Now Reading: Ancient Wildfires Shaped Antarctica and Atacama into Earth’s Harshest Landscapes
-
01
Ancient Wildfires Shaped Antarctica and Atacama into Earth’s Harshest Landscapes
Ancient Wildfires Shaped Antarctica and Atacama into Earth’s Harshest Landscapes

Quick Summary
- Antarctica and Atacama Desert History: Millions of years ago, Antarctica and the Atacama Desert were lush forested landscapes with araucaria trees, giant ferns, and rich vegetation.
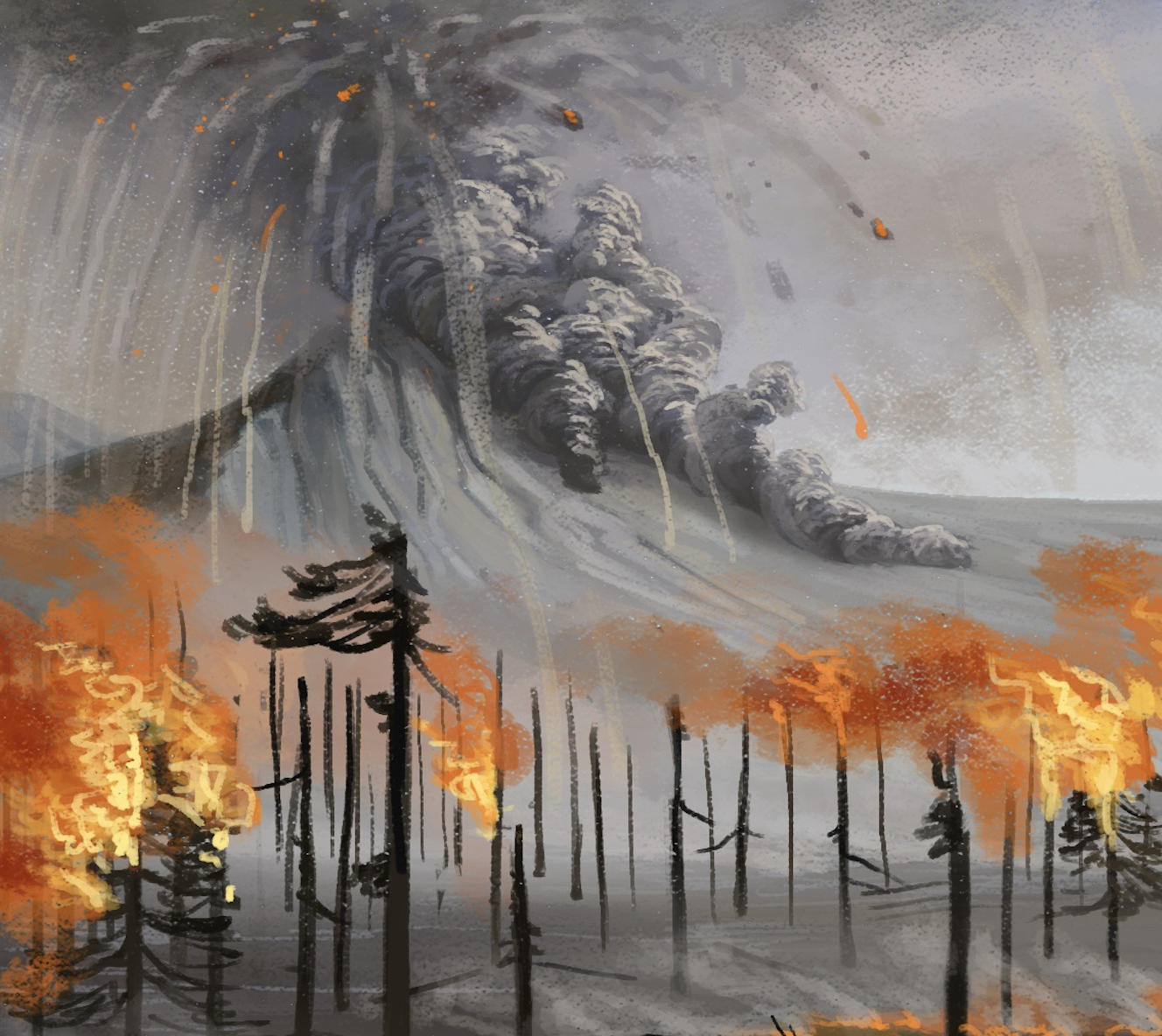
- Role of Ancient Fires: Research led by paleobotanist Joseline Manfroi suggests that fires were frequent during the Cretaceous period (~75 million years ago), driven by high oxygen levels and intense volcanic activity. Fires served as an evolutionary pressure shaping ancient ecosystems.
