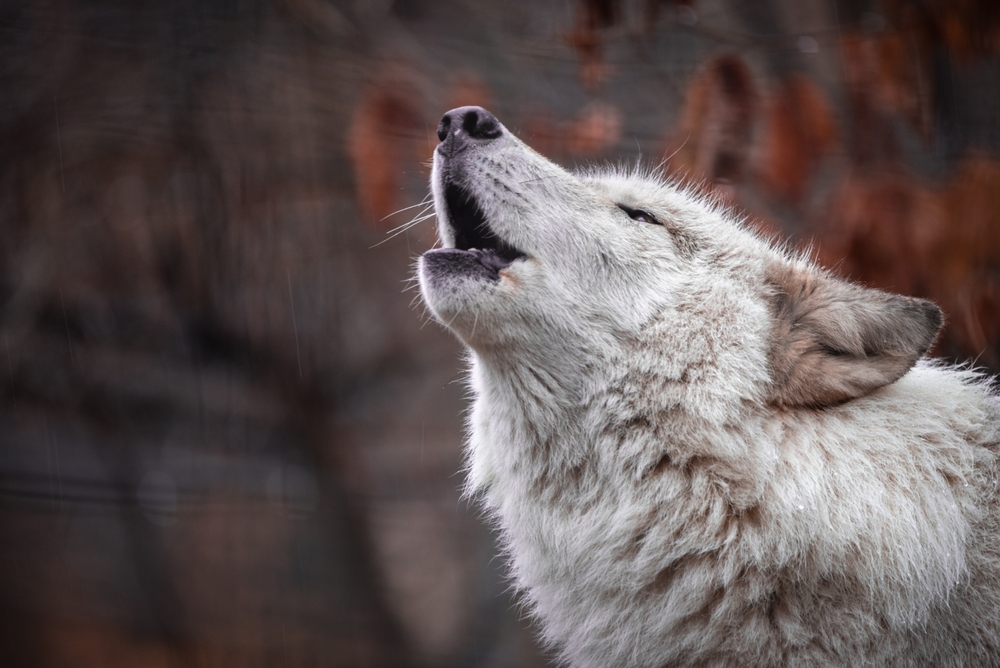
- Wolves and their communication: Wolf howls are crucial for expressing pack solidarity, tracking members, and signaling territories. these sounds can travel over five miles and are complex when combined into chorus howls.
- New conservation effort: The Colossal Foundation has partnered with Yellowstone Forever and the Yellowstone Wolf Project to advance wolf conservation using AI-powered monitoring technologies.
- Technology deployment: 25 GrizCam units will be installed at wolf denning sites in Yellowstone to record 360-degree video footage and acoustic data, offering non-invasive alternatives to traditional tracking methods like collars.
- AI algorithms in research: Machine-learning models will classify wolf howls with a reported accuracy of 92%, helping researchers analyze pack size, identity, behavior patterns, and ecosystem dynamics.
- Broader reach of technology: Pilot projects involving GrizCam units are planned for tribal lands across Idaho linked to the Nez Perce Tribe.
- Ecological importance of wolves: Wolves serve as keystone species; their presence is essential for maintaining biodiversity by controlling prey populations like elk.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The integration of AI-driven monitoring technologies into wildlife conservation marks a important step forward in advancing non-invasive research methodologies. While this specific initiative focuses on wolves in the United States at Yellowstone National Park, it underscores the broader potential applications globally-including india-where protecting vulnerable predator species may similarly hinge on technological innovations.
India’s vast biodiversity includes apex predators such as tigers and leopards that play vital roles within ecosystems akin to wolves’ role in Yellowstone. The increasing use of AI tools could aid Indian conservation efforts by streamlining data collection while reducing stress on wildlife caused by invasive tactics like collaring. Furthermore, deploying advanced acoustic monitoring systems could enhance existing programs targeting animal populations through real-time tracking-a crucial element given India’s densely populated landscapes where human-animal conflicts often arise.
This partnership also highlights a commitment to leveraging local communities through pilot projects with Indigenous groups-a strategy India might consider adapting with tribal communities near forested reserves. Ultimately, embracing technology that adequately deciphers animal behaviors promises mutual benefits; scientific advancements meet ecological preservation goals seamlessly without disrupting habitats.