Now Reading: Ancient Denisovan Interbreeding Shaped Modern Human Evolution
-
01
Ancient Denisovan Interbreeding Shaped Modern Human Evolution
Ancient Denisovan Interbreeding Shaped Modern Human Evolution

Quick Summary:
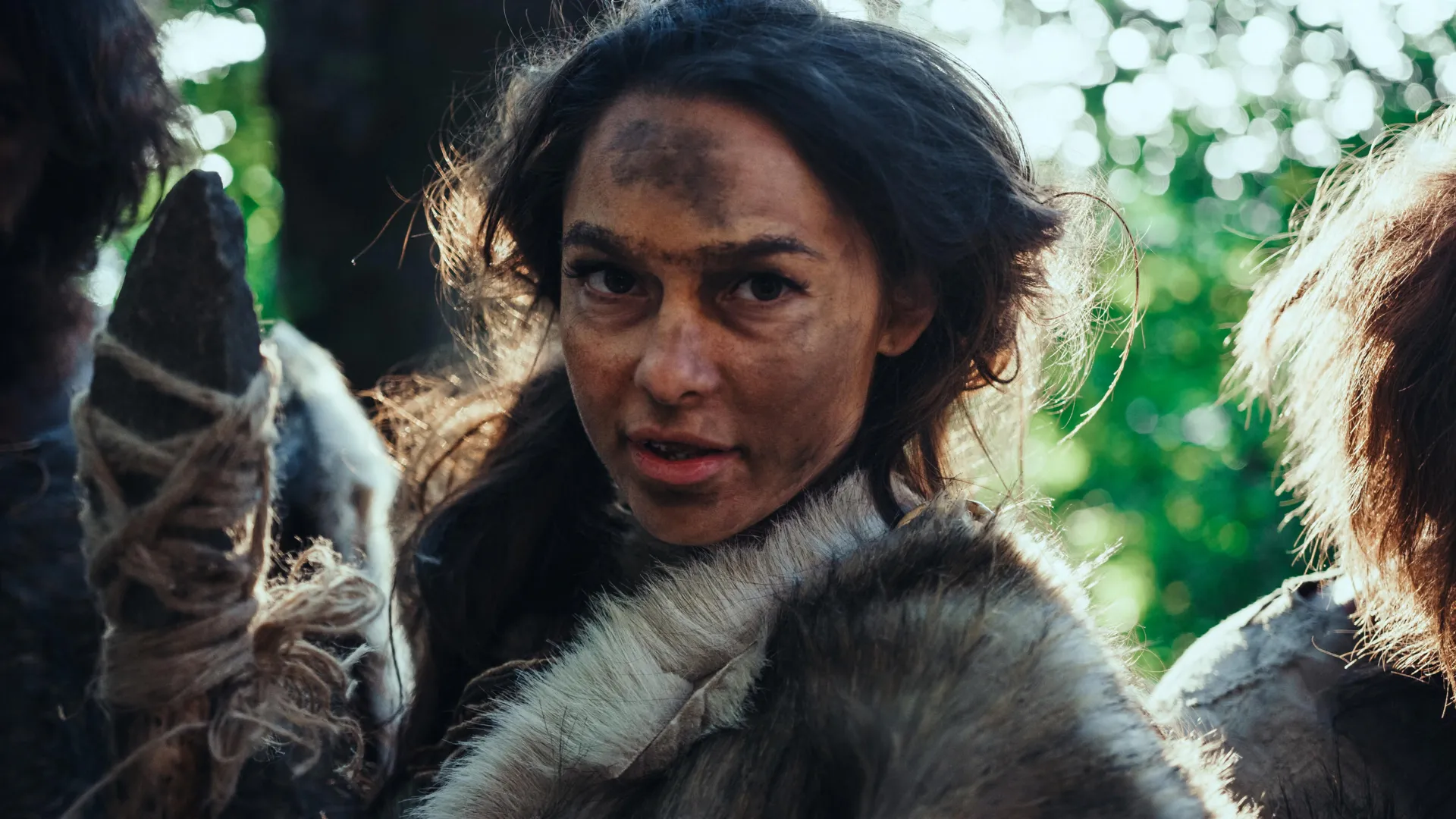
- Researchers have identified genetic contributions from Denisovans, a recently recognized hominin group, to modern humans through interbreeding events.
- The Denisovan genome was uncovered following the finding of a finger bone in Siberia’s Denisova Cave in 2010, marking one of the decade’s major findings in human evolution.
- Evidence indicates at least three separate instances where genes from different Denisovan populations were inherited by modern human groups.
- Denisovans lived across vast regions (Siberia,Southeast Asia,Oceania,and South america),with specific adaptations to their environments.
- Several advantageous genes of Denisovan origin include:
– Tolerance to low oxygen conditions (seen in Tibetan populations).
– Enhanced immunity genes.- Genes affecting lipid metabolism for generating heat in Arctic populations like Inuit groups.
- Ongoing research aims to discover hidden traces of Denisovan ancestry and link more genetic and archaeological evidence.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The identification of genetic contributions from the archaic hominin species known as the Denisovans offers critically important insights into how early humans evolved and adapted to various environmental challenges. For India specifically, it may illuminate regional variations in human genetic history and adaptations given South Asia’s proximity to key sites associated with early hominins.
Understanding these interbreeding events broadens scientific perspectives on human development beyond the previously linear view. It underscores that gene sharing between distinct hominin populations was crucial for survival-a concept relevant across disciplines such as genetics and anthropology.
Future studies integrating broader genetic datasets from understudied regions could potentially reveal novel aspects about India’s ancestral connections with archaic humans like the Denisovans.This would help contextualize certain physiological traits or health predispositions observed within local populations today while contributing globally toward reconstructing humanity’s complex evolutionary narrative.