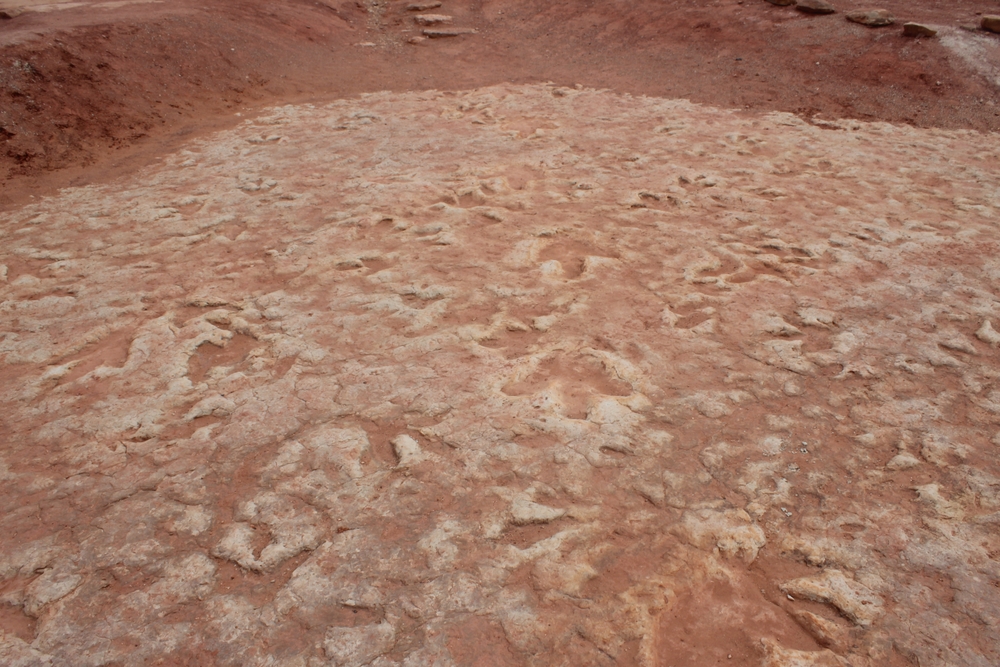
- Fossil Discoveries: Fossilized plants showing evidence of paleofires have been found in multiple Antarctic locations (e.g., Vega Island, King George Islands). Evidence ties similar fire events to regions like Patagonia, Brazil, and the present-day Atacama Desert.
- Geological Transformations: Tectonic shifts like the formation of the Drake Passage influenced climate changes-creating Antarctic ice sheets and arid conditions in northern Chile via ocean currents like the Humboldt Current.The Andes blocked moisture contributing to this arid climate.
- Future Implications: Scientists rule out a return to greenery for these regions unless drastic geological changes occur over millions of years.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study on ancient fires sheds light on Earth’s evolving ecosystems while offering insights into long-term impacts climate systems leave on landscapes. For India-a nation grappling with issues related to deforestation,land degradation,biodiversity loss,and changing weather patterns-the findings drive home an vital realization about preservation amid shifting environments.
India can learn from how geological factors enabled extreme transformations over millions of years-a reminder that even resilient ecosystems are vulnerable when faced with combined natural forces such as tectonics or climate imbalances. While modern challenges may differ from those witnessed in Antarctica’s historical evolution (like volcanic or tectonic events), addressing cumulative impacts on forests today-including wildfires exacerbated by human-induced activities-is critical to ensuring enduring environmental futures.
India’s role in global conservation efforts becomes pivotal as countries work collaboratively not only toward local ecosystem protection but also understanding broader shifts affecting planetary health.