Now Reading: Ancient Egyptian DNA Analysis Unveils Clues About Occupation
-
01
Ancient Egyptian DNA Analysis Unveils Clues About Occupation
Ancient Egyptian DNA Analysis Unveils Clues About Occupation
Speedy Summary
- Researchers have successfully sequenced the first whole genome from ancient Egyptian remains, marking a major milestone in egyptology.
- The DNA came from a tooth belonging to an individual buried in Nuwayrat (excavated in 1902) and dates back to the Early Dynastic-Old Kingdom periods (2855-2570 BCE).
- Genetic analysis revealed 80% linkage to North Africa and 20% to the Mesopotamian Fertile Crescent, suggesting regional ancestry. The man grew up locally in Egypt based on dietary chemical evidence.
- Skeleton clues indicate he lived a physically demanding life, likely as a potter using early pottery wheel technology. Foot arthritis aligns with this activity.
- Despite his labor-intensive occupation, the individual’s burial treatment was higher-class than expected for someone of his profession. This suggests possible social elevation due to skill or success.
- Researchers hope that similar DNA sequencing projects will uncover more details about ancient migrations and social structures.
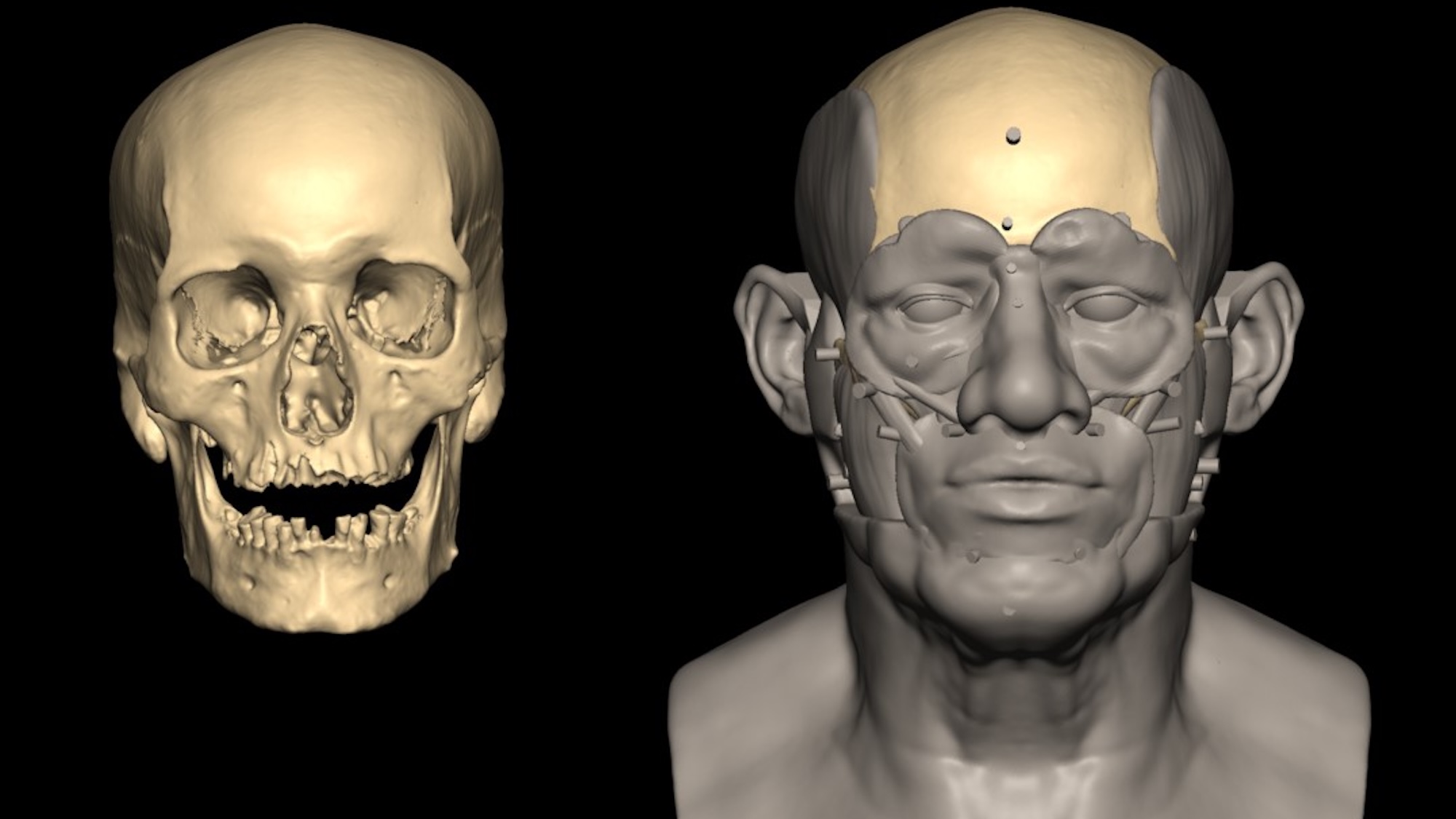
(image description: Facial reconstruction of the Nuwayrat individual derived via 3D scan data.)
!Facial reconstruction
(Image description: Pottery coffin and archaeological remains of the Nuwayrat individual discovered in 1902.)
!Pottery coffin
Indian Opinion Analysis
This breakthrough highlights how advancements in genomics are reshaping our understanding of ancient civilizations globally. For India, which boasts its own deep history spanning millennia-from Harappan culture to Vedic traditions-such technologies may aid existing efforts into unraveling ancestral links or resolving contested theories about ancient migrations within South Asia. It also underscores interdisciplinary approaches combining genetics with archaeology as pivotal for reconstructing human history.
India’s archaeological community coudl draw lessons from this research by integrating genomic studies into investigations like those of skeletal remains from Indus Valley sites or other non-standard burial practices preserved across diverse environments within India’s climatic range. However, prioritizing ethical considerations over genomic preservation practices is equally crucial due to cultural sensitivities surrounding historical artifacts here.
discoveries such as these reiterate the need for India’s scientific institutions to invest further into cutting-edge genetic tools-not merely for advancing past inquiries but also enabling wider global collaboration that may contextualize South Asia’s role within broader human migration narratives.