Now Reading: Anamalai Tiger Reserve Hosts Eight Firefly Species
-
01
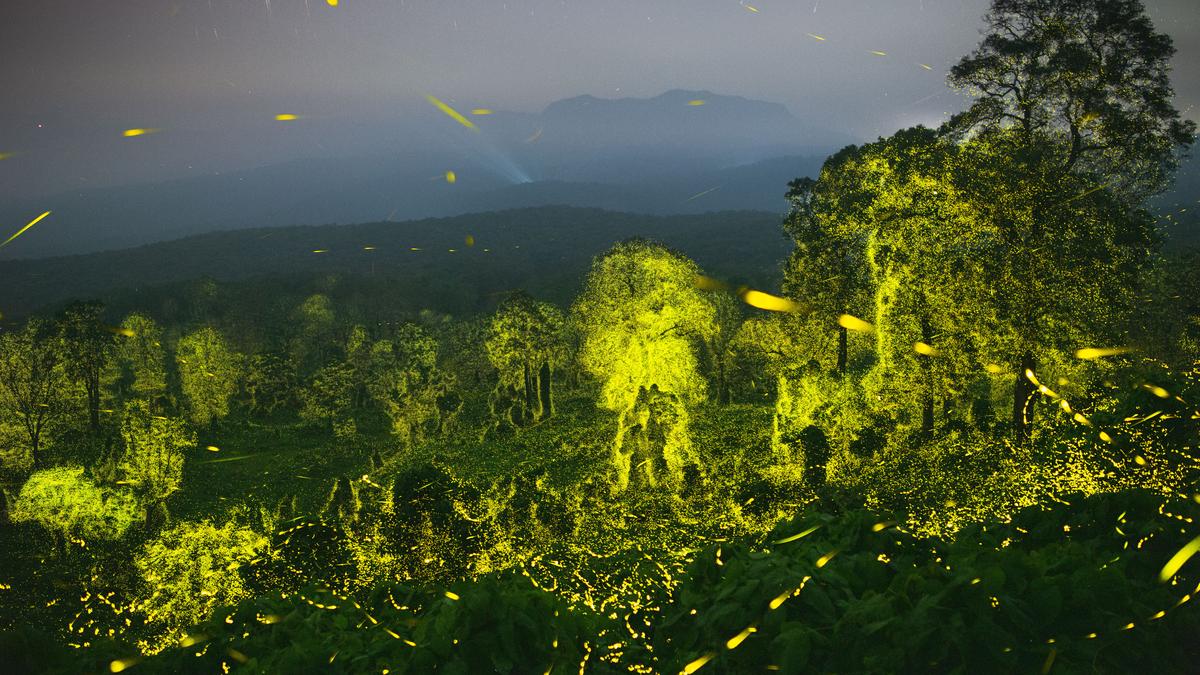
Anamalai Tiger Reserve Hosts Eight Firefly Species
Anamalai Tiger Reserve Hosts Eight Firefly Species

Swift Summary
- Location: The Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) in Tamil nadu is known for the rare synchronous lighting phenomenon by fireflies annually.
- Study Conducted: A year-long research (April 2024 – March 2025) by Tamil Nadu Forest Department and Advanced Institute for Wildlife Conservation (AIWC) identified eight firefly species in ATR using DNA barcoding.
- Findings:
– Species identified include Abscondita perplexa, Abscondita terminalis, Asymmetricata humeralis, Curtos sp. (three variants), Lamprigera sp., and Pyrocoelia sp.
– Genetic sequences submitted to GenBank were assigned accession numbers.
– Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, wind velocity, and light intensity were documented during collection.
- light Pollution Impact: Light pollution disrupts natural behaviors of wildlife including fireflies. Fireflies are deemed indicators of environmental health.
- Community Insights: A local survey shows 97% awareness about fireflies; population decline attributed to pesticide use and water pollution.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study on ATR’s firefly populations marks a notable milestone as it offers the first systematic genetic analysis within Tamil Nadu. By identifying eight distinct species using advanced techniques like DNA barcoding, researchers have laid a strong foundation for future ecological studies concerning conservation biology. Fireflies may serve as key biodiversity indicators linked to threats like light pollution-a growing concern around natural areas.
Moreover, community involvement highlights public awareness but also underscores the adverse effects of agrochemical practices on biodiversity. Minimizing light pollution near protected forests could safeguard ecological balance while aiding broader efforts against wildlife disruptions from human activity.
This research holds relevance beyond pure scientific interest-it reinforces India’s responsibility towards preserving delicate ecosystems amidst rapid development challenges.
Read More link: Visit full article
Images from the raw news: