Now Reading: Ancient DNA Uncovers Lost Indigenous Group in Colombia from 2,000 Years Ago
-
01
Ancient DNA Uncovers Lost Indigenous Group in Colombia from 2,000 Years Ago
Ancient DNA Uncovers Lost Indigenous Group in Colombia from 2,000 Years Ago
Fast Summary
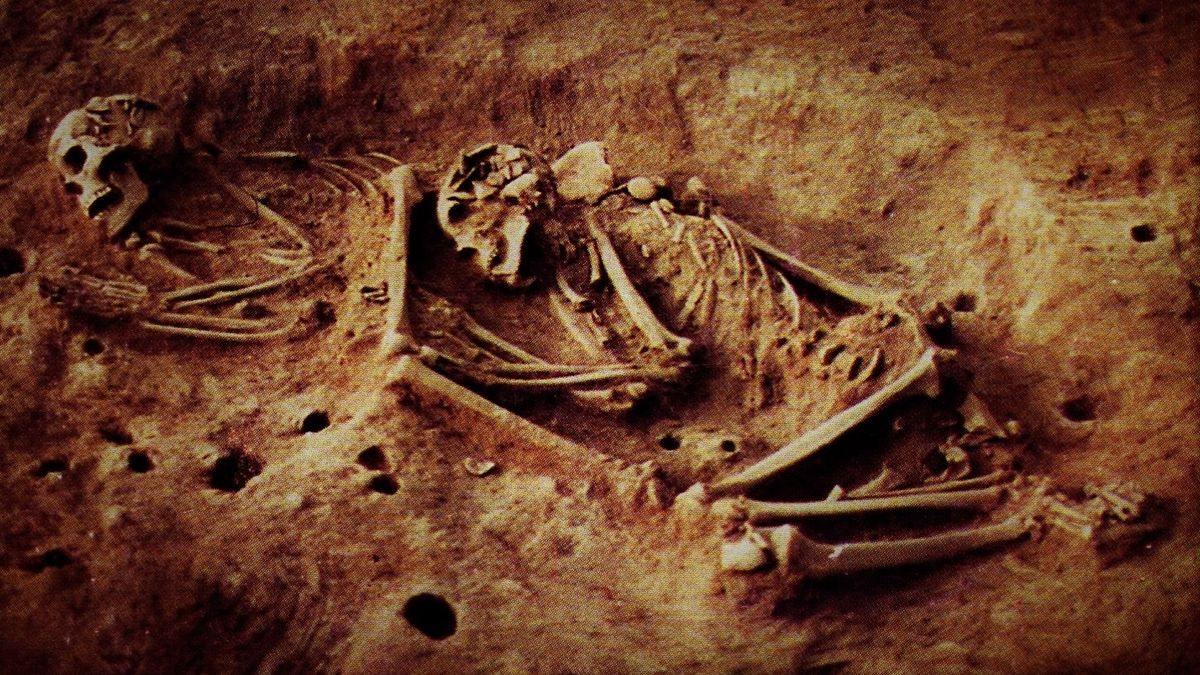
- Researchers in Colombia have sequenced ancient DNA from 21 skeletons found at five archaeological sites near Bogotá,spanning a history of 5,500 years.
- The study unearthed a previously unknown genetic lineage of hunter-gatherers who lived in the region approximately 6,000 years ago but vanished without descendants about 4,000 years later.
- Starting from the herrera period (~2,800 years ago), migrating groups brought widespread cultural changes-such as ceramics and Chibchan languages-into the area.
- Chibchan-related ancestry originating from Central America was detected in remains dating back ~2,000 years; it spread widely by mixing with other populations over multiple occasions.
- Ancient genomes revealed little similarity between early hunter-gatherers and later populations such as Indigenous Colombians or ancient groups elsewhere in Central and South America.
Images:
- Skeleton remains of ancient hunter-gatherers (Credit: Ana María Groot/Universidad Nacional de Colombia)
- A view of Altiplano near Bogotá where these populations lived (Credit: William Usaquen/Universidad Nacional de Colombia)
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings provide intriguing insights into human migrations and population exchanges thousands of kilometers away but resonant for studies on ancient cultures. India’s own diverse ancestry stems from migrations similar to these-from early genomic splits to language expansions during prehistoric times. This research highlights how geographical barriers like plateaus facilitated complex shifts in technology and culture through incoming populations.
India’s archaeological focus could gain valuable viewpoint by delving deeper into genome sequencing for extinct lineages within its borders.For example, it could aid debates surrounding cultural exchanges tied to ceramics during India’s Chalcolithic period or the emergence of Indo-European languages paralleling historical movements akin to Chibchan-speaking arrivals observed here.
Such comparative studies underscore shared global phenomena where technological advancements are often linked with migratory interactions rather than independent development alone-a bridge across continents toward understanding evolutionary progressions better.