Now Reading: Anteaters Show Evolutionary Adaptability with Over a Dozen Variations
-
01
Anteaters Show Evolutionary Adaptability with Over a Dozen Variations
Anteaters Show Evolutionary Adaptability with Over a Dozen Variations

Rapid Summary
- Mammals evolved as ant-eaters (myrmecophages) independently over 12 times in the past 66 million years.
- The evolution of myrmecophages was linked to the mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, which created an ecosystem favorable for ants and termites to thrive.
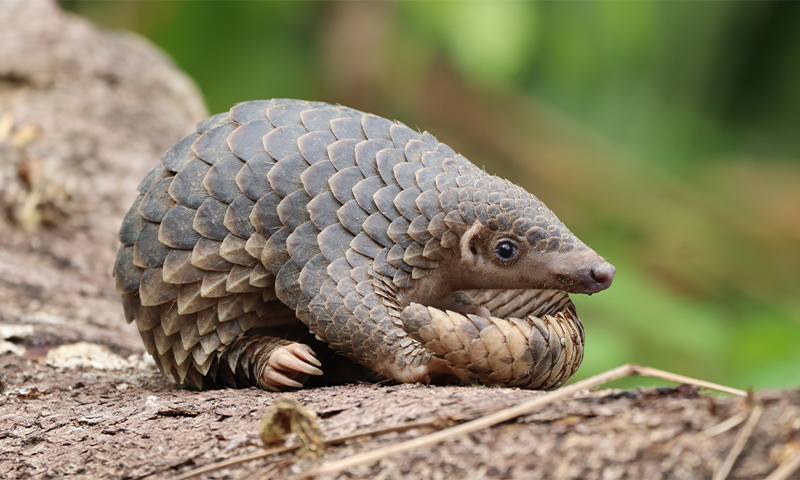
- Myrmecophages include species like aardvarks, pangolins, and anteaters, with adaptations such as elongated claws and specialized tongues for consuming ants/termites efficiently.
- The study analyzed data on diets from over 4,000 mammal species using statistical models to trace evolutionary patterns.
- Despite recurring evolution in this niche lifestyle across mammalian lineages,only eight unique species currently represent distinct ant-eating lineages.
- Researchers observed that all ant-eating mammals evolved from carnivores or insectivores but remained consistent in their dietary habits accept a genus of elephant shrews which shifted to omnivory later on.
- Social insects like ants and termites dominate global biomass today more than wild mammals combined-potentially conferring adaptive advantages to myrmecophages amid climate change.
(Image included: Visualization of mammalian family tree highlighting dietary evolution.)
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings regarding the independent emergence of myrmecophagy highlight engaging global ecological dynamics. While India has rich biodiversity including termite-dominated ecosystems that support native pangolins – one of India’s most critically endangered species – insights from this research could be pertinent for conservation strategies. adaptations seen among these specialized feeders also suggest resilience against changing climates. Given ongoing threats such as habitat destruction and illegal wildlife trade specifically concerning pangolins within India, understanding evolutionary predispositions can help inform policy frameworks safeguarding both ecosystems and vulnerable fauna reliant on social insects.
moreover, with increasing challenges posed by invasive insect populations like fire ants potentially thriving under warming conditions globally, India might also need proactive monitoring mechanisms ensuring balance maintaining local cycles preventing interruptions harmfully cascading across unknown territories extensions their population bio